semantics More to give than just the div: and how to get them right Hidde de Vries, Frontmania, Utrecht, 2022 @hdv
Slide 1

Slide 2

Hi, I’m Hidde • • • @hdv blogger (hidde.blog) accessibility specialist developer relations
Slide 3
Sanity.io Content management platform that is equally great for developers, content creators and businesses @hdv
Slide 4

semantics @hdv
Slide 5

Correspondence theories of meaning @hdv
Slide 6

Wittgenstein: “the meaning of a word is its use in the language” Ludwig Wittgenstein, Philosophical Investigations (1953) @hdv
Slide 7

Wittgenstein: no such thing as a private language, there can only be meaning if it’s shared Ludwig Wittgenstein, Philosophical Investigations (1953) @hdv
Slide 8
Your design system is a shared language. @hdv
Slide 9

Your API is a shared language. @hdv
Slide 10

Your Vue/Svelte/<customelement> component names are a shared language. @hdv
Slide 11

Classi cation depends on place and culture fi @hdv
Slide 12

Classi cation is hard and AI aren’t great at it fi @hdv
Slide 13

Semantics on the web @hdv
Slide 14

For the web, you could have a lot semantics… @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 15
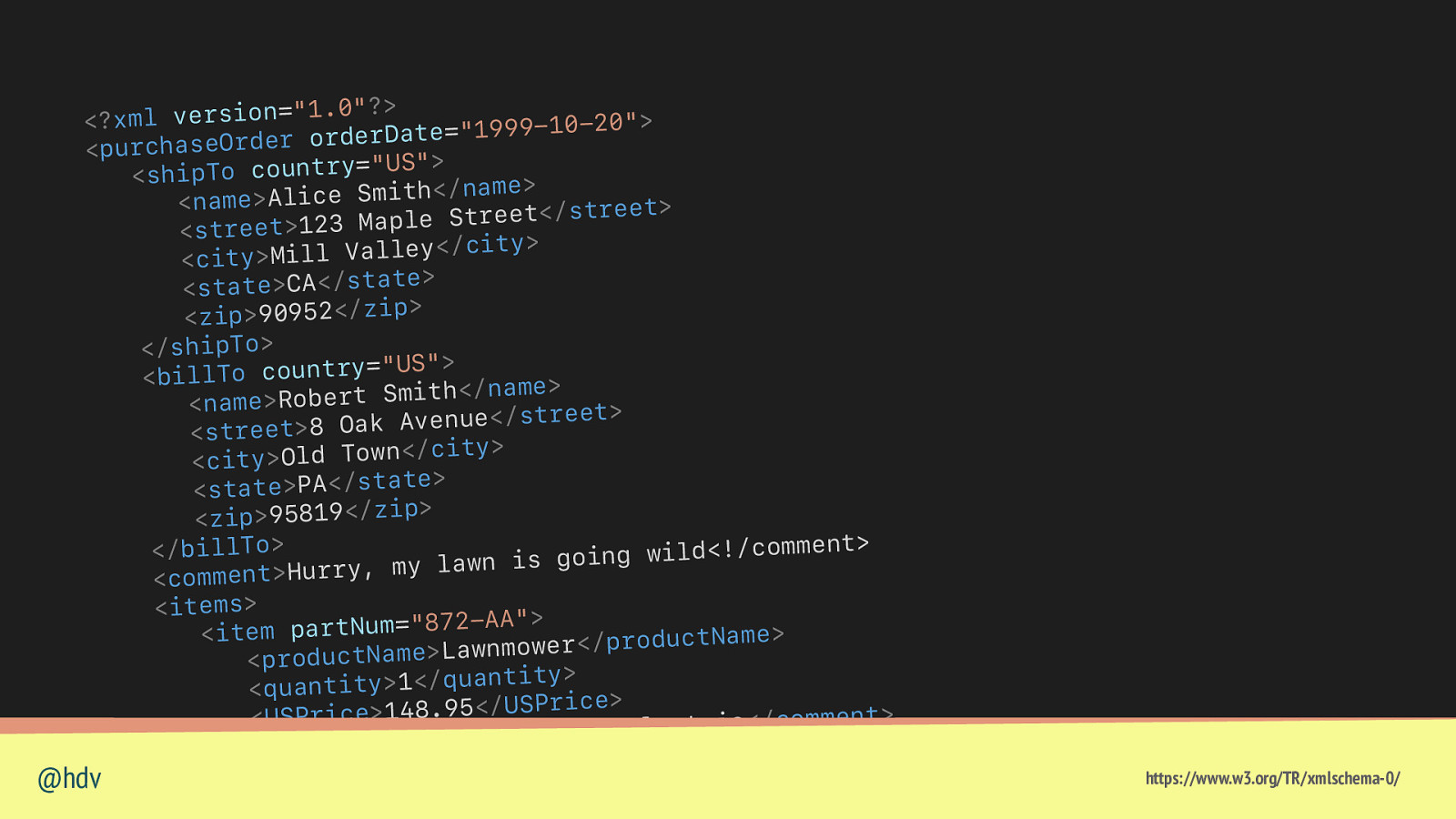
? ” 0 . 1 ” = n o i s r e > < ?x m l v ” 0 2 0 1 9 9 9 1 ” = e t a D r e d r o r e d r O <purchase > ” S U ” = y r t n u o c <shipTo > e m a n / < h t i m S e < n a m e> A l i c > t e e r t s / < t e e r t S e l p a M 3 2 1 > t e <stre > y t i c / < y e l l a V < c i t y> M i l l > e t a t s / < A C > e t <sta > p i z / < 2 5 9 0 9 > p i <z </shipTo> > ” S U ” = y r t n u o c o T <bill > e m a n / < h t i m S < n a m e> R o b e r t > t e e r t s / < e u n e v A <street>8 Oak > y t i c / < n w o T d < c i t y> O l > e t a t s / < A P > e t a t <s < z i p > 9 5 8 1 9< / z i p > > t n e m m o c / ! < </billTo> d l i w g n i o g s i n w a l y m , y r r u H > t n e m m <co < i t e m s> > ” A A 2 7 8 ” = m u N t r > e <item pa m a N t c u d o r p / < r e w o m n w a L > e m a N t <produc > y t i t n a u q / < 1 > y <quantit > e c i r P S U / < 5 9 . 8 4 > t n e m m <USPrice>1 o c / < c i r t c e l e s i s i h t m r i f <comment>Con < / i t e m> @hdv > ” A A 6 2 9 ” = m u N t r a <item p oductName> https://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-0/
Slide 16
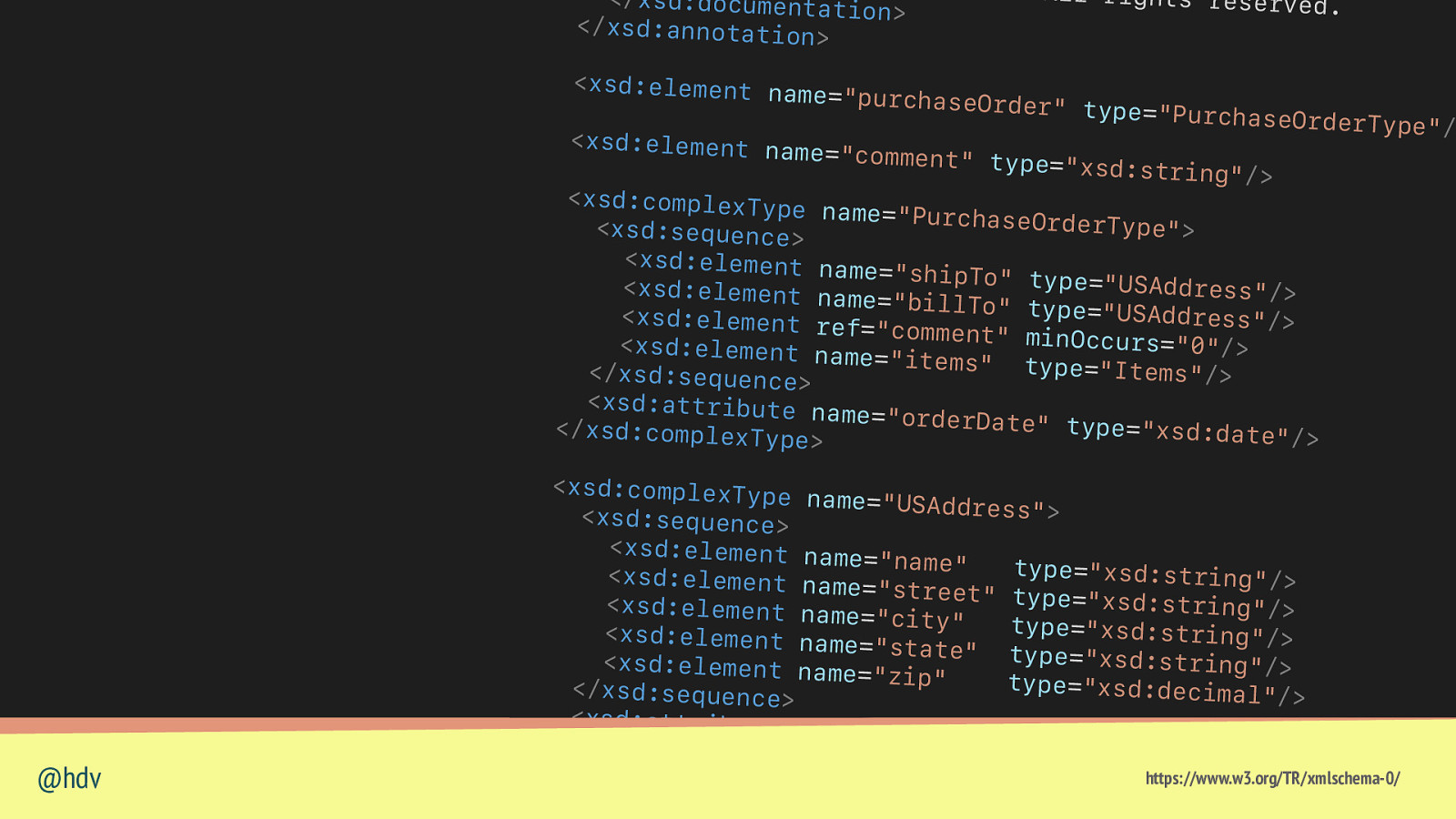
< /x s d : d o c u m e n t a t ion> < /x s d : a n n o t a t i o n > <xsd:element nam e= ” p u r c h a s e O r All rights reser ved. d e r ” t y p e= ” P u r c h aseOrde <xsd:element nam e= ” c o m m e n t ” t y p e =”xsd:string”/> <xsd:complexType n a m e= ” P u r c h a s e O r derType”> xsd:sequence <xsd:element nam e= ” s h i p T o ” t y p e= “USAddress”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” b i l l T o ” t y p e= “USAddress”/> <xsd:element ref =”comment” minOc curs=”0”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” i t e m s ” t y p e= “Items”/> </xsd:sequence> <xsd:attribute n a m e= ” o r d e r D a t e ” type=”xsd:date”/ < /x s d : c o m p l e x T y p > e> @hdv rType”/ <xsd:complexType n a m e= ” U S A d d r e s s ” > xsd:sequence <xsd:element nam e= ” n a m e ” t y p e= ” x s d : s t r i n g <xsd:element nam “/> e= ” s t r e e t ” t y p e= “xsd:string”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” c i t y ” t y p e= ” x s d : s t r i n g <xsd:element nam “/> e= ” s t a t e ” t y p e= “xsd:string”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” z i p ” t y p e= ” x s d : d e c i m a </xsd:sequence> l”/> <xsd:attribute n a m e= ” c o u n t r y ” t y p e= ” x s d : N M T O K E N ” f i x e d= ” U S ” / > < /x s d : c o m p l e x T y p https://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-0/ e>
Slide 17

…but for accessibility, we need one, agreed-upon set @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 18

HTML is a standard way for your website to declare its semantics @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 19

HTML is not a way to declare what stuff looks like on a page @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 20

It’s a way to declare what stuff is on a page @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 21

HTML semantics are not behaviour, but are often tied to it @hdv
Slide 22

Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… Photo: Jeremy Keith; from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cuddling_with_multiple_devices.jpg
Slide 23

This NeXT machine was used to develop and run the rst WWW server, multimedia browser and web editor @hdv fi Copyright: CERN (http://cds.cern.ch/record/42413)
Slide 24

Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… Photo: Jeremy Keith; from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cuddling_with_multiple_devices.jpg
Slide 25

Default stylesheets Multi device web @hdv HTML enables…
Slide 26

Default stylesheets Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… ‘Browse by heading’ “Heading structures are tables of contents” - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 27
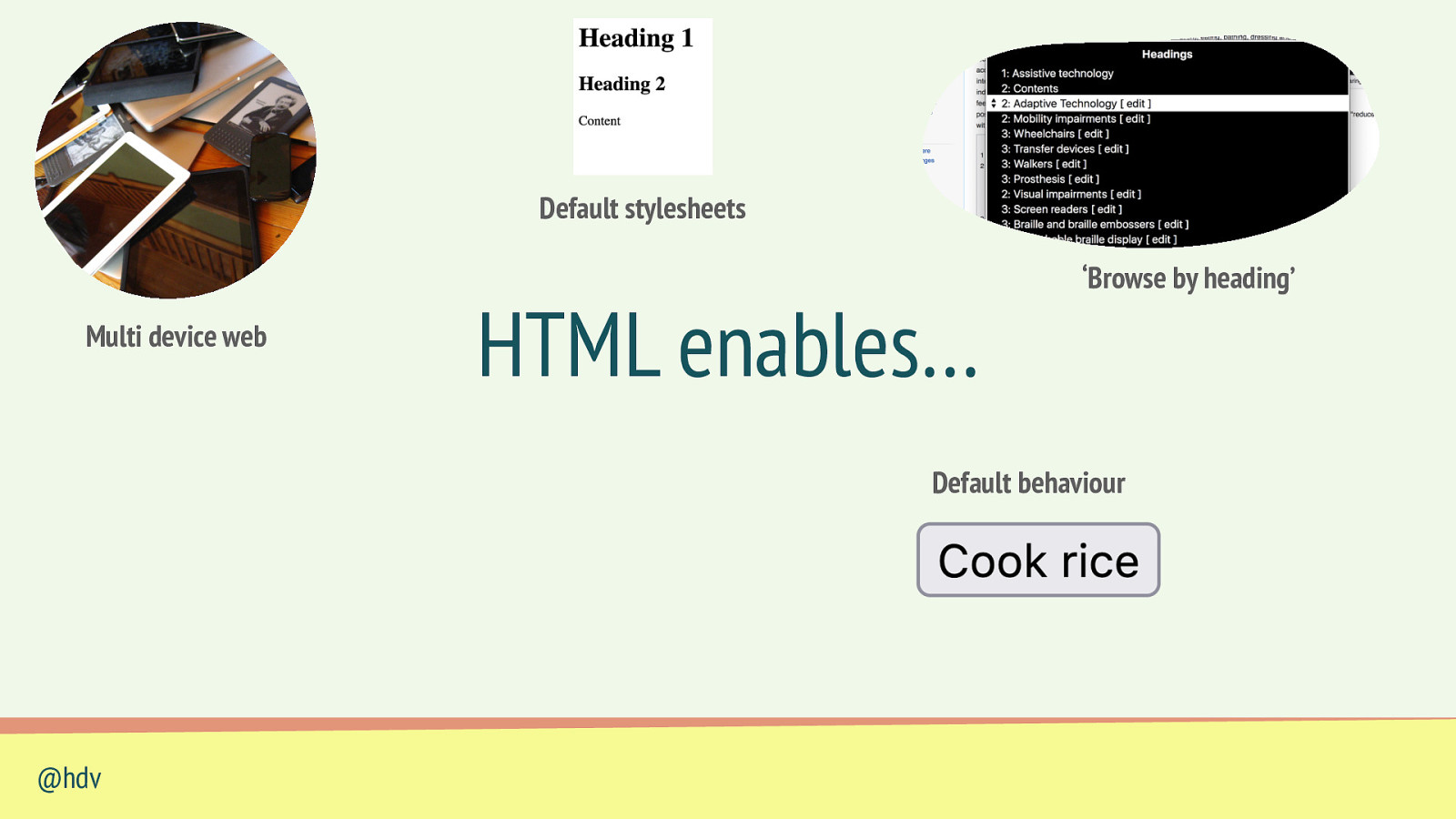
Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour @hdv
Slide 28

Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… Reader mode @hdv ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour
Slide 29
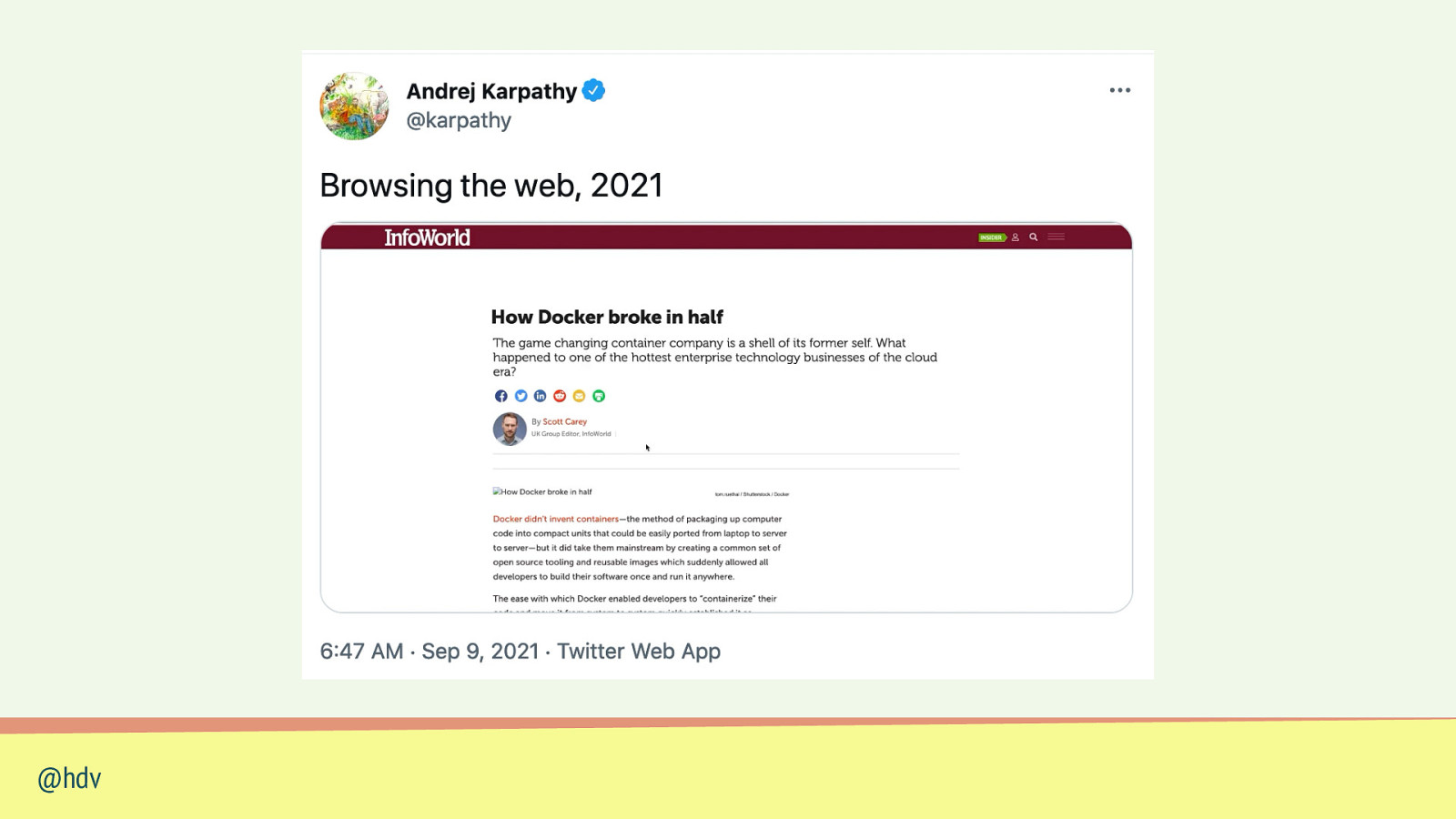
@hdv
Slide 30

Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… Reader mode @hdv ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour
Slide 31

HTML points machines at what stuff is @hdv
Slide 32

HTML points assistive technology at what stuff is @hdv
Slide 33

Hire for HTML expertise @hdv
Slide 34

In practice @hdv
Slide 35
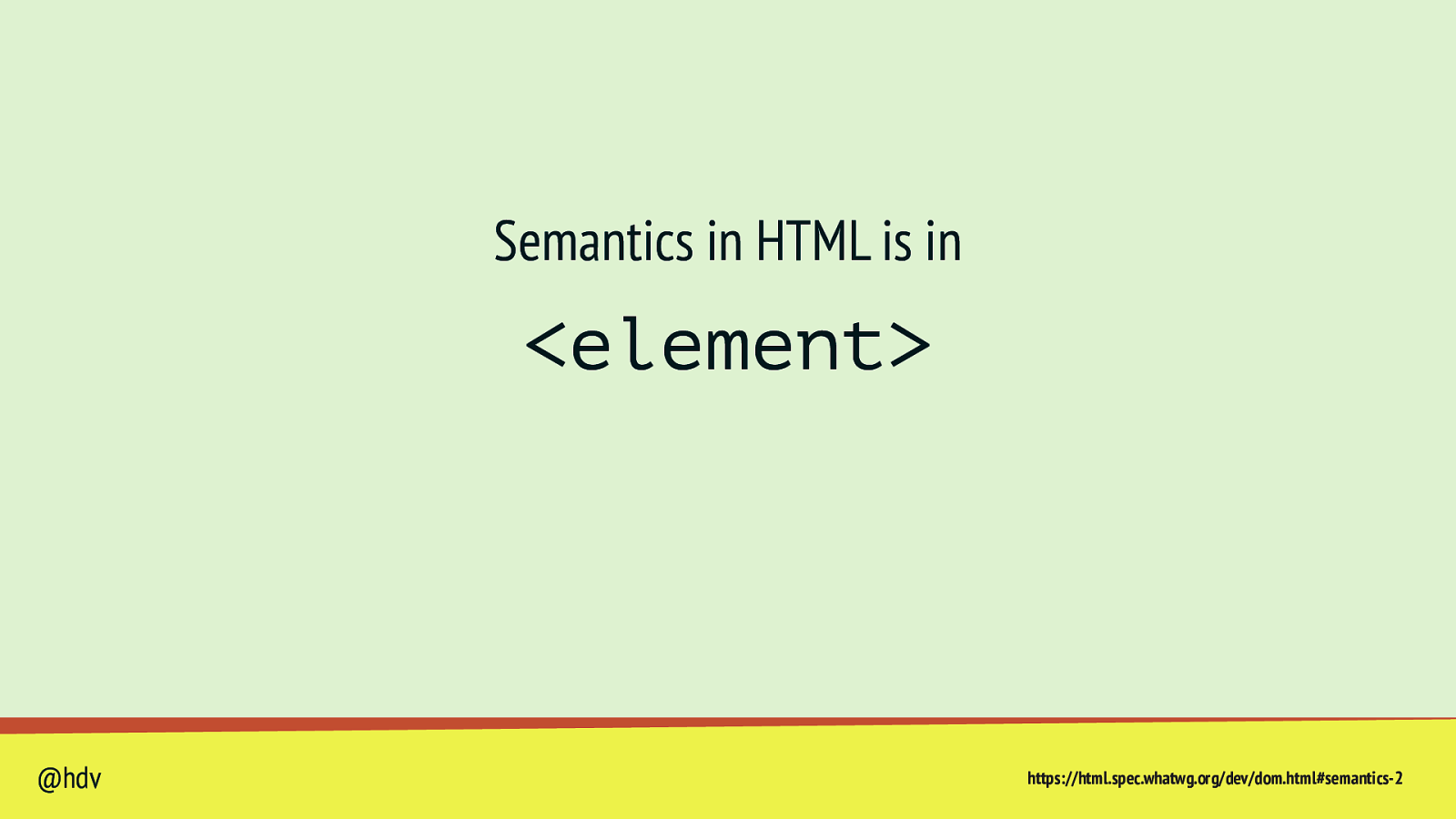
Semantics in HTML is in <element> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 36

Semantics in HTML is in <element attribute> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 37
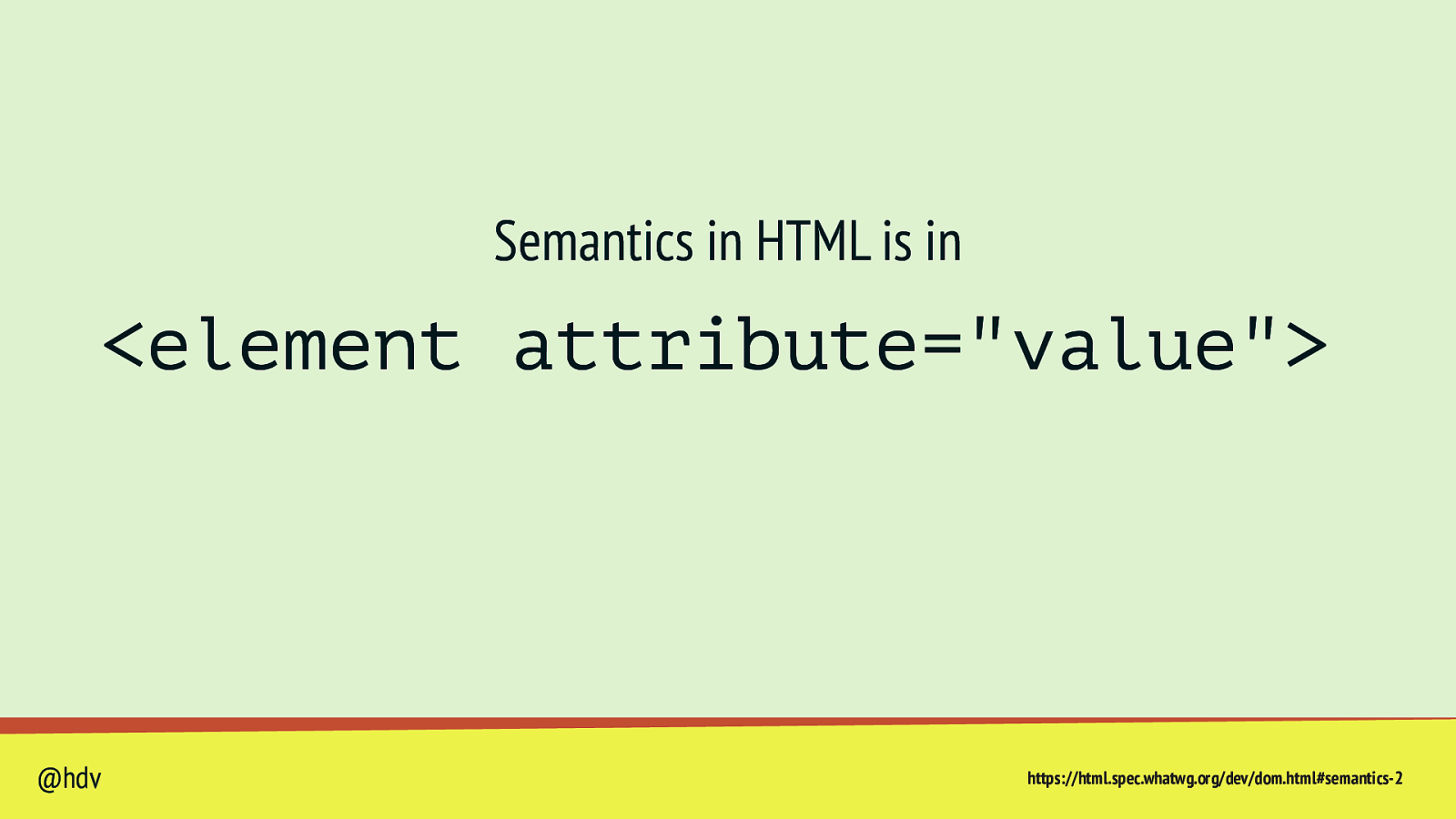
Semantics in HTML is in <element attribute=”value”> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 38

WAI-ARIA de nes semantics beyond HTML fi @hdv
Slide 39

“ WAI-ARIA is designed to provide semantic information about objects when host languages lack native semantics […] Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.2, §8.4 @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/
Slide 40

“ host languages […] can evolve and provide new native features that correspond to WAIARIA features [so] there are many situations in which WAI-ARIA semantics are redundant Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.2, §8.4 @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/
Slide 41

