More to give than just the div: semantics and how to get them right Hidde de Vries, Beyond Tellerrand, Düsseldorf, 2021 @hdv
Slide 1

Slide 2

semantics @hdv
Slide 3

Correspondence theories of meaning @hdv
Slide 4

Wittgenstein: “the meaning of a word is its use in the language” Ludwig Wittgenstein, Philosophical Investigations (1953) @hdv
Slide 5

Wittgenstein: no such thing as a private language, there can only be meaning if it’s shared Ludwig Wittgenstein, Philosophical Investigations (1953) @hdv
Slide 6
Your design system is a shared language. @hdv
Slide 7

Your API is a shared language. @hdv
Slide 8

Your Vue/Svelte/<customelement> component names are a shared language. @hdv
Slide 9

Classification depends on place and culture @hdv
Slide 10

Classification is hard and AI aren’t great at it @hdv
Slide 11

Semantics on the web @hdv
Slide 12

For the web, you could have a lot semantics… @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 13
? ” 0 . 1 ” = n o i s r e > ” <?xml v 0 2 0 1 9 9 9 1 ” = e t a D r e d r o r e d r O <purchase > ” S U ” = y r t n u o c <shipTo > e m a n / < h t i m S e < n a m e> A l i c > t e e r t s / < t e e r t S e l p a M 3 2 1 > t e <stre > y t i c / < y e l l a V < c i t y> M i l l > e t a t s / < A C > e <stat > p i z / < 2 5 9 0 9 > p <zi < / s h i p T o> > ” S U ” = y r t n u o c o <billT > e m a n / < h t i m S < n a m e> R o b e r t > t e e r t s / < e u n e v A < s t r e e t> 8 O a k > y t i c / < n w o T d < c i t y> O l > e t a t s / < A P > e t a t <s > p i z / < 9 1 8 5 9 > <zip > t n e m m o c / ! < d < / b i l l T o> l i w g n i o g s i n w a l y m , y r r u H > t n e m m <co < i t e m s> > ” A A 2 7 8 ” = m u N t r > e m <item pa a N t c u d o r p / < r e w o m n w a L > e m a N t <produc > y t i t n a u q / < 1 > y <quantit > e c i r P S U / < 5 9 . 8 4 > t n e m m o < U S P r i c e> 1 c / < c i r t c e l e s i s i h t m r i f n o C > t n e m m o c < < /i t e m> @hdv > ” A A 6 2 9 ” = m u <item partN o d u c t N a m e> https://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-0/
Slide 14
</xsd:documentat ion> </xsd:annotation > <xsd:element nam e= ” p u r c h a s e O r . All rights res erved. d e r ” t y p e= ” P u r c h aseOr <xsd:element nam e= ” c o m m e n t ” t y p e =”xsd:string”/> <xsd:complexType n a m e= ” P u r c h a s e O r derType”> xsd:sequence <xsd:element nam e= ” s h i p T o ” t y p e= ” U S A d d r e s s “/ > <xsd:element nam e= ” b i l l T o ” t y p e= ” U S A d d r e s s “/ > <xsd:element ref =”comment” minOc c u r s= ” 0 ” / > <xsd:element nam e= ” i t e m s ” t y p e= ” I t e m s “/ > </xsd:sequence> <xsd:attribute n a m e= ” o r d e r D a t e ” t y p e = ” x s d : d a t e “/ </xsd:complexTyp > e> @hdv derType” <xsd:complexType n a m e= ” U S A d d r e s s ” > xsd:sequence <xsd:element nam e= ” n a m e ” t y p e= ” x s d : s t r i n g <xsd:element nam “/> e= ” s t r e e t ” t y p e= “xsd:string”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” c i t y ” t y p e= ” x s d : s t r i n g <xsd:element nam “/> e= ” s t a t e ” t y p e= “xsd:string”/> <xsd:element nam e= ” z i p ” t y p e= ” x s d : d e c i m a </xsd:sequence> l”/> <xsd:attribute n a m e= ” c o u n t r y ” t y p e= ” x s d : N M T O K E N ” f i x e d= ” U S “/ > </xsd:complexTyp https://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-0/ e>
Slide 15

…but for accessibility, we need one, agreed-upon set @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 16

HTML is a standard way for your website to declare its semantics @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 17

HTML is not a way to declare what stuff looks like on a page @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 18

It’s a way to declare what stuff is on a page @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 19

HTML semantics are not behaviour, but are often tied to it @hdv
Slide 20

Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… Photo: Jeremy Keith; from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cuddling_with_multiple_devices.jpg
Slide 21

This NeXT machine was used to develop and run the first WWW server, multimedia browser and web editor @hdv Copyright: CERN (http://cds.cern.ch/record/42413)
Slide 22

Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… Photo: Jeremy Keith; from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cuddling_with_multiple_devices.jpg
Slide 23

Default stylesheets Multi device web @hdv HTML enables…
Slide 24

Default stylesheets Multi device web @hdv HTML enables… ‘Browse by heading’ “Heading structures are tables of contents” - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 25
Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour @hdv
Slide 26

Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… Reader mode @hdv ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour
Slide 27
@hdv
Slide 28

Default stylesheets Multi device web HTML enables… Reader mode @hdv ‘Browse by heading’ Default behaviour
Slide 29

HTML points machines at what stuff is @hdv
Slide 30

HTML points assistive technology at what stuff is @hdv
Slide 31

Hire for HTML expertise @hdv
Slide 32

In practice @hdv
Slide 33
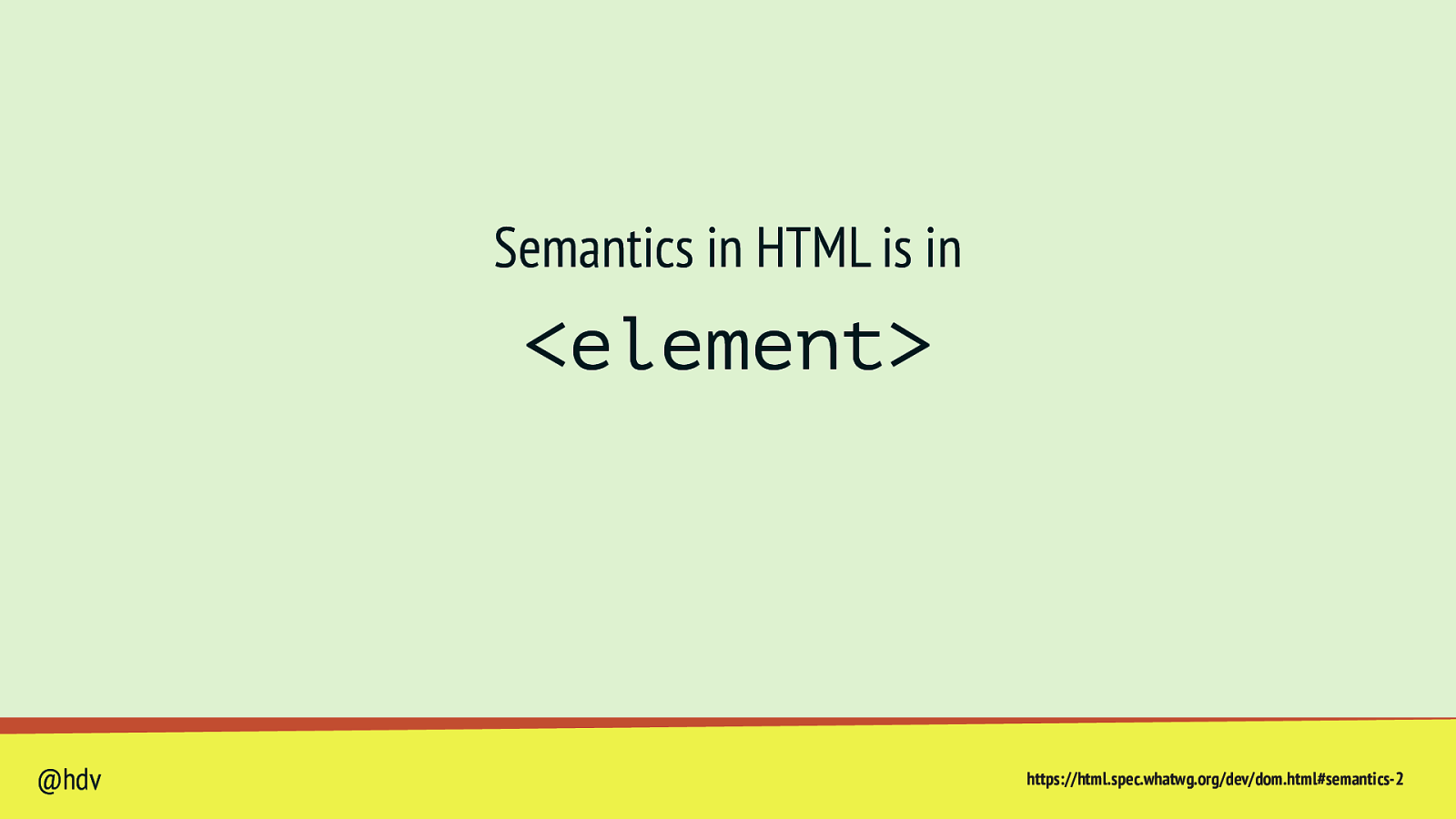
Semantics in HTML is in <element> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 34

Semantics in HTML is in <element attribute> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 35
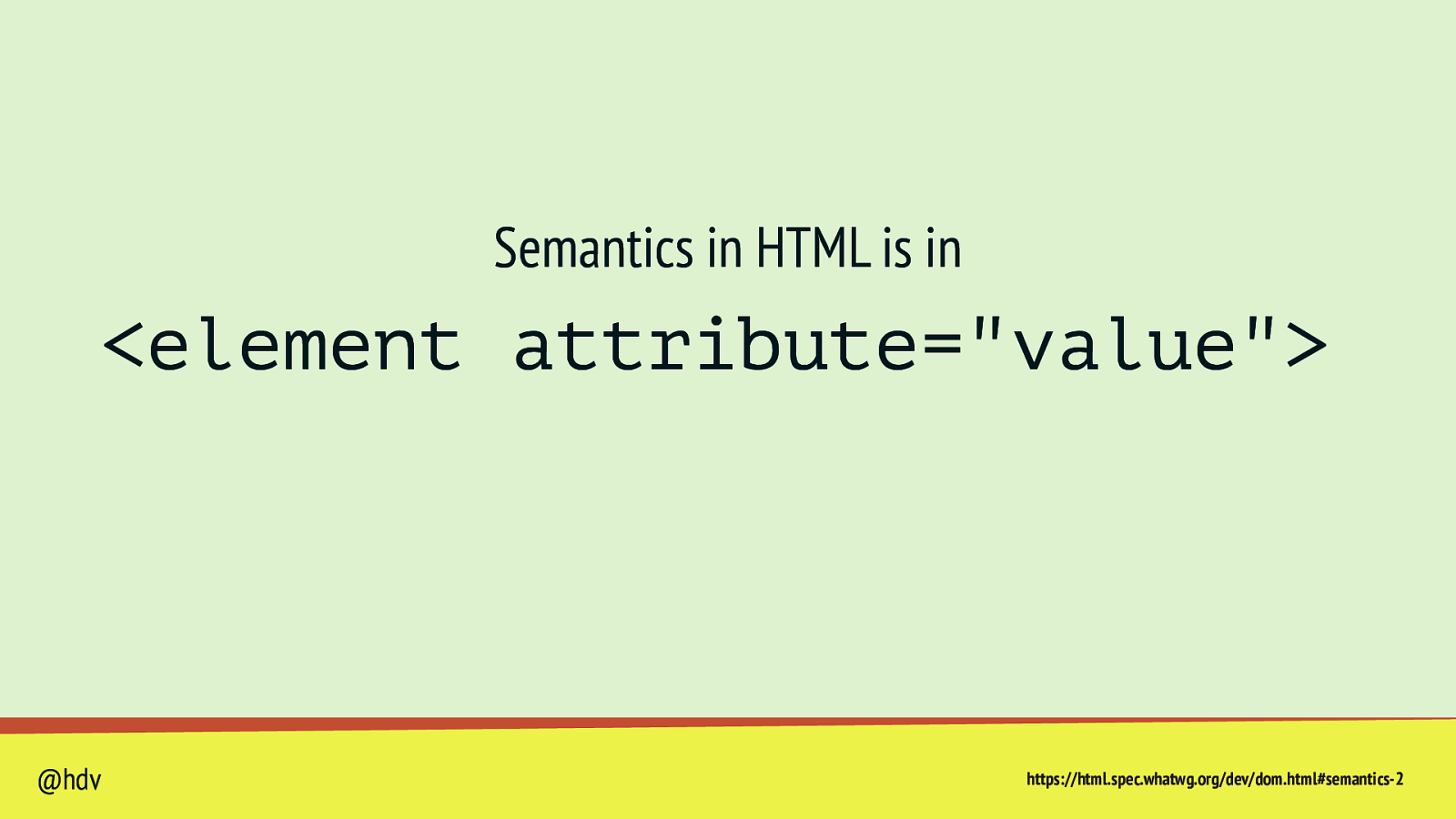
Semantics in HTML is in <element attribute=”value”> @hdv https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/dom.html#semantics-2
Slide 36

WAI-ARIA defines semantics beyond HTML @hdv
Slide 37

“ WAI-ARIA is designed to provide semantic information about objects when host languages lack native semantics […] Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.2, §8.4 @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/
Slide 38

“ host languages […] can evolve and provide new native features that correspond to WAIARIA features [so] there are many situations in which WAI-ARIA semantics are redundant Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.2, §8.4 @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/
Slide 39