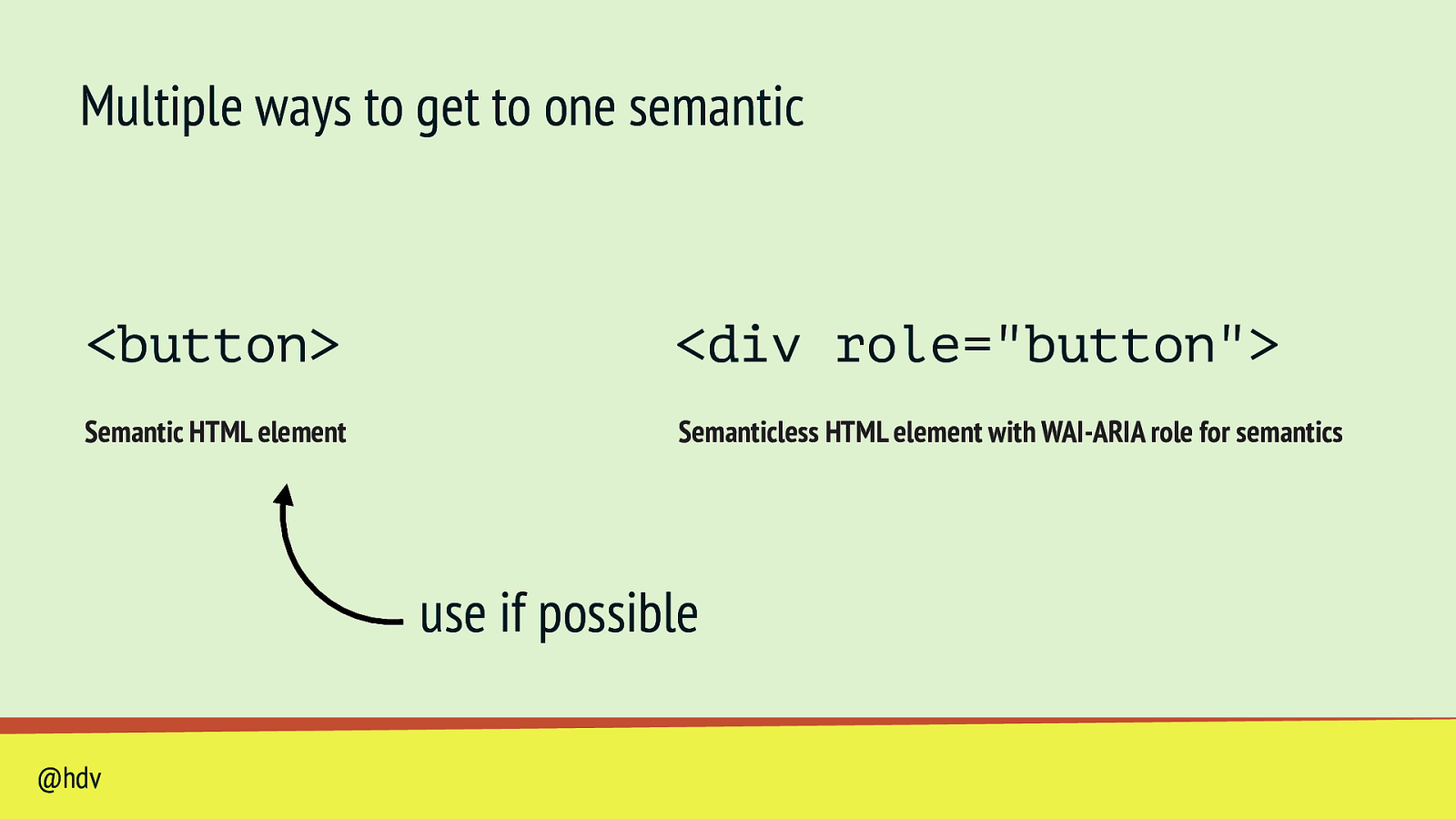
Multiple ways to get to one semantic <button>
<div role=”button”> Semantic HTML element Semanticless HTML element with WAI-ARIA role for semantics @hdvSlide 42
Multiple ways to get to one semantic <button>
<div role=”button”> Semantic HTML element Semanticless HTML element with WAI-ARIA role for semantics use if possible @hdvSlide 43

Speaking of buttons… @hdv https://www.abeautifulsite.net/posts/on-buttons-and-links/
Slide 44

@hdv Products Add to cart Products Add to cart
Slide 45
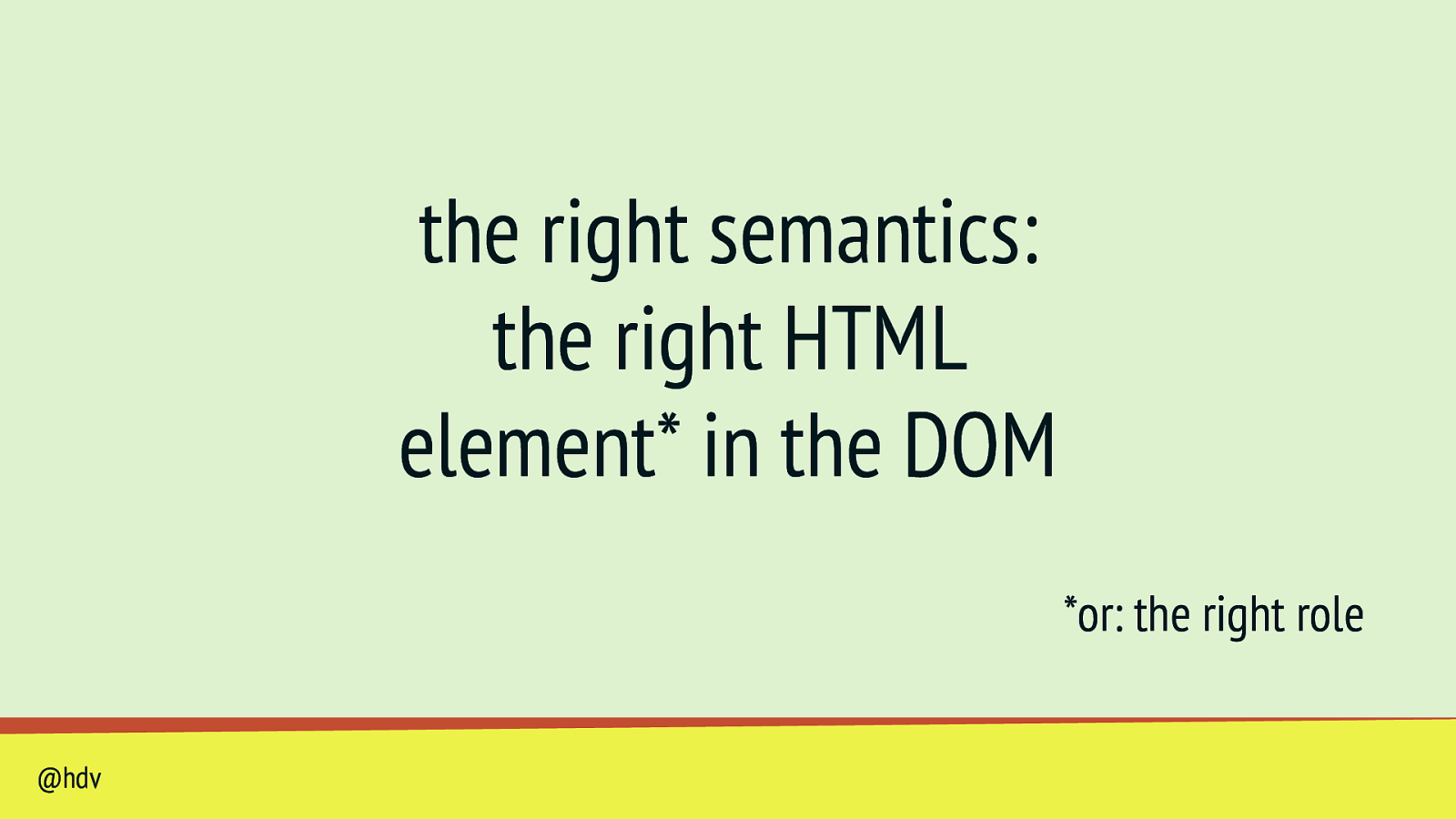
the right semantics: the right HTML element* in the DOM *or: the right role @hdv
Slide 46
@hdv
Slide 47
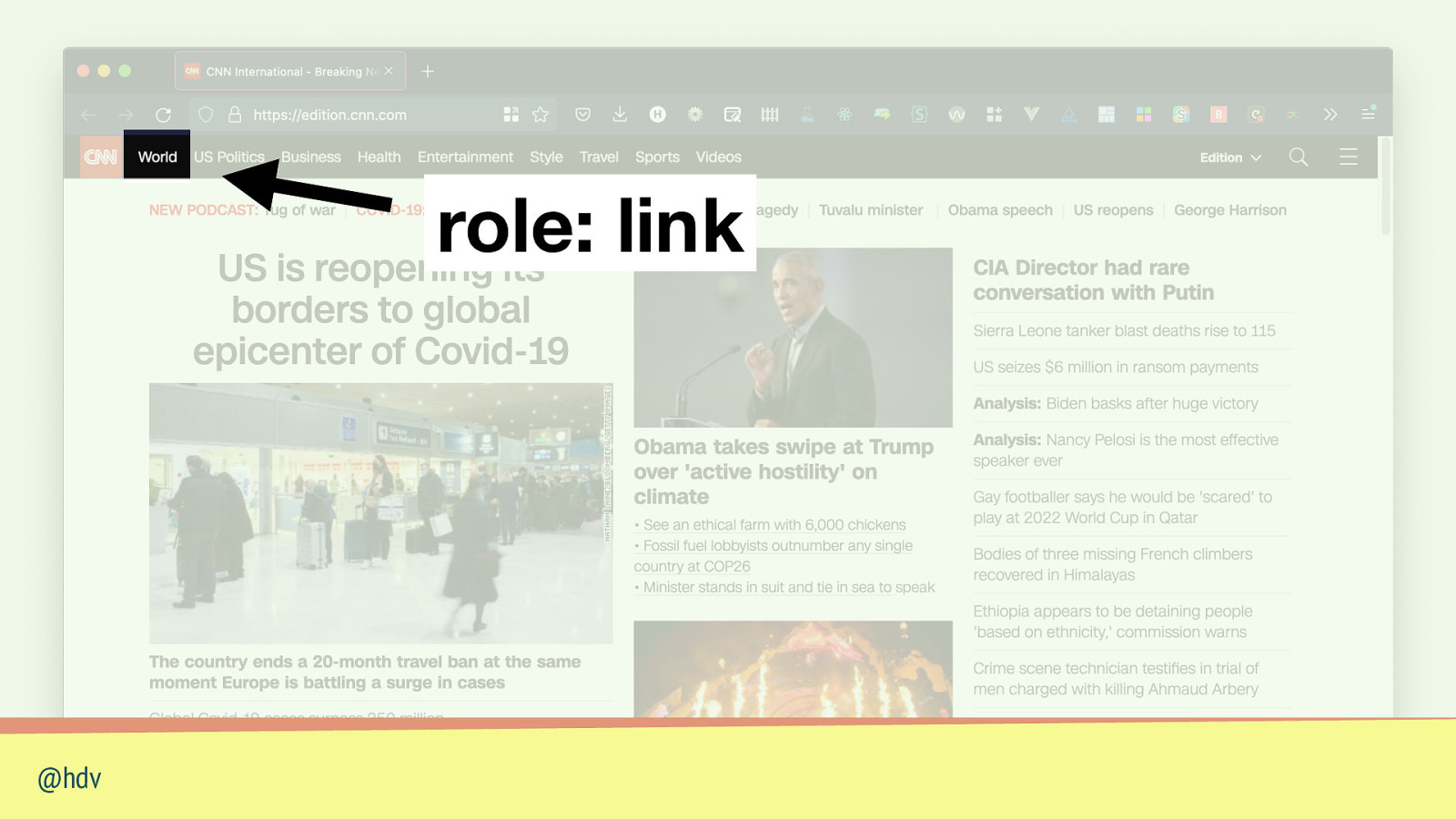
role: link @hdv
Slide 48
role: link @hdv
Slide 49
role: link @hdv
Slide 50
role: button @hdv
Slide 51
@hdv
Slide 52
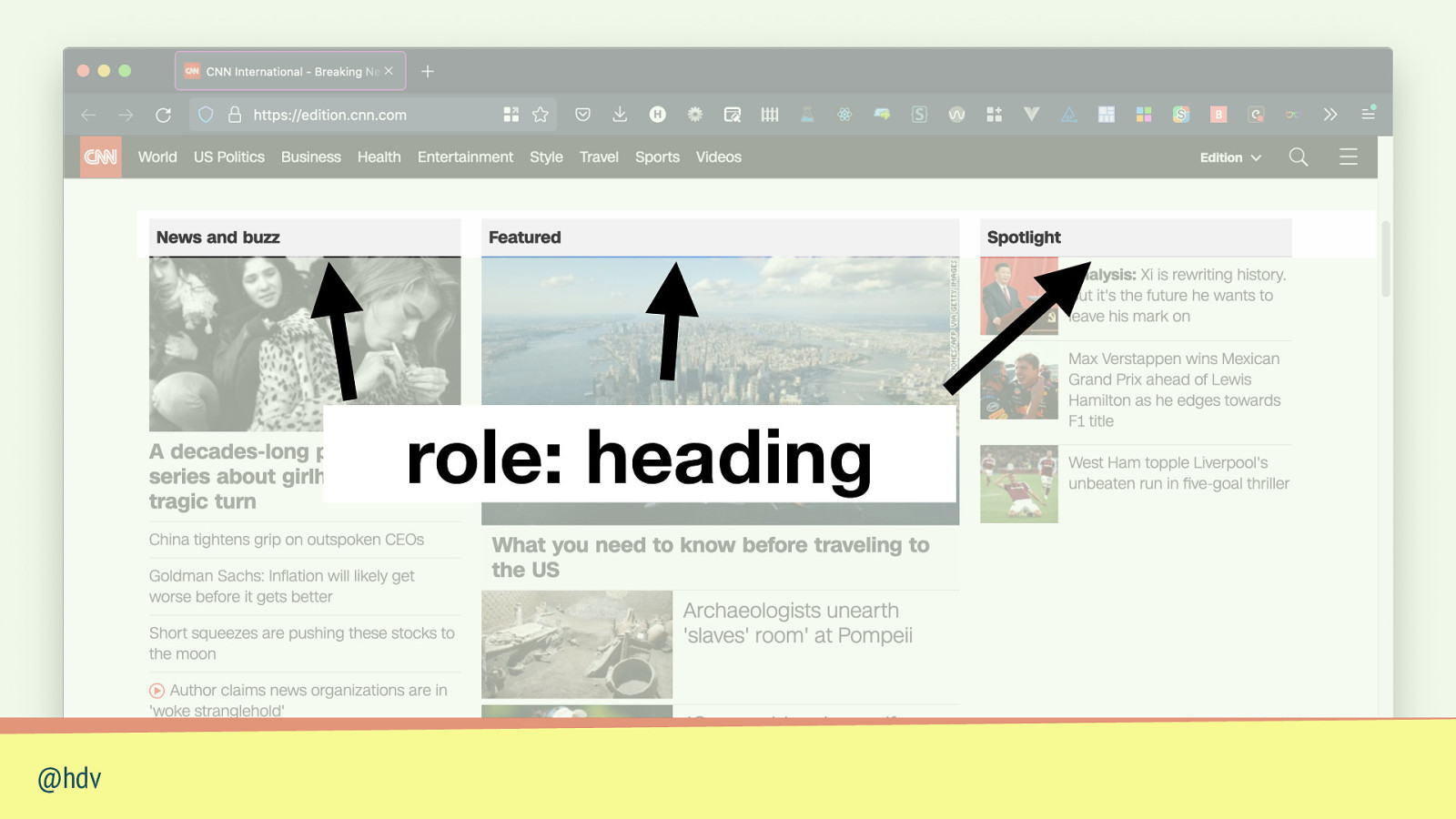
role: heading @hdv
Slide 53
@hdv
Slide 54
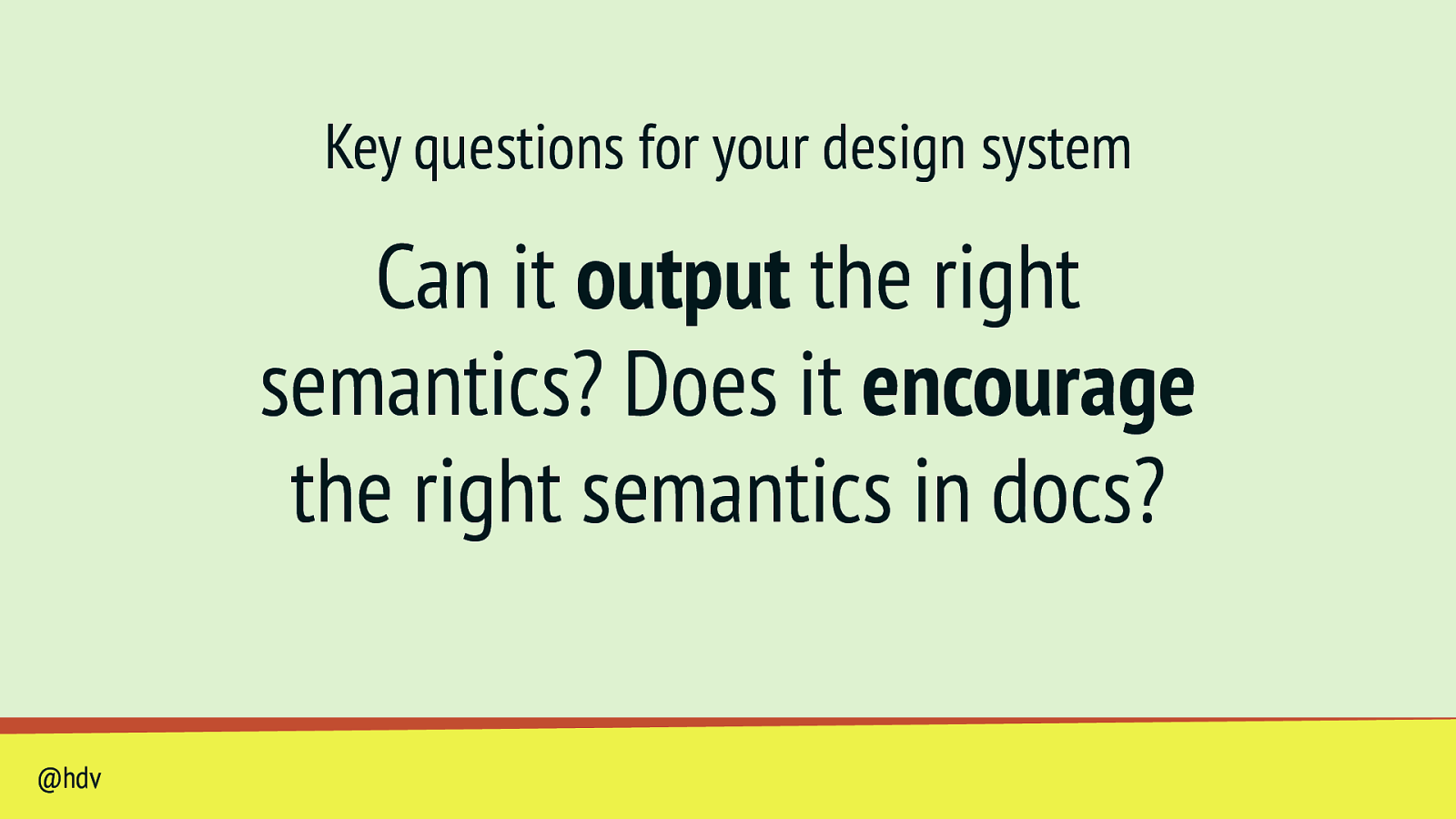
Key questions for your design system Can it output the right semantics? Does it encourage the right semantics in docs? @hdv
Slide 55

meaning = use @hdv
Slide 56

“ (…) semantic HTML, a posh term for choosing the right HTML element for the content. This isn’t a philosophical exercise; it has directly observable practical bene ts. Bruce Lawson, “The practical value of semantic HTML” @hdv fi https://brucelawson.co.uk/2018/the-practical-value-of-semantic-html/
Slide 57
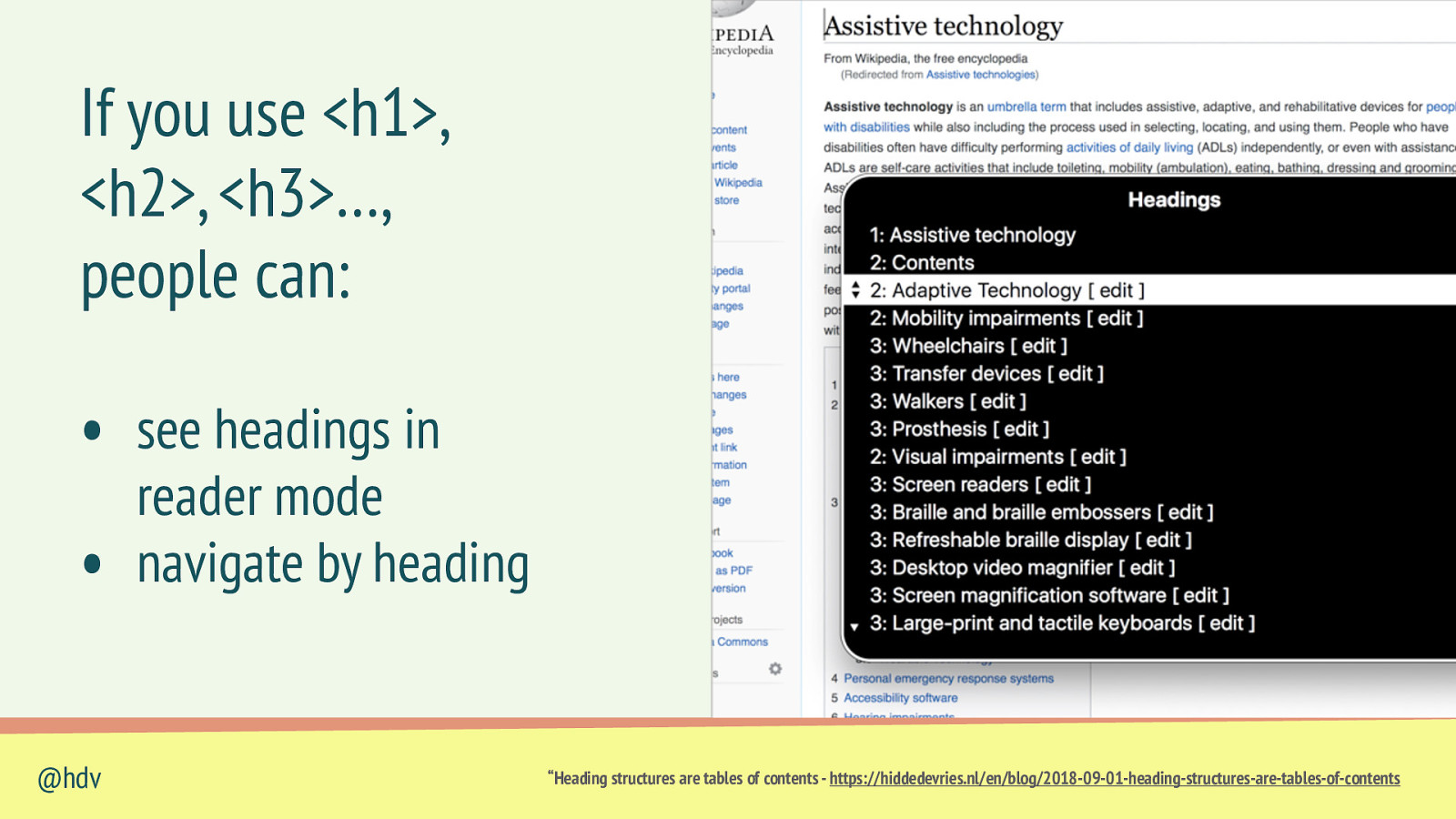
If you use <h1>, <h2>, <h3>…, people can: • see headings in • @hdv reader mode navigate by heading “Heading structures are tables of contents - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 58
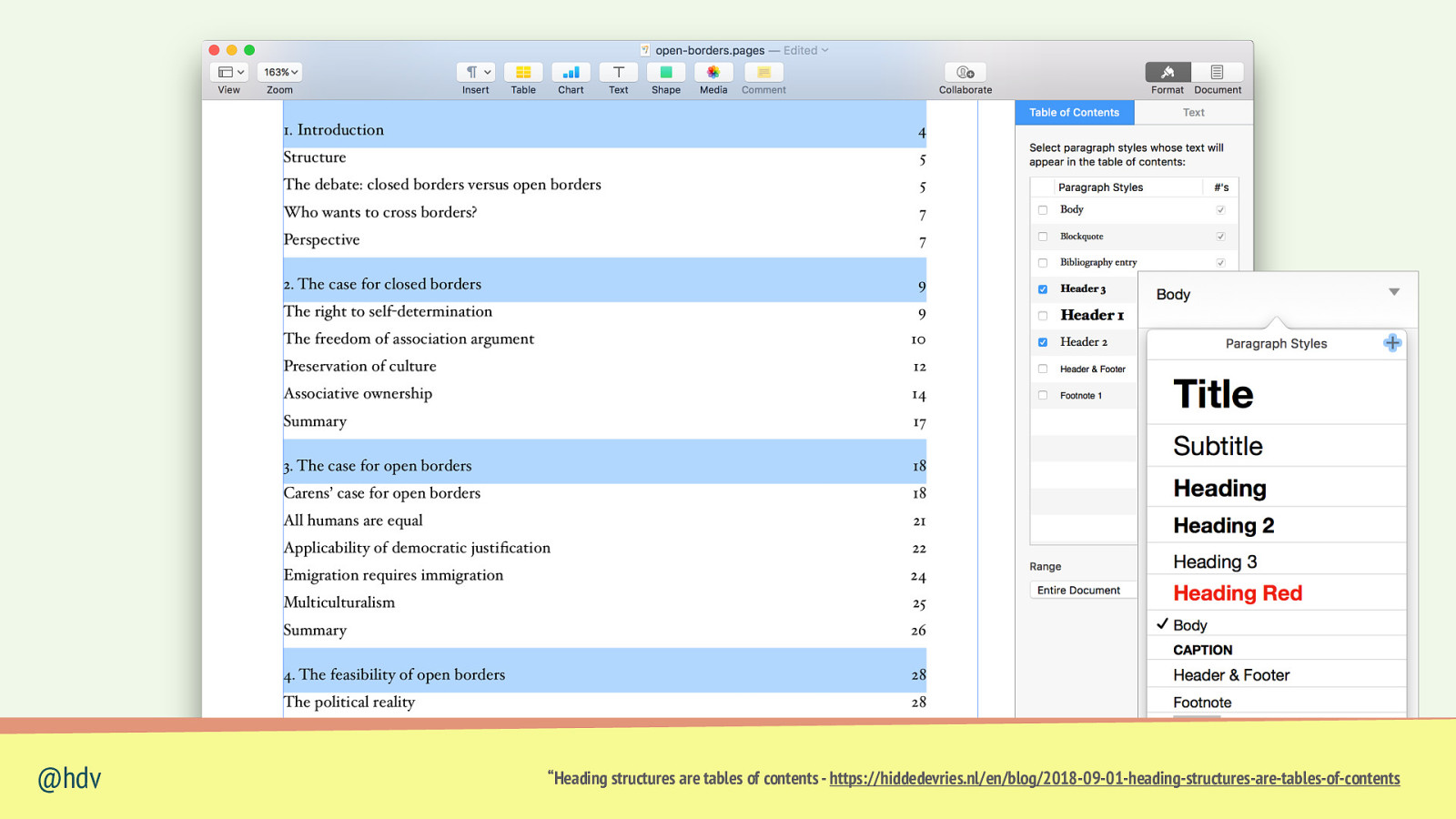
@hdv “Heading structures are tables of contents - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 59

fi If you use <button>, people can: • nd it in the TAB order • press it with just a keyboard • submit the form, even if your JavaScript failed @hdv
Slide 60

If you use <ol>, <ul> or <dl>, people can: • Hear it’s a list and with how many items • Still see it’s a list in reader mode @hdv
Slide 61

If you use autocomplete on inputs, users can: • Tell their browser to ll in data for them • Assistive tech can announce input purpose • Use plugins for personalisation, e.g. with icons fi @hdv
Slide 62

If you use table with a caption, ths for headers and scope attributes for direction: • Assistive tech can provide useful affordances to end users @hdv
Slide 63

The HTML spec is the place to nd out how to use HTML developers.whatwg.org fi @hdv
Slide 64
HTMHell collects examples of how not to use HTML @hdv
Slide 65