Multiple ways to get to one semantic <button>
<div role=”button”> Semantic HTML element Semanticless HTML element with WAI-ARIA role for semantics @hdvSlide 40
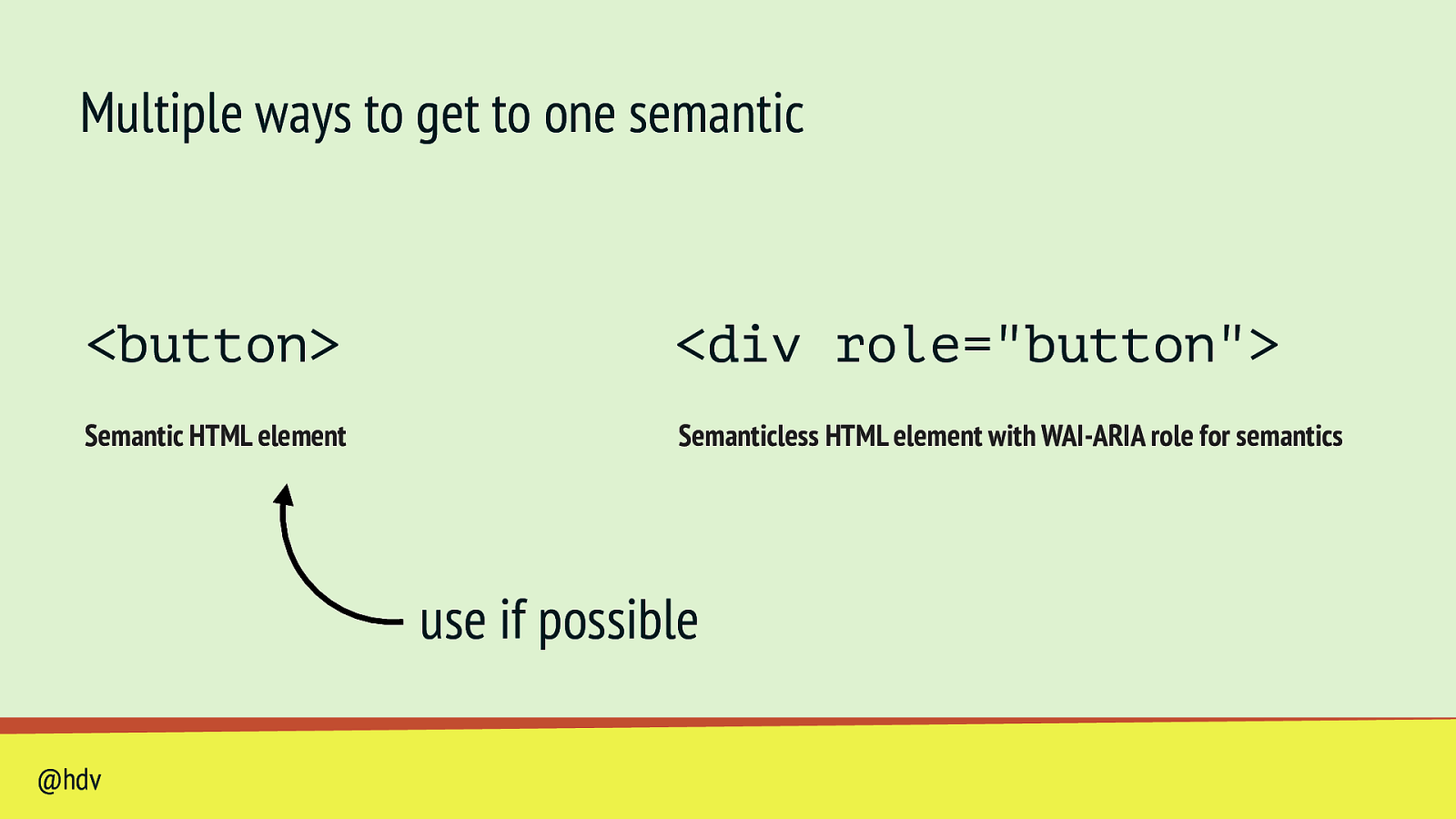
Multiple ways to get to one semantic <button>
<div role=”button”> Semantic HTML element Semanticless HTML element with WAI-ARIA role for semantics use if possible @hdvSlide 41
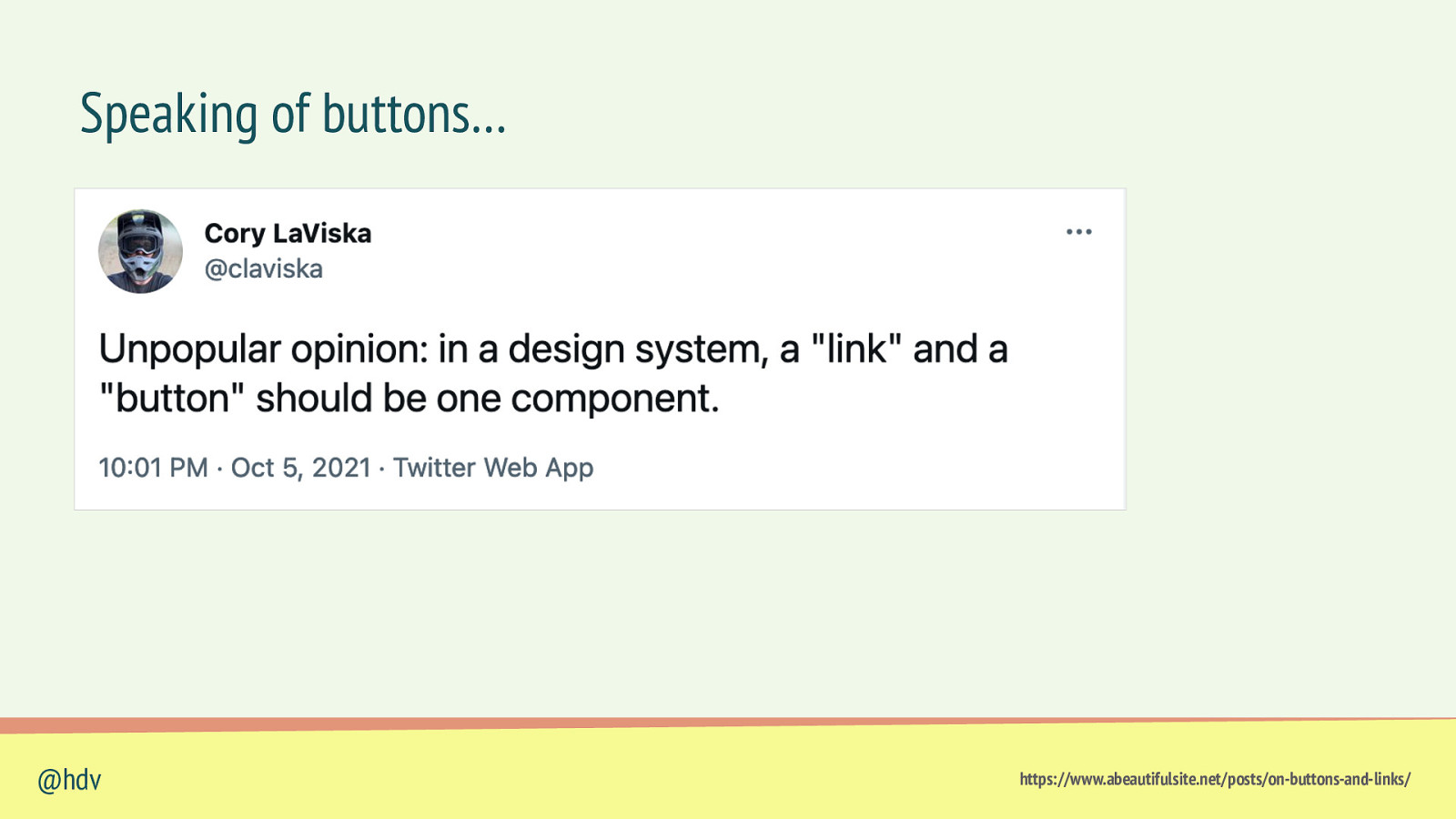
Speaking of buttons… @hdv https://www.abeautifulsite.net/posts/on-buttons-and-links/
Slide 42