Intentions vs reality @hdv
Slide 66

Sometimes, semantics are undone if you use speci c CSS fi @hdv
Slide 67

display overrides semantics display: display: display: display: display: display: @hdv block; inline; grid; flex; contents; none; “a11yTO Conf: CSS Display Properties versus HTML Semantics” - https://adrianroselli.com/2020/10/a11yto-conf-css-display-properties-versus-html-semantics.html
Slide 68
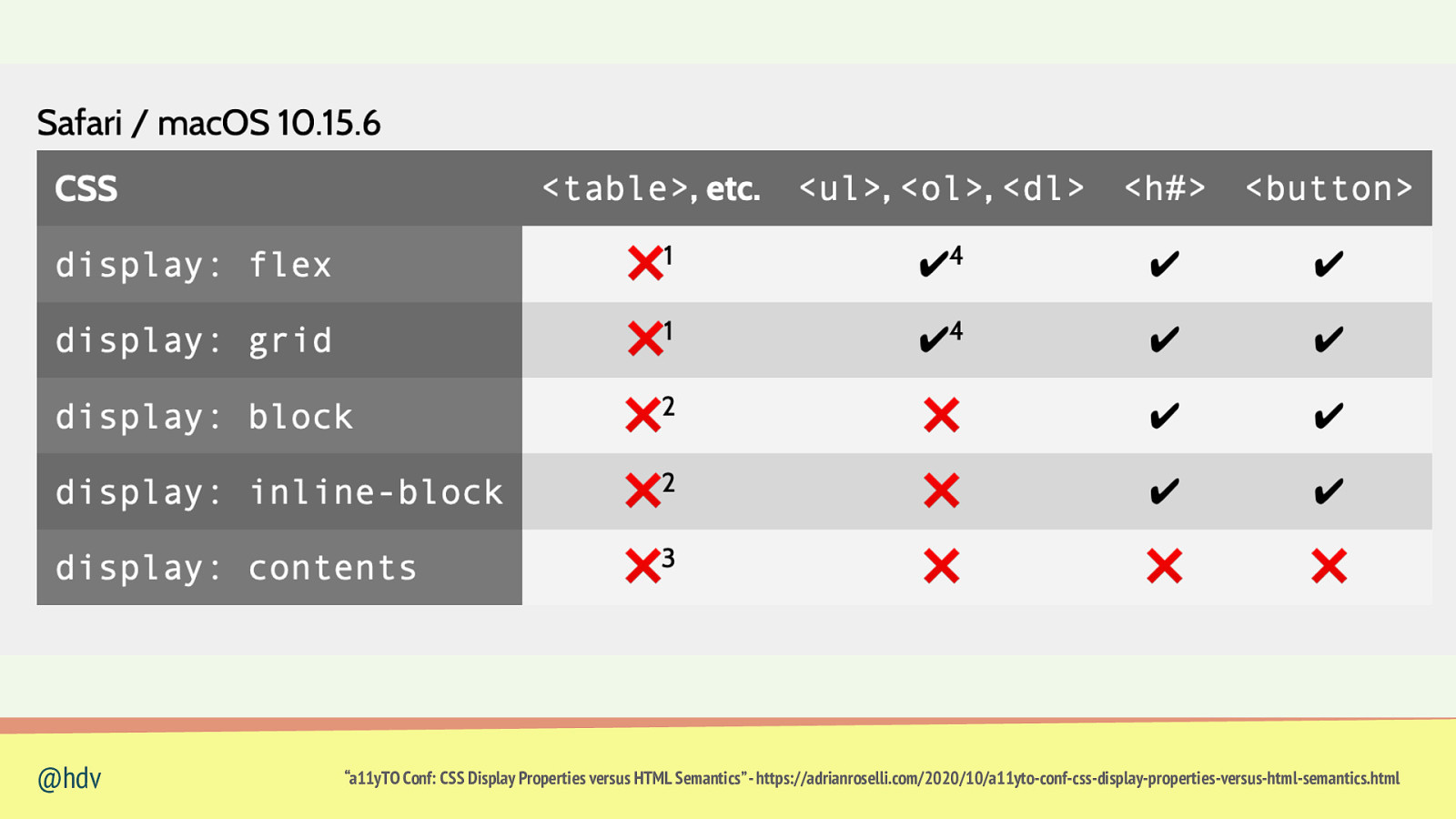
@hdv “a11yTO Conf: CSS Display Properties versus HTML Semantics” - https://adrianroselli.com/2020/10/a11yto-conf-css-display-properties-versus-html-semantics.html
Slide 69

Lists can lose list semantics when you set list-style-type: none (in Safari) @hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 70

• courgette • feta • basil • garlic @hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 71
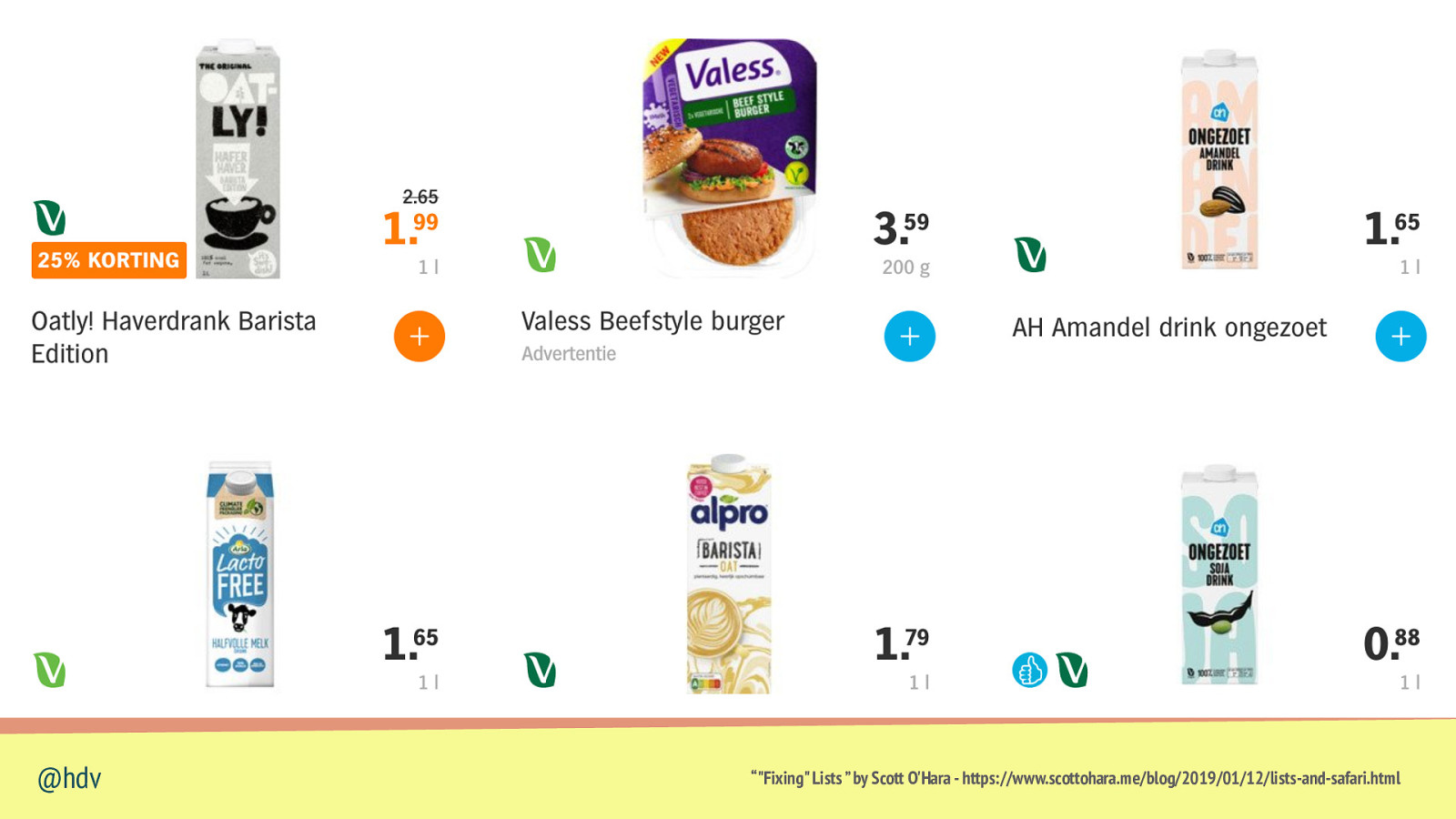
@hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 72
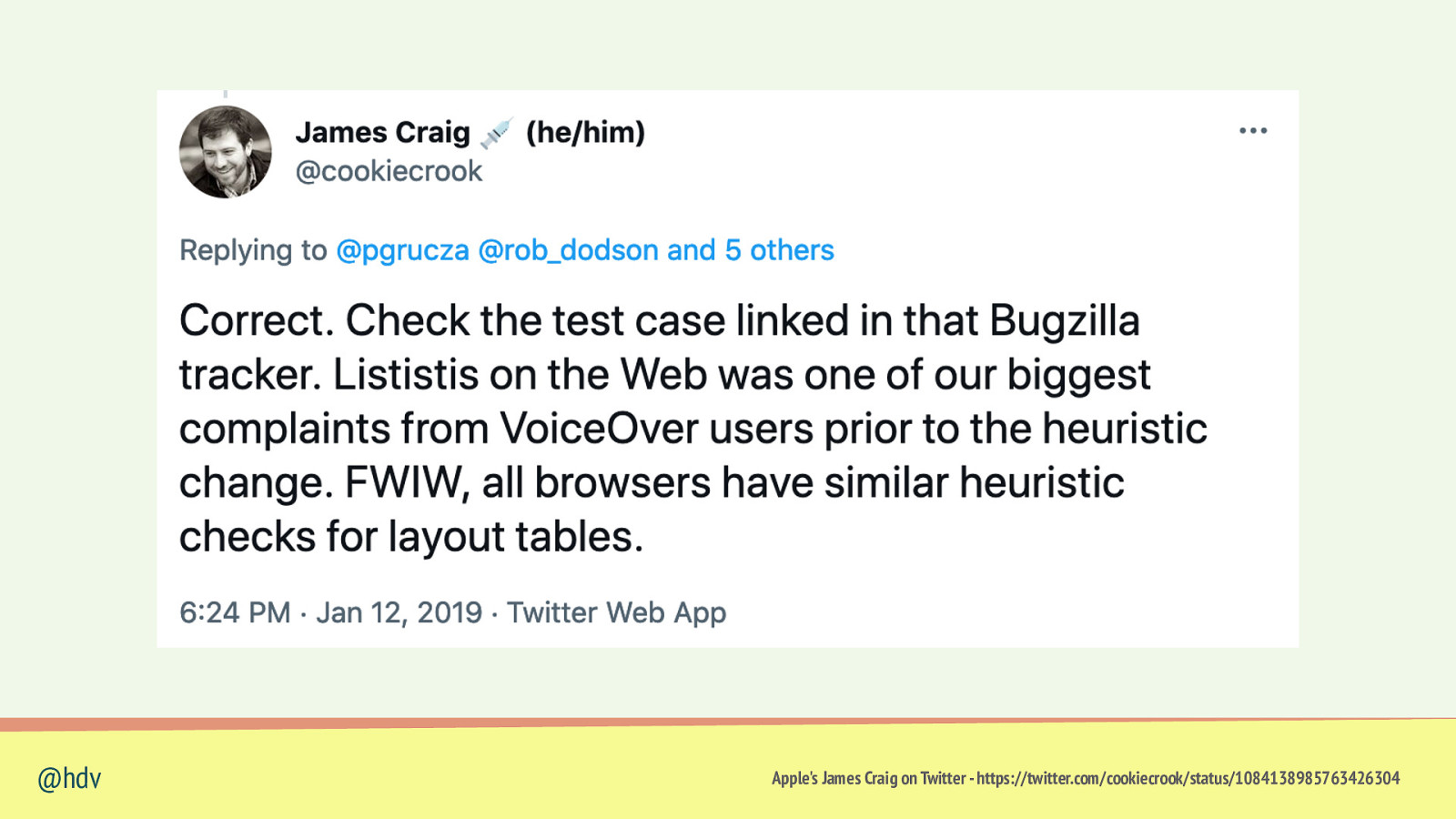
@hdv Apple’s James Craig on Twitter - https://twitter.com/cookiecrook/status/1084138985763426304
Slide 73
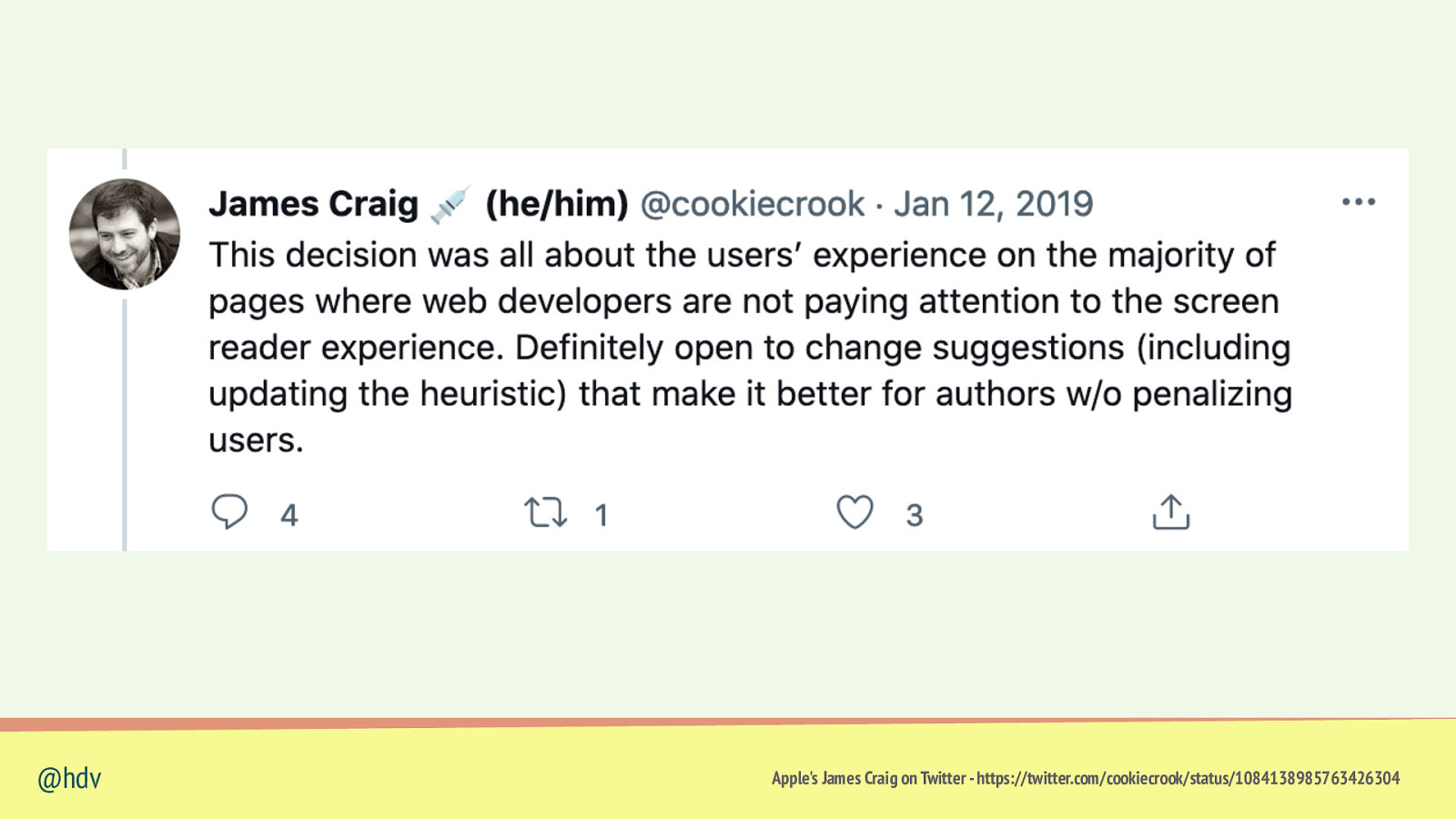
@hdv Apple’s James Craig on Twitter - https://twitter.com/cookiecrook/status/1084138985763426304
Slide 74

Sometimes, semantics are undone when you nest unexpectedly @hdv
Slide 75

Semantics in summary <details> <summary>Ingredients</summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv ▶︎ Ingredients
Slide 76

Semantics in summary <details open> <summary>Ingredients</summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Ingredients • courgette • peas • basil • feta ▼
Slide 77

Semantics in summary <details> <summary> <h2>Ingredients</h2> </summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Ingredients • courgette • peas • basil • feta ▼
Slide 78
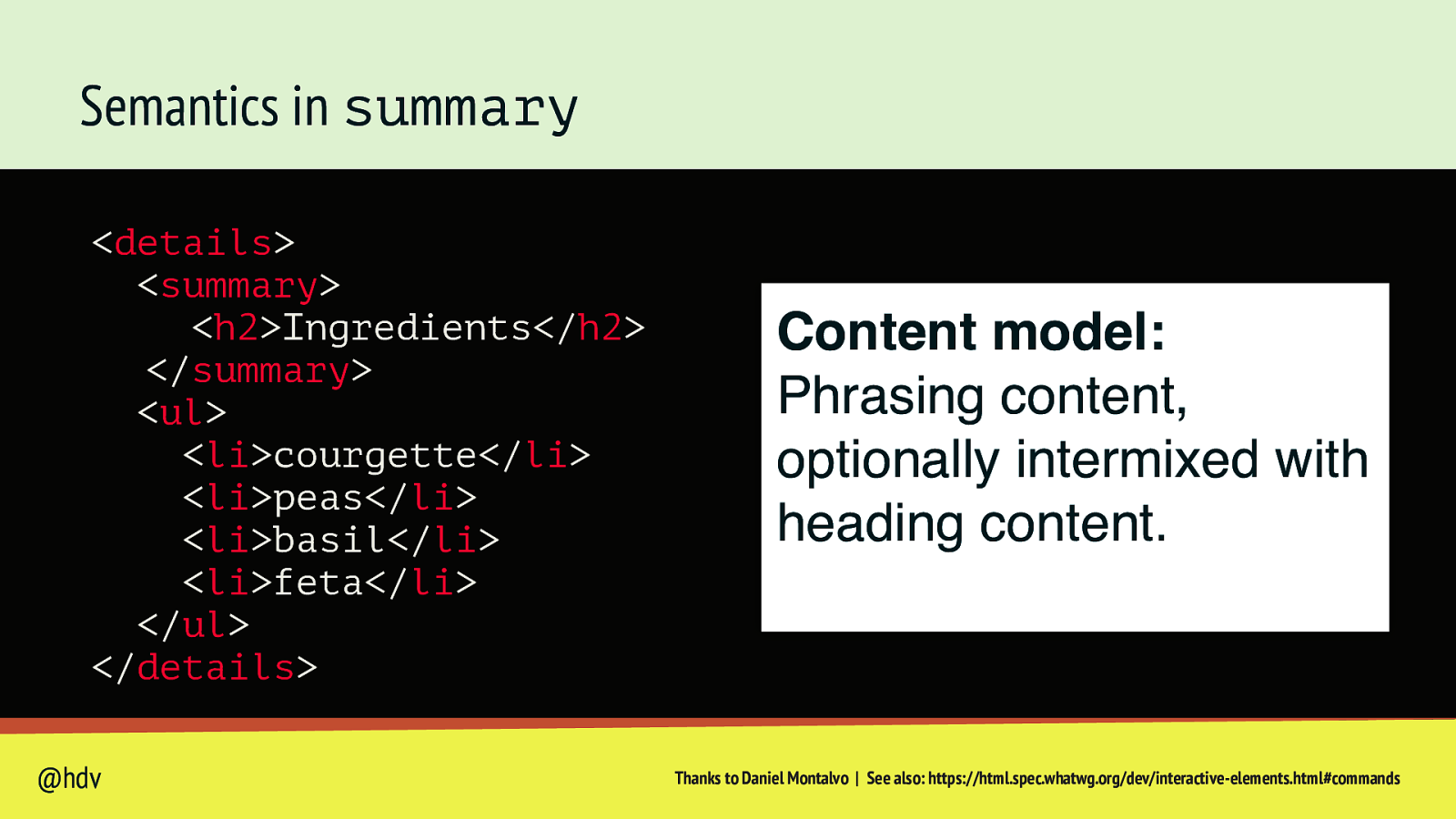
Semantics in summary <details> <summary> <h2>Ingredients</h2> </summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Content model: Phrasing content, optionally intermixed with heading content. Thanks to Daniel Montalvo | See also: https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/interactive-elements.html#commands
Slide 79

Heuristics in the platform and assistive technologies @hdv
Slide 80

When you set text-transform: uppercase, some assistive technologies will read it like an abbreviation “CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ fl fl @hdv
Slide 81
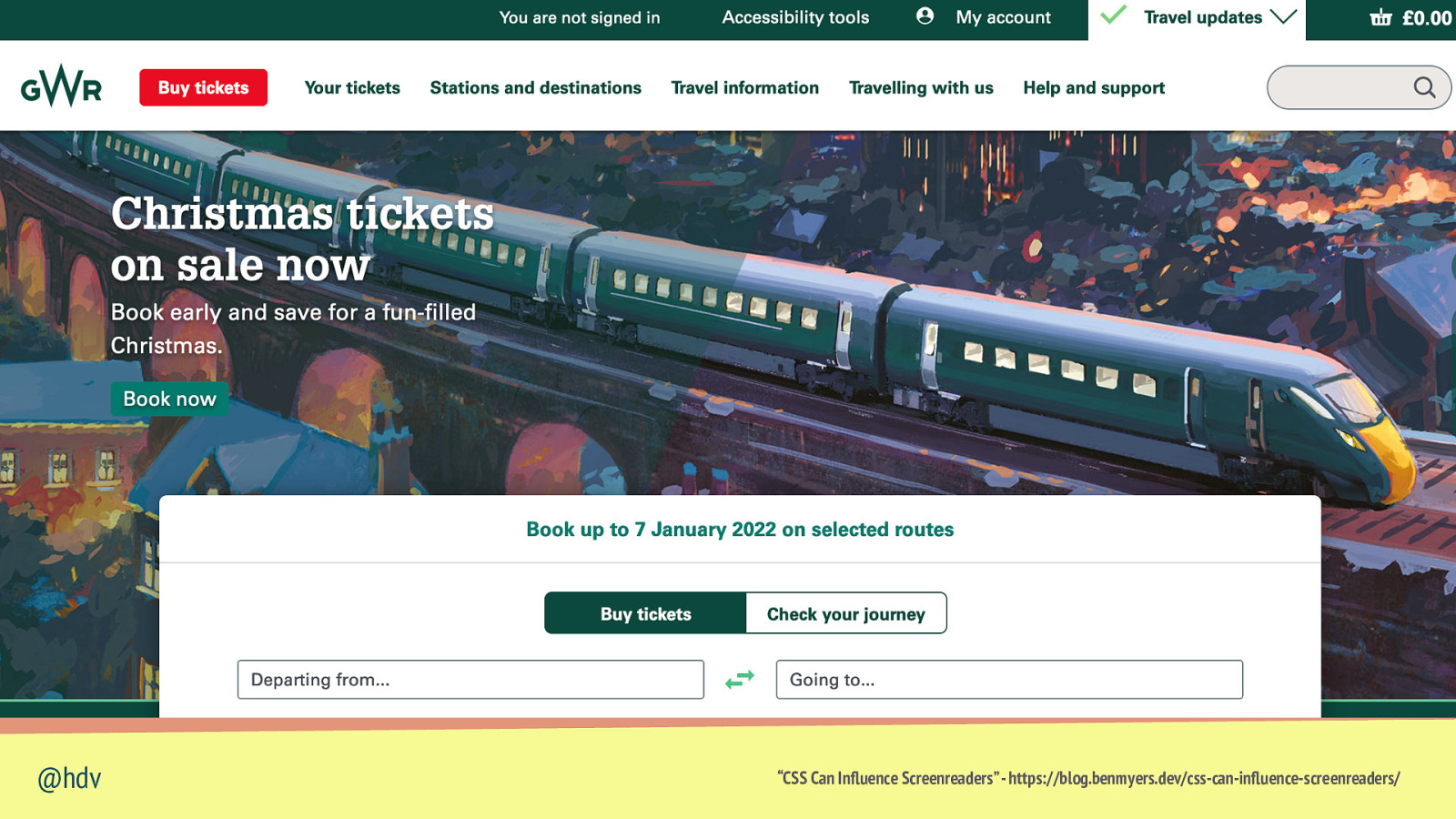
“CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ fl fl @hdv
Slide 82

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation “CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii fl fl @hdv
Slide 83

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation <button>Buy product</button> Buy product “CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii fl fl @hdv
Slide 84

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation <button>Buy product</button> button::before { content: “💸”; } “CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii fl fl @hdv 💸 Buy product
Slide 85
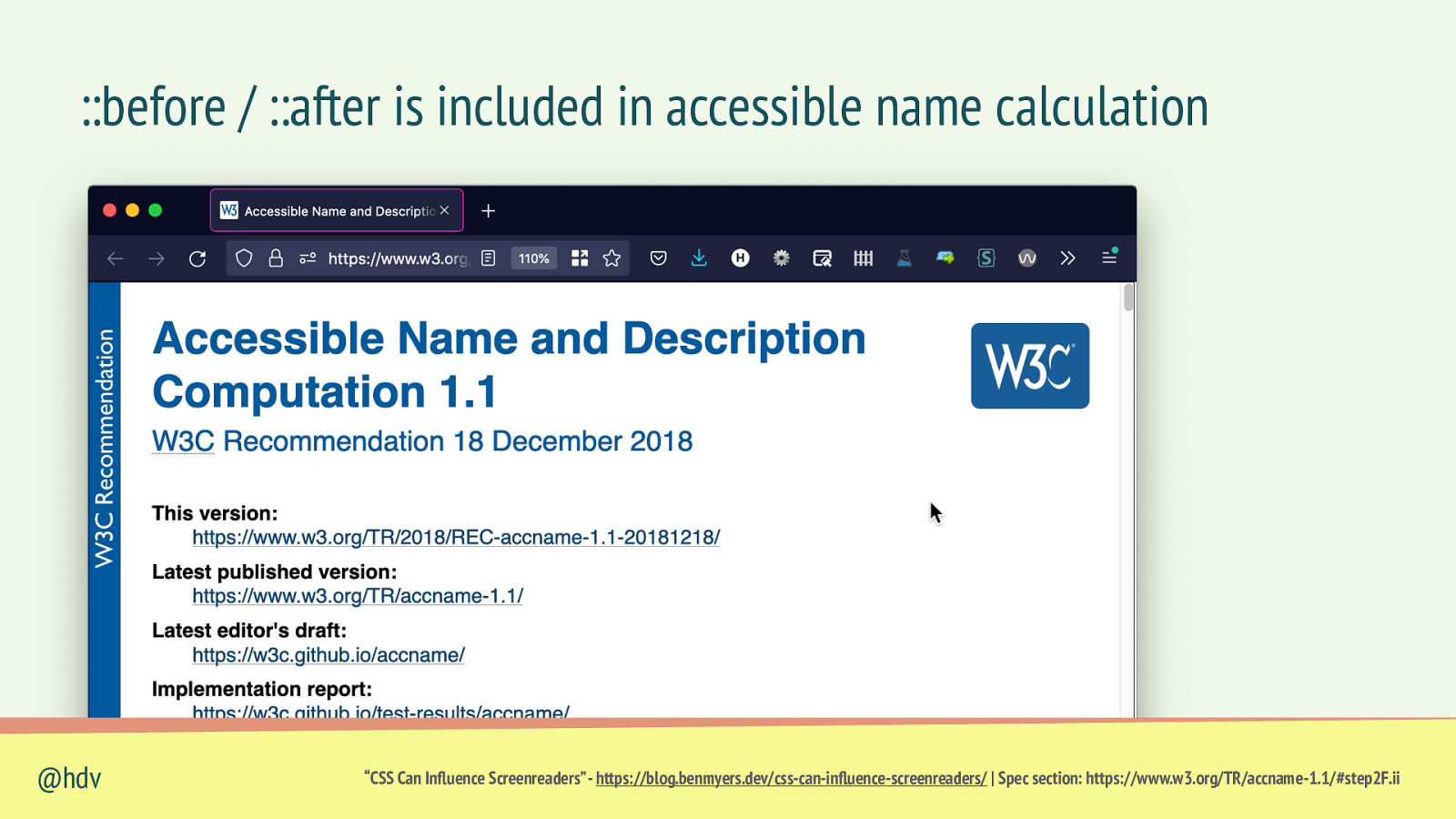
::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation “CSS Can In uence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-in uence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii fl fl @hdv
Slide 86

The future @hdv
Slide 87

Our design systems commonly contain things that are not built into HTML @hdv
Slide 88

Sometimes, our design systems contain things that do exist, but not with our desired level of style-ability @hdv
Slide 89