@hdv Products Add to cart Products Add to cart
Slide 43
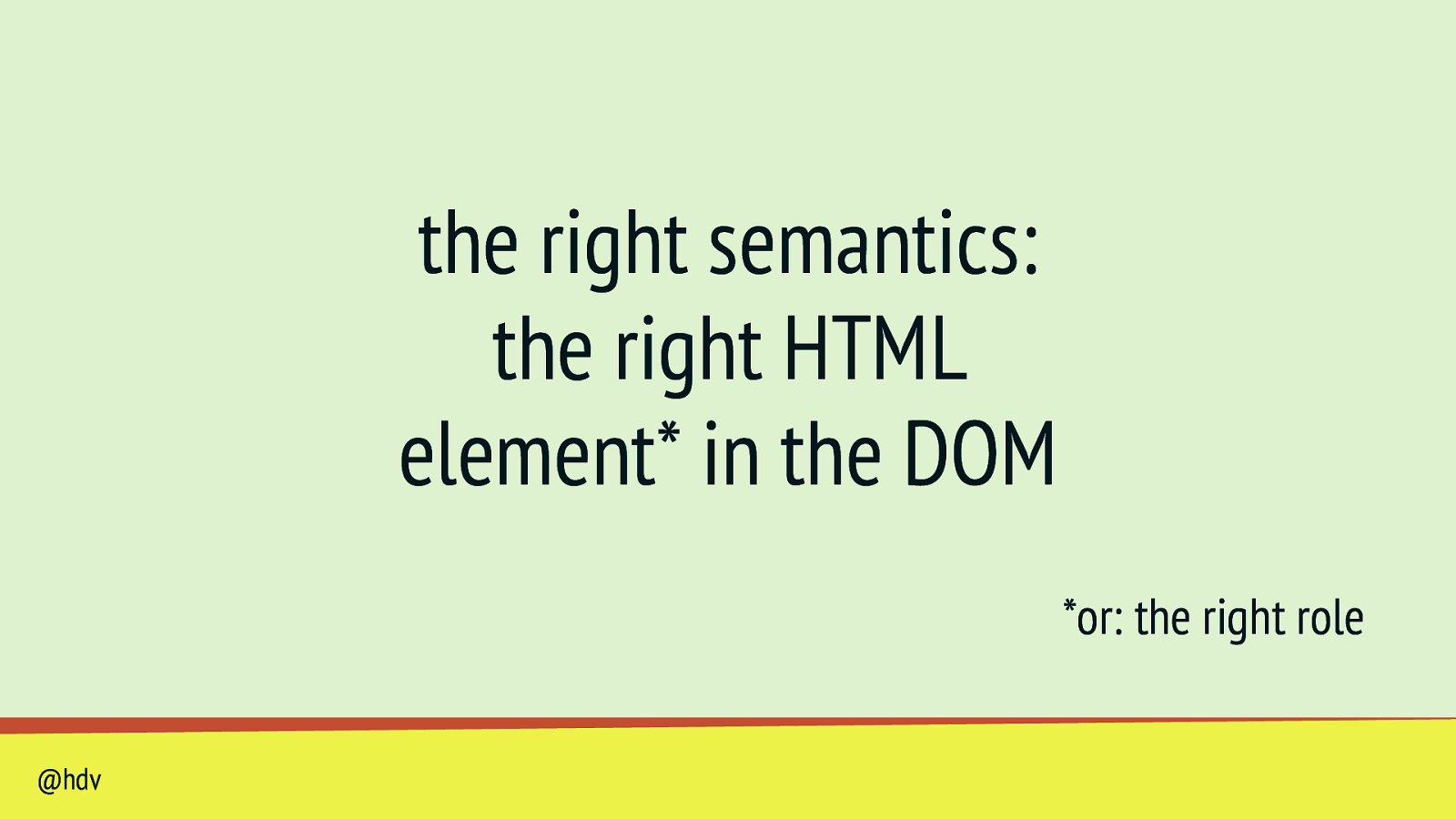
the right semantics: the right HTML element* in the DOM *or: the right role @hdv
Slide 44
@hdv
Slide 45
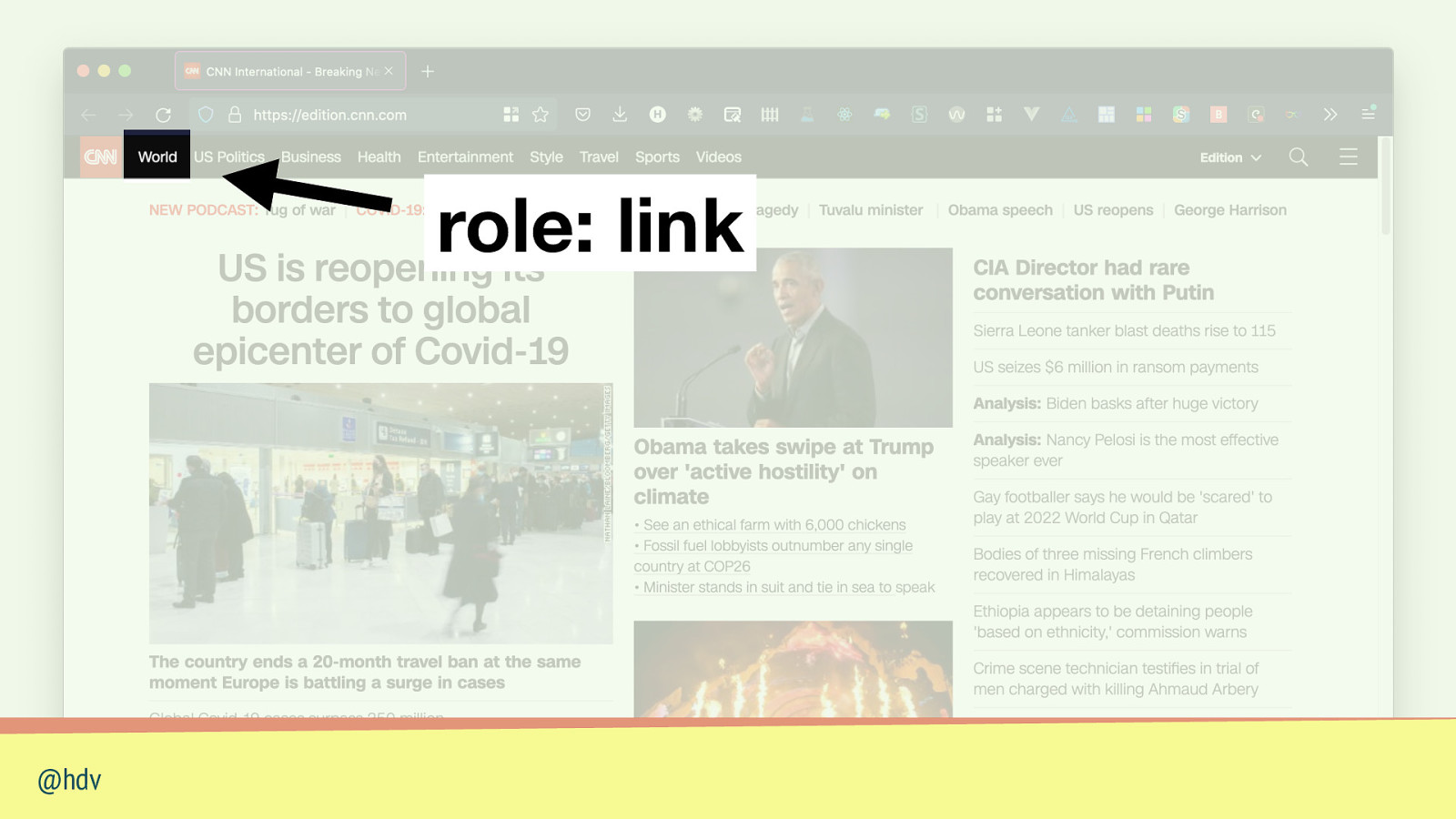
role: link @hdv
Slide 46
role: link @hdv
Slide 47
role: link @hdv
Slide 48
role: button @hdv
Slide 49
@hdv
Slide 50
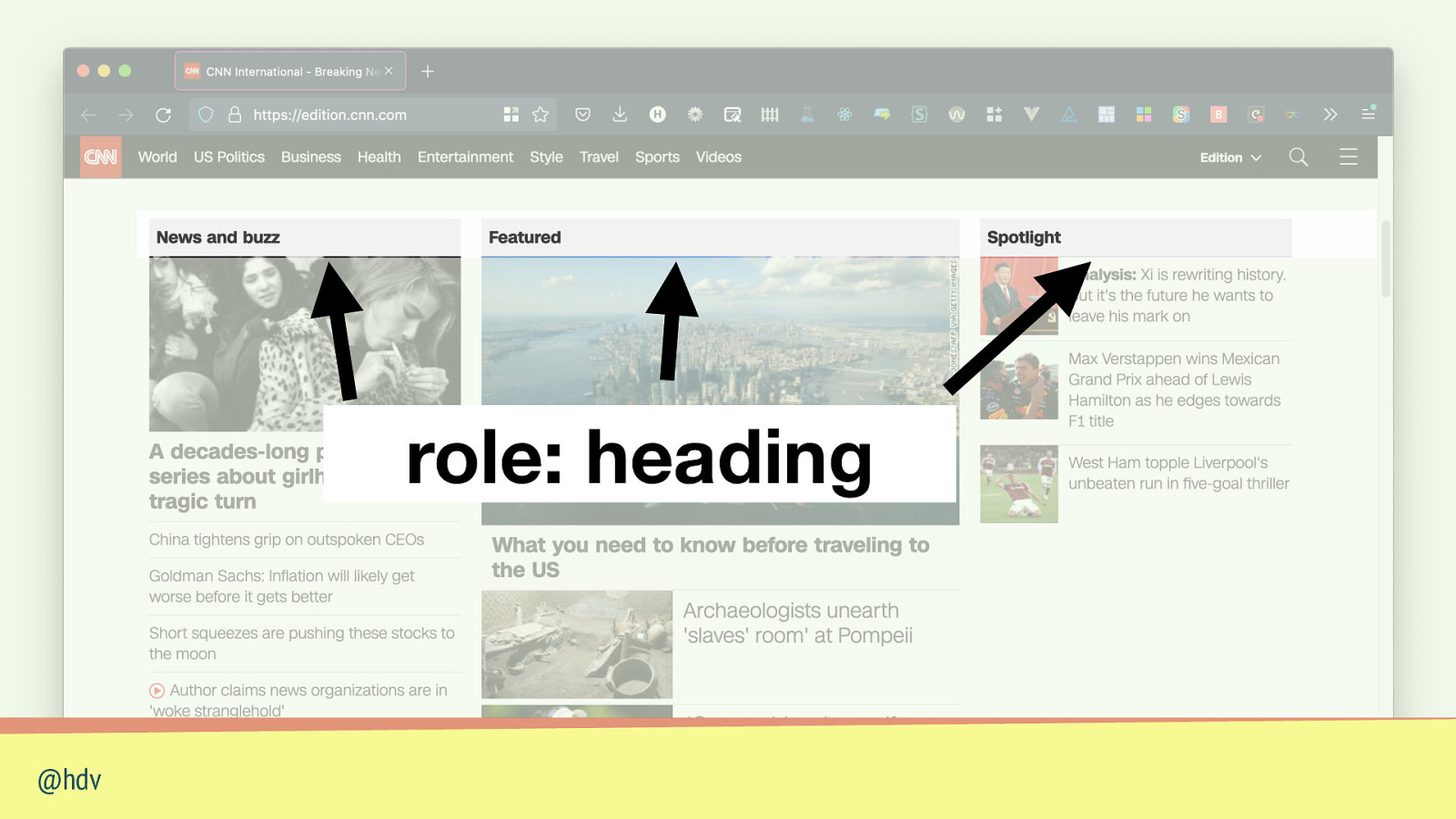
role: heading @hdv
Slide 51
@hdv
Slide 52
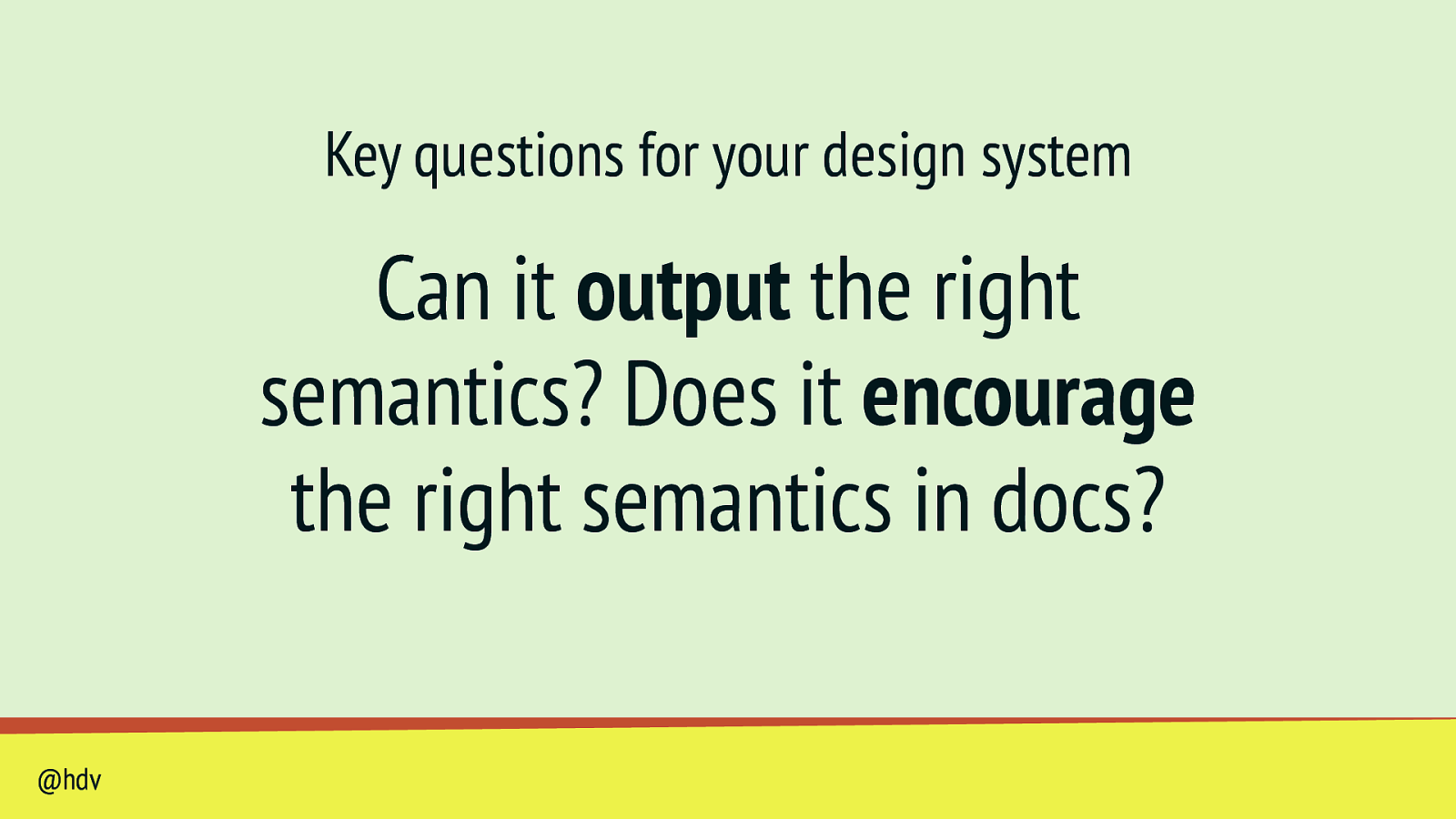
Key questions for your design system Can it output the right semantics? Does it encourage the right semantics in docs? @hdv
Slide 53