“ We hope to make it unnecessary to reinvent built-in UI controls Open UI Homepage, https://open-ui.org @hdv https://open-ui.org
Slide 90
Goals of OpenUI Document component names as they exist today @hdv A common language for describing UIs and design systems Browser standards for web app components Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 91
Goals of OpenUI Document component names as they exist today @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 92
Slide 93
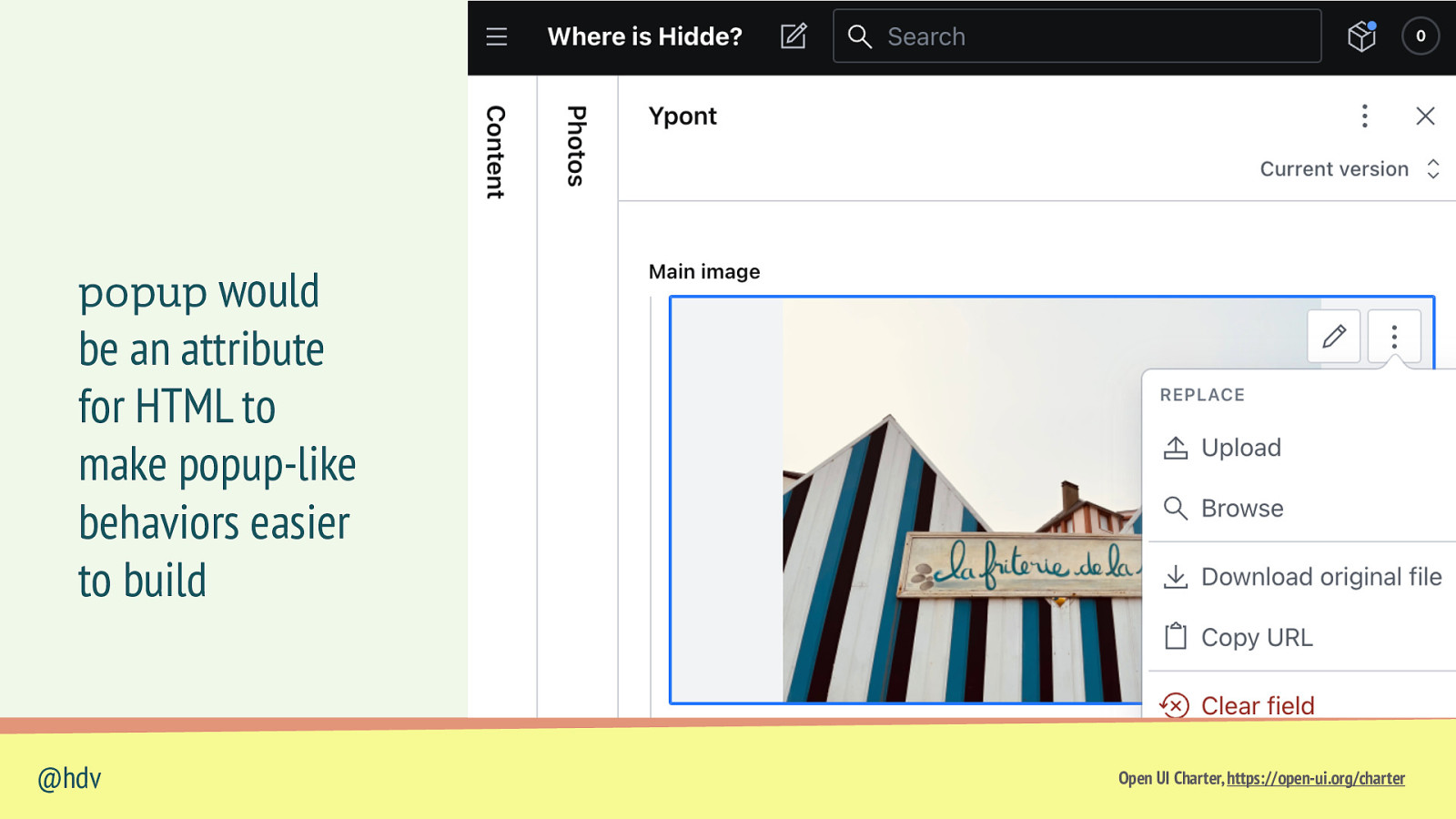
Slide 94
popup examples menus teaching UI form element suggestions content pickers <select>’s listbox
Slide 95
Common behaviours on top of other page content @hdv only open when it needs to be usually one at the time Chrome Platform Status: The Popup API・ https://chromestatus.com/feature/5463833265045504
Slide 96
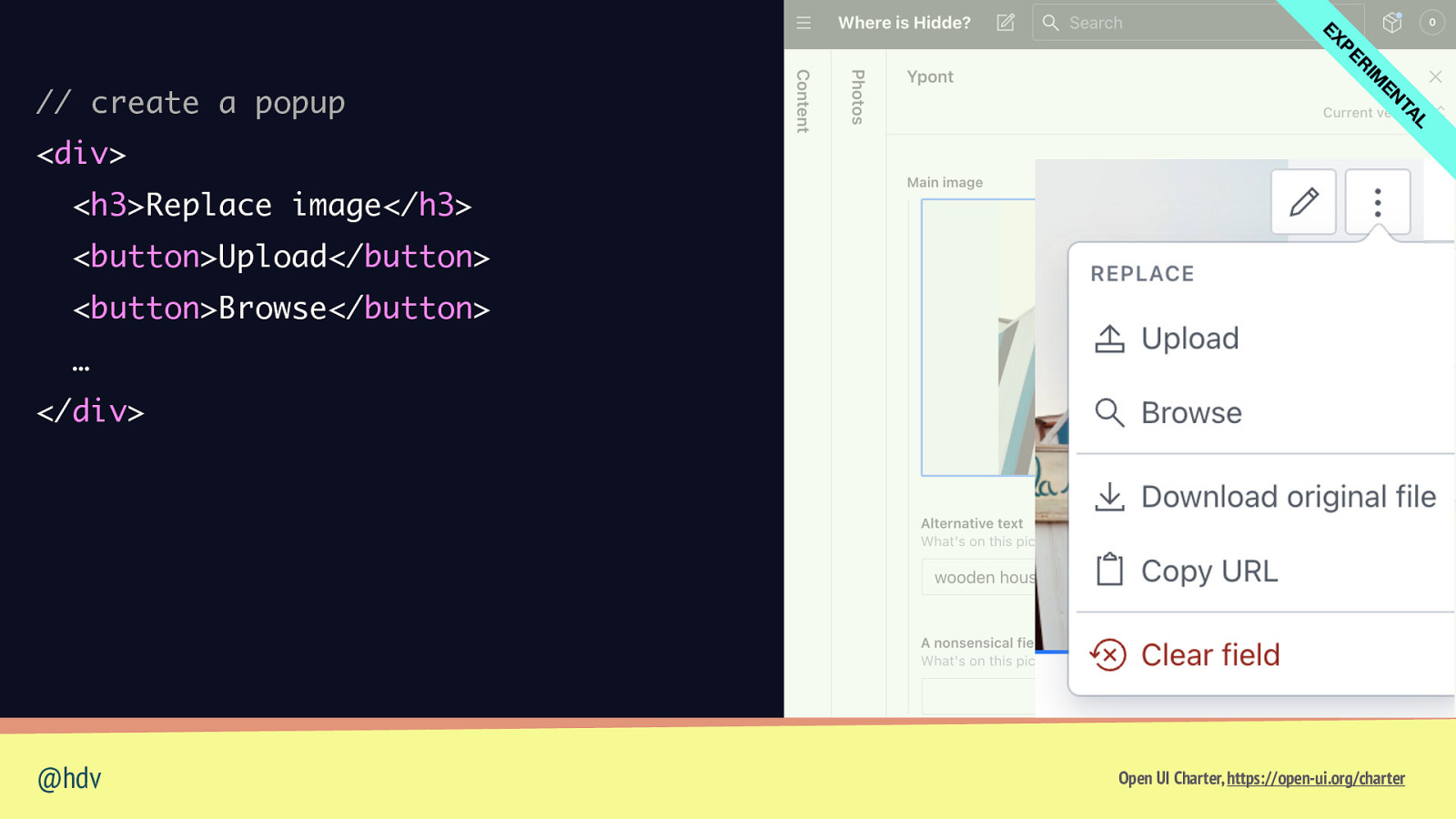
L TA EN IM R PE EX // create a popup <div> <h3>Replace image</h3> <button>Upload</button> <button>Browse</button> … </div> @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 97
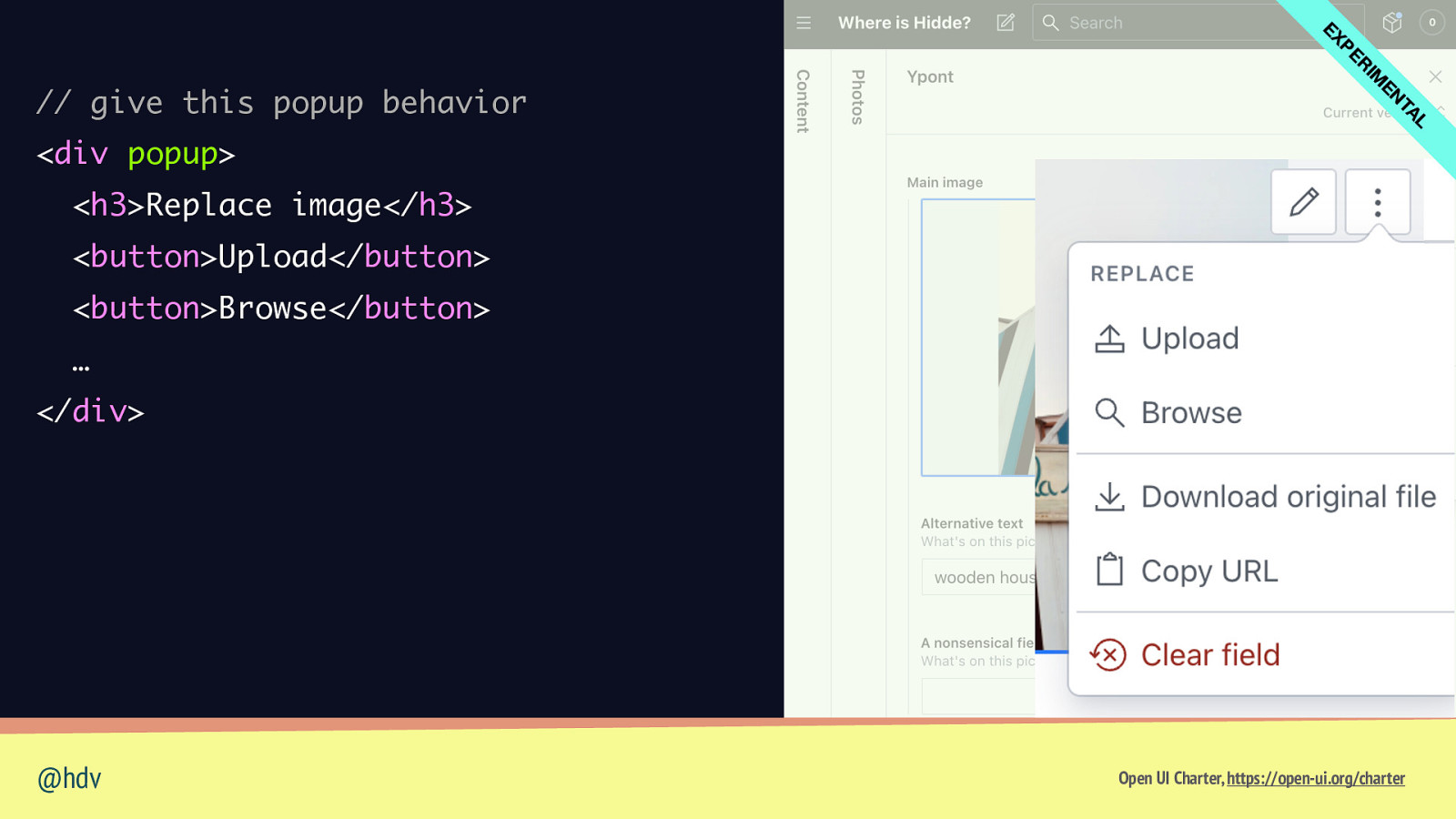
L TA EN IM R PE EX // give this popup behavior <div popup> <h3>Replace image</h3> <button>Upload</button> <button>Browse</button> … </div> @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 98
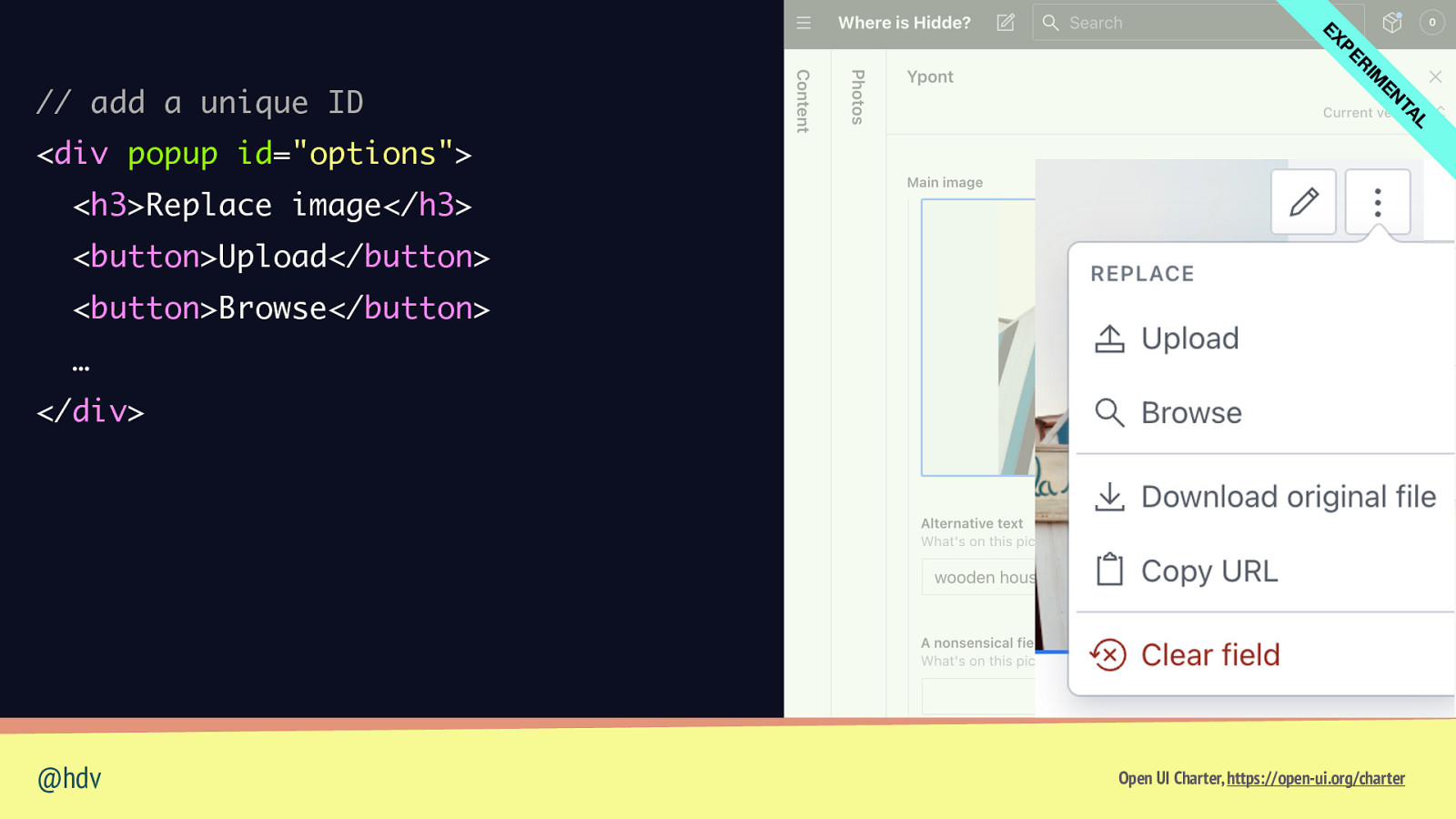
L TA EN IM R PE EX // add a unique ID <div popup id=”options”> <h3>Replace image</h3> <button>Upload</button> <button>Browse</button> … </div> @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 99
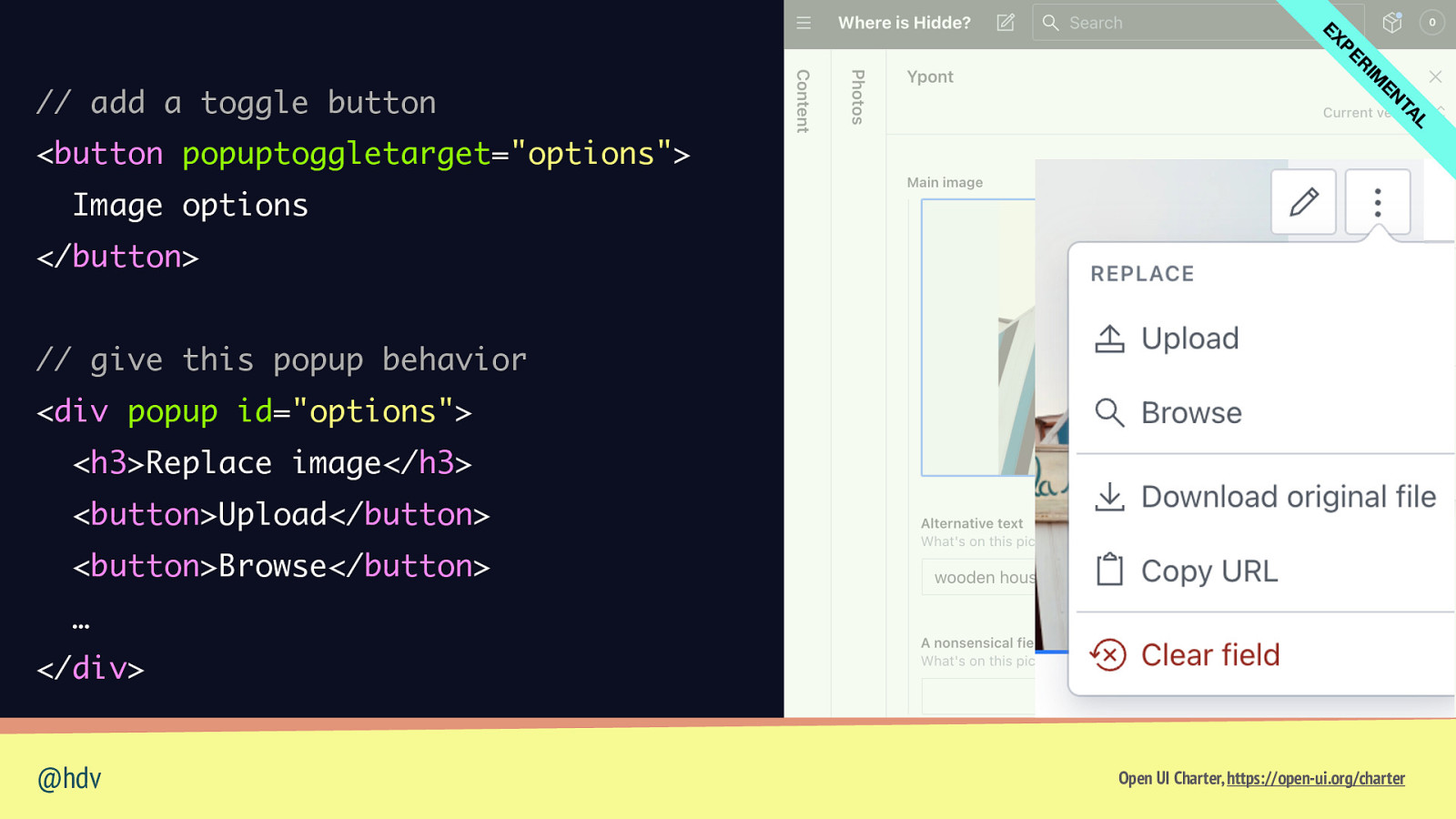