meaning = use @hdv
Slide 54

“ (…) semantic HTML, a posh term for choosing the right HTML element for the content. This isn’t a philosophical exercise; it has directly observable practical benefits. Bruce Lawson, “The practical value of semantic HTML” @hdv https://brucelawson.co.uk/2018/the-practical-value-of-semantic-html/
Slide 55

If you use <h1>, <h2>, <h3>…, people can: • see headings in • @hdv reader mode navigate by heading “Heading structures are tables of contents - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 56
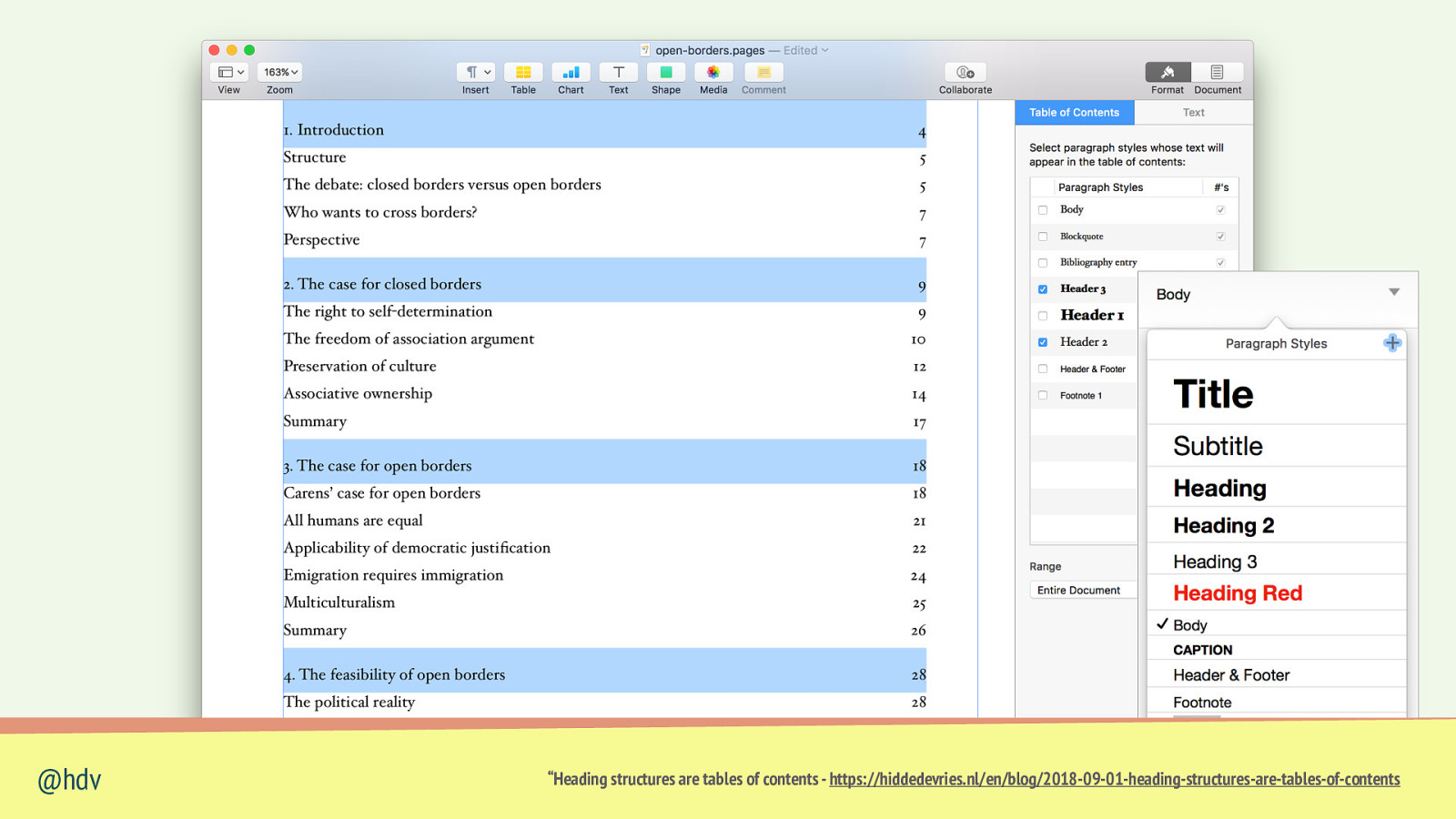
@hdv “Heading structures are tables of contents - https://hiddedevries.nl/en/blog/2018-09-01-heading-structures-are-tables-of-contents
Slide 57

If you use <button>, people can: • find it in the TAB order • press it with just a keyboard • submit the form, even if your JavaScript failed @hdv
Slide 58

If you use <ol>, <ul> or <dl>, people can: • Hear it’s a list and with how many items • Still see it’s a list in reader mode @hdv
Slide 59

If you use autocomplete on inputs, users can: • Tell their browser to fill in data for them • Assistive tech can announce input purpose • Use plugins for personalisation, e.g. with icons @hdv
Slide 60
If you use table with a caption, ths for headers and scope attributes for direction: • Assistive tech can provide useful affordances to end users @hdv
Slide 61

The HTML spec is the place to find out how to use HTML developers.whatwg.org @hdv
Slide 62
HTMHell collects examples of how not to use HTML @hdv
Slide 63

Intentions vs reality @hdv
Slide 64

Sometimes, semantics are undone if you use specific CSS @hdv
Slide 65

display overrides semantics display: display: display: display: display: display: @hdv block; inline; grid; flex; contents; none; “a11yTO Conf: CSS Display Properties versus HTML Semantics” - https://adrianroselli.com/2020/10/a11yto-conf-css-display-properties-versus-html-semantics.html
Slide 66
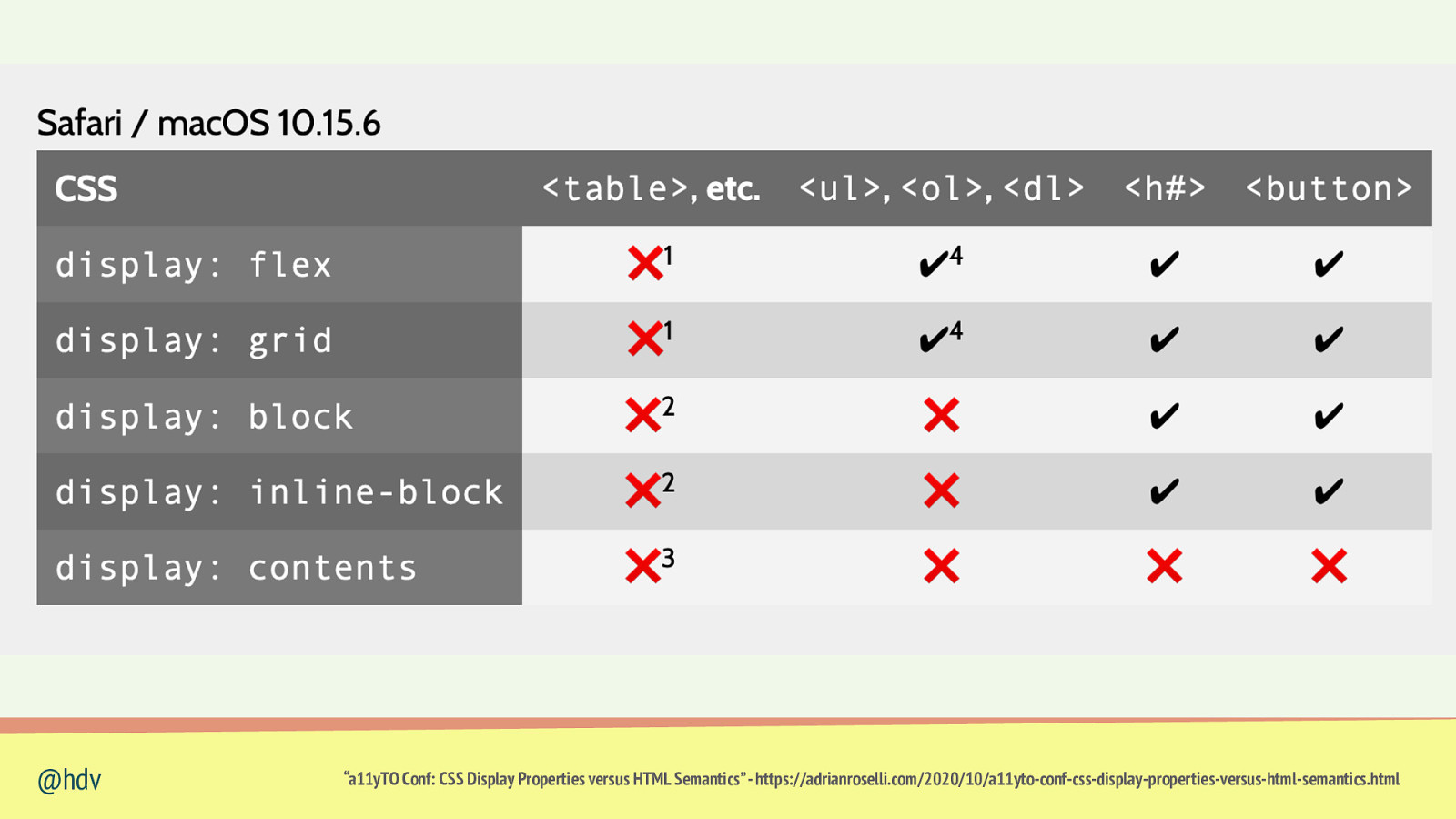
@hdv “a11yTO Conf: CSS Display Properties versus HTML Semantics” - https://adrianroselli.com/2020/10/a11yto-conf-css-display-properties-versus-html-semantics.html
Slide 67

Lists can lose list semantics when you set list-style-type: none (in Safari) @hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 68