L TA EN IM R PE EX // add a toggle button <button popuptoggletarget=”options”> Image options </button> // give this popup behavior <div popup id=”options”> <h3>Replace image</h3> <button>Upload</button> <button>Browse</button> … </div> @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 100
L TA EN IM R PE EX // make an async popup <div popup=”async” id=”statusMessage”> </div> @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 101
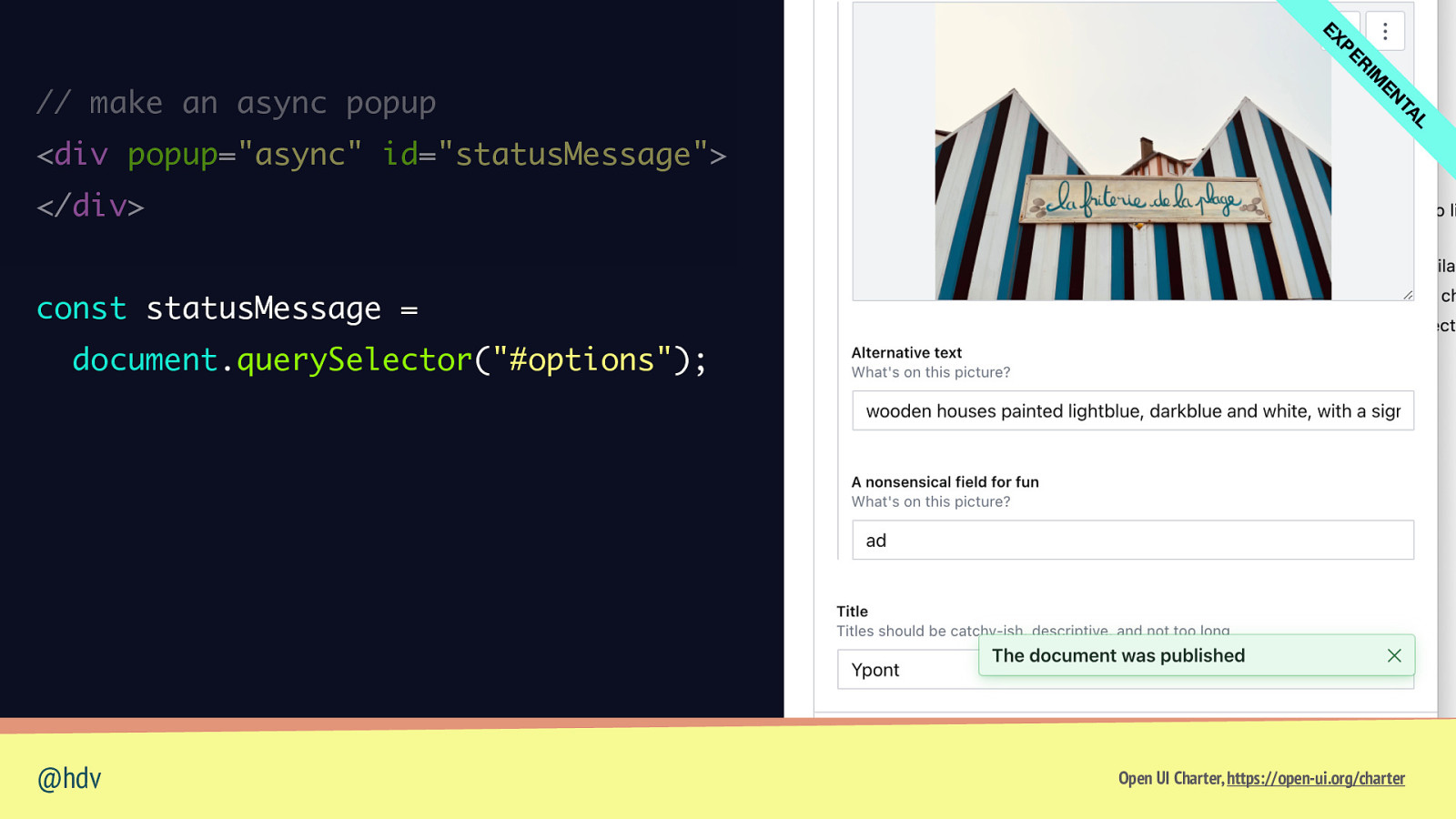
L TA EN IM R PE EX // make an async popup <div popup=”async” id=”statusMessage”> </div> const statusMessage = document.querySelector(“#options”); @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 102
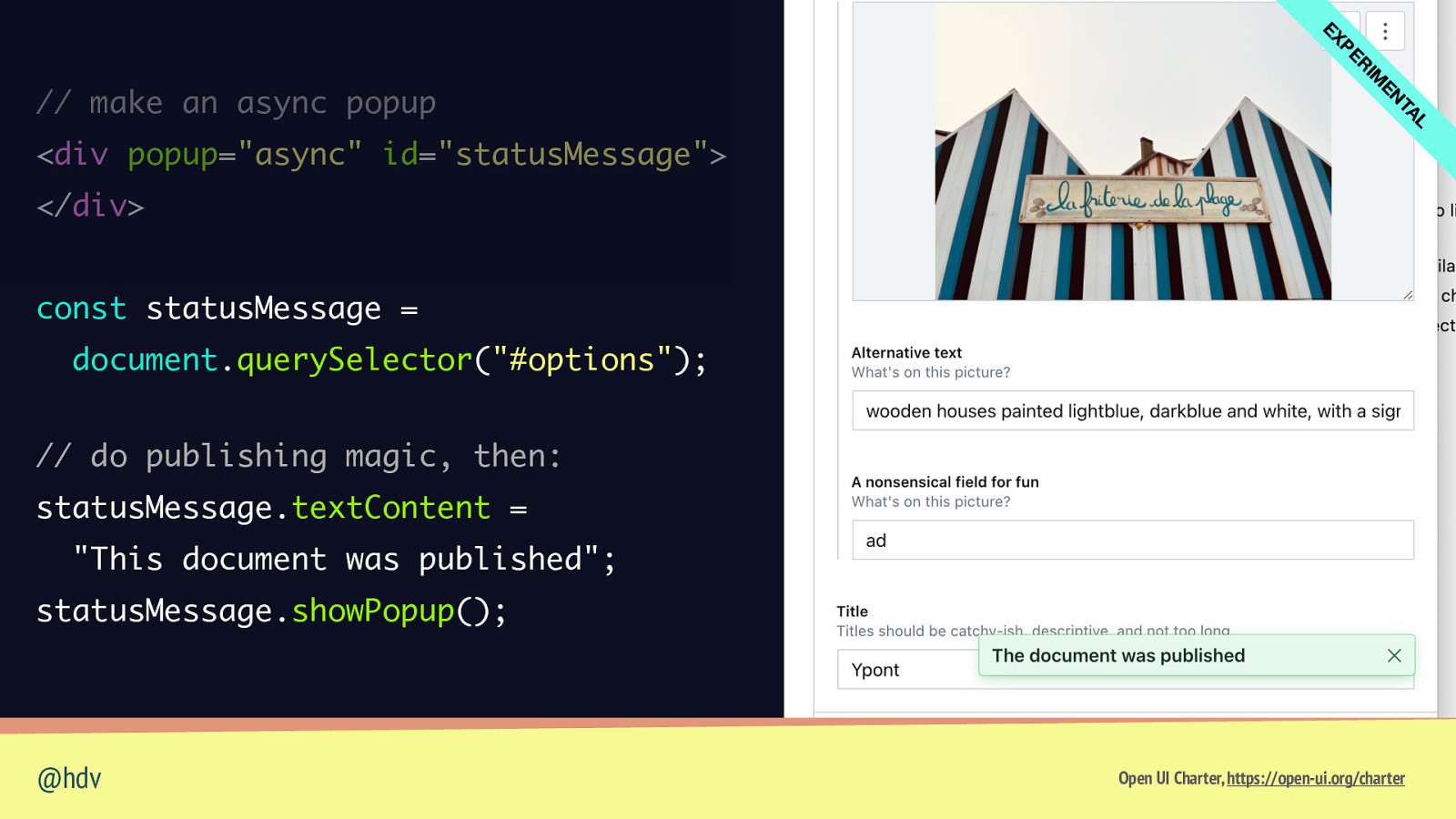
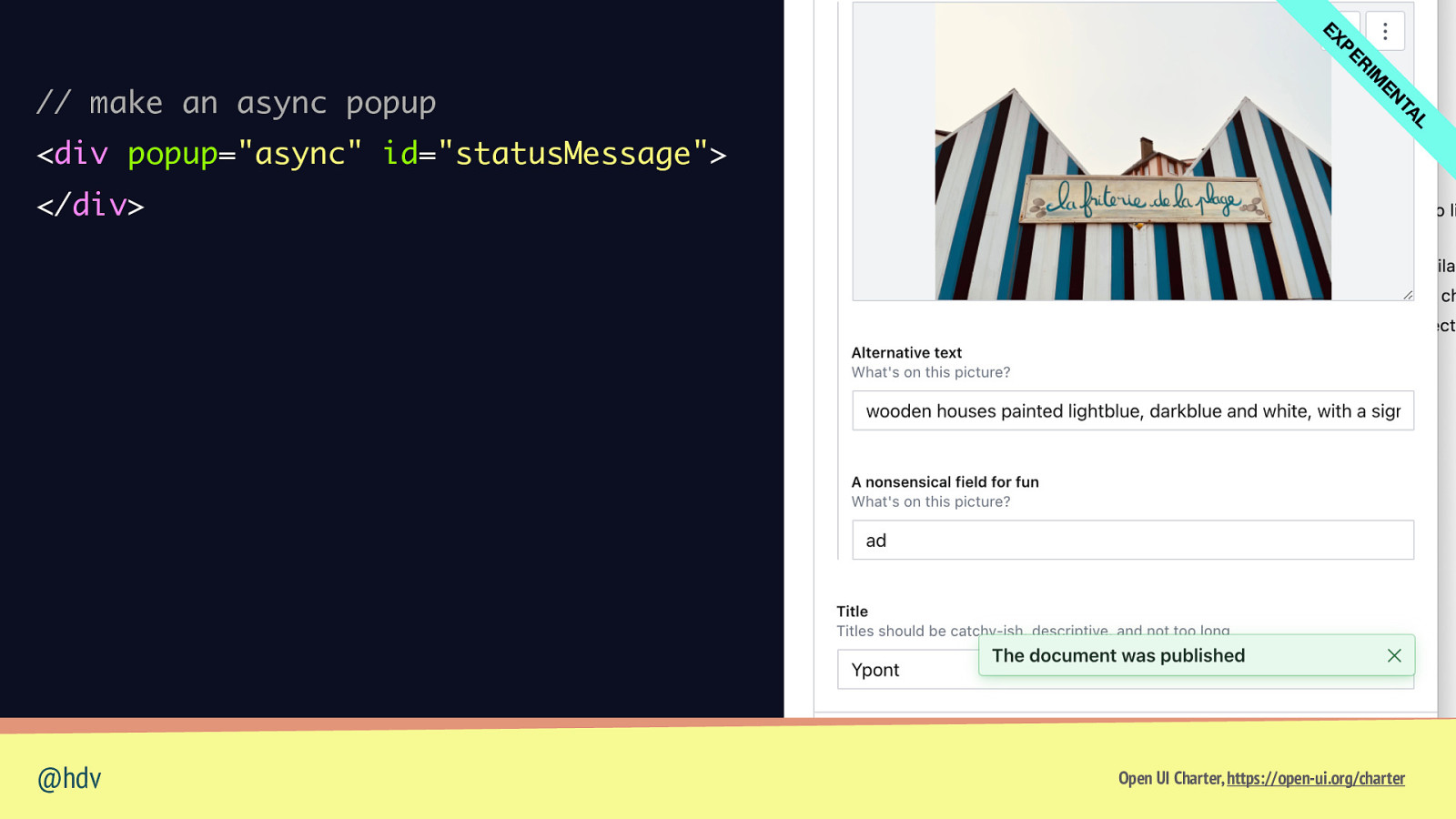
L TA EN IM R PE EX // make an async popup <div popup=”async” id=”statusMessage”> </div> const statusMessage = document.querySelector(“#options”); // do publishing magic, then: statusMessage.textContent = “This document was published”; statusMessage.showPopup(); @hdv Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 103
Browser support Experimental, behind ags, known accessibility issues about: ags, “Experimental Web Features” Chrome Platform Status: The Popup API・ https://chromestatus.com/feature/5463833265045504 fl fl @hdv
Slide 104

Conclusion @hdv
Slide 105
Semantics only works if shared (use the HTML standard) Semantic HTML has many bene ts, some unexpected Beware of how CSS, ARIA and AT can impact semantics fi @hdv
Slide 106

Thanks for listening! hidde@hiddedevries.nl hidde.blog Links on talks.hiddedevries.nl @hdv