• courgette • feta • basil • garlic @hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 69
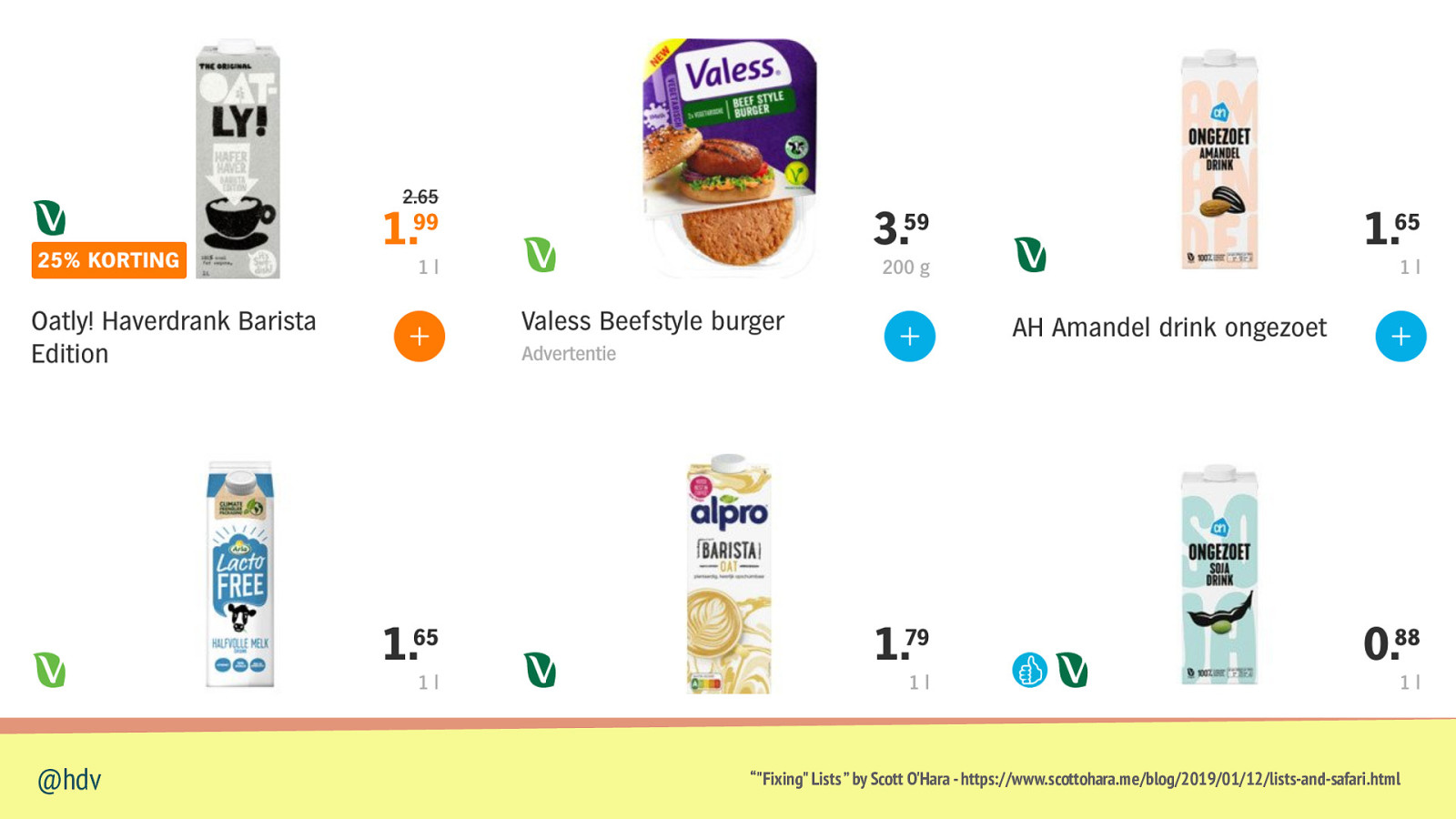
@hdv “”Fixing” Lists ” by Scott O’Hara - https://www.scottohara.me/blog/2019/01/12/lists-and-safari.html
Slide 70
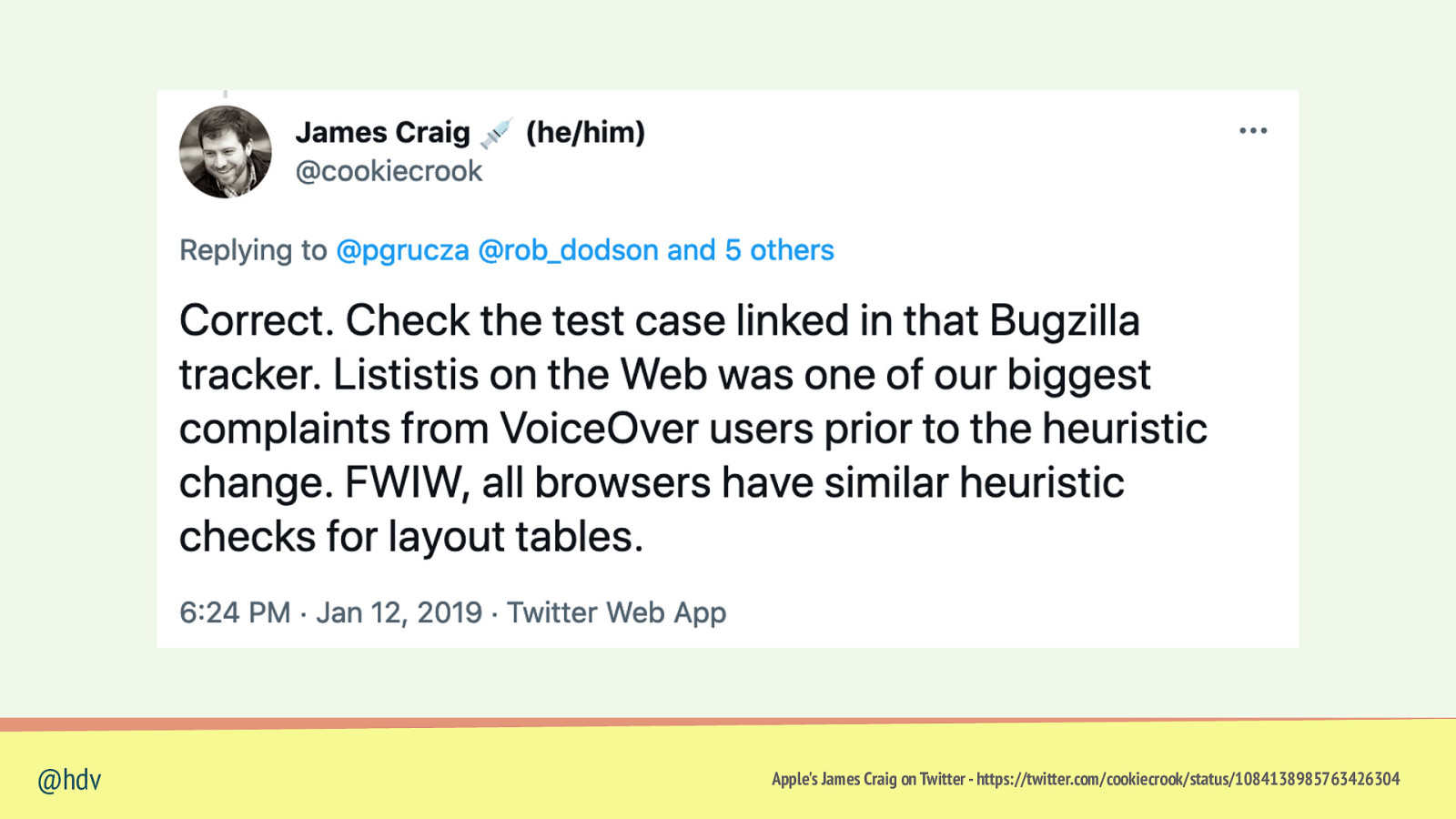
@hdv Apple’s James Craig on Twitter - https://twitter.com/cookiecrook/status/1084138985763426304
Slide 71
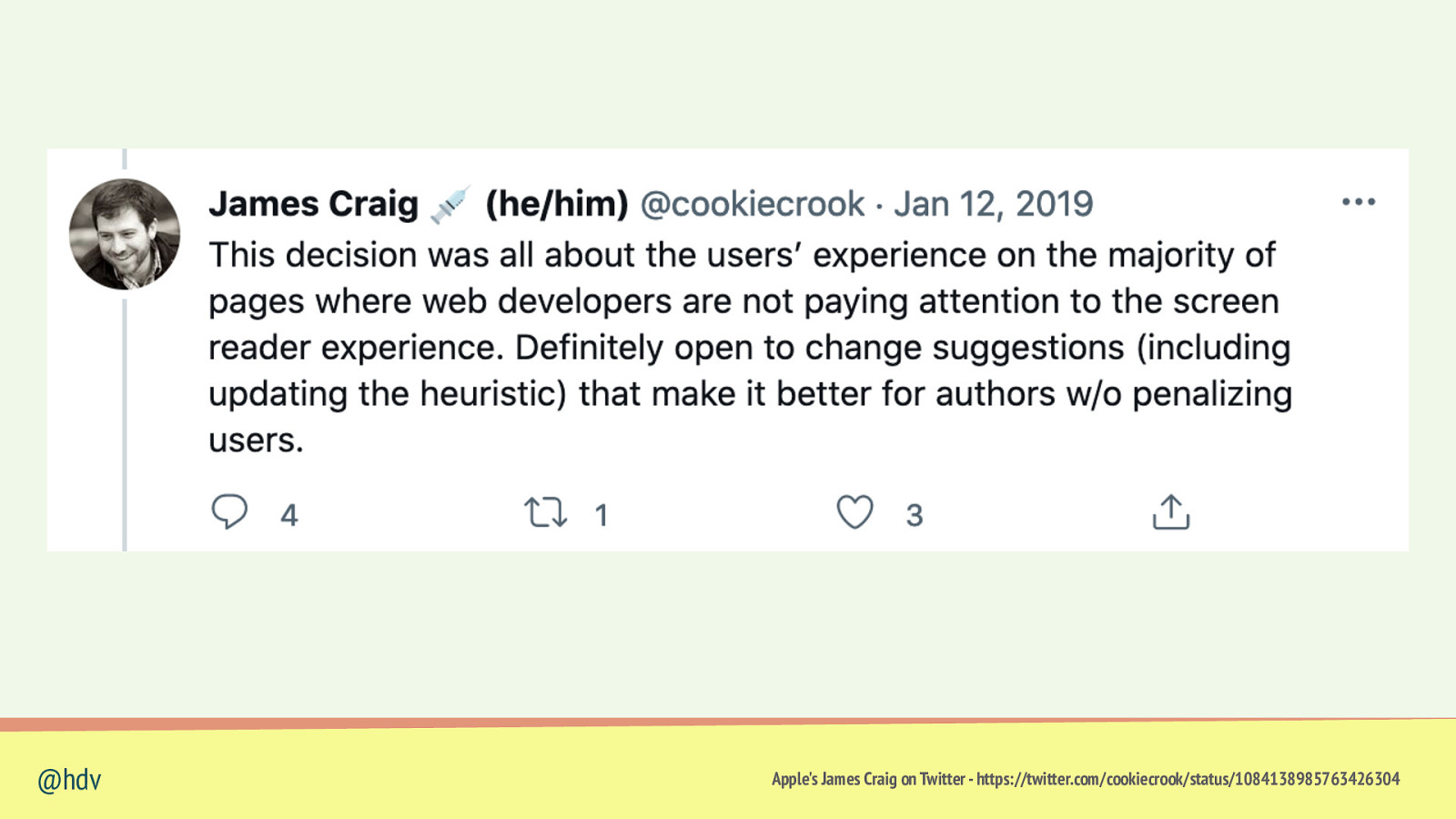
@hdv Apple’s James Craig on Twitter - https://twitter.com/cookiecrook/status/1084138985763426304
Slide 72

Sometimes, semantics are undone when you nest unexpectedly @hdv
Slide 73

Semantics in summary <details> <summary>Ingredients</summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv ▶︎ Ingredients
Slide 74

Semantics in summary <details open> <summary>Ingredients</summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Ingredients • courgette • peas • basil • feta ▼
Slide 75

Semantics in summary <details> <summary> <h2>Ingredients</h2> </summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Ingredients • courgette • peas • basil • feta ▼
Slide 76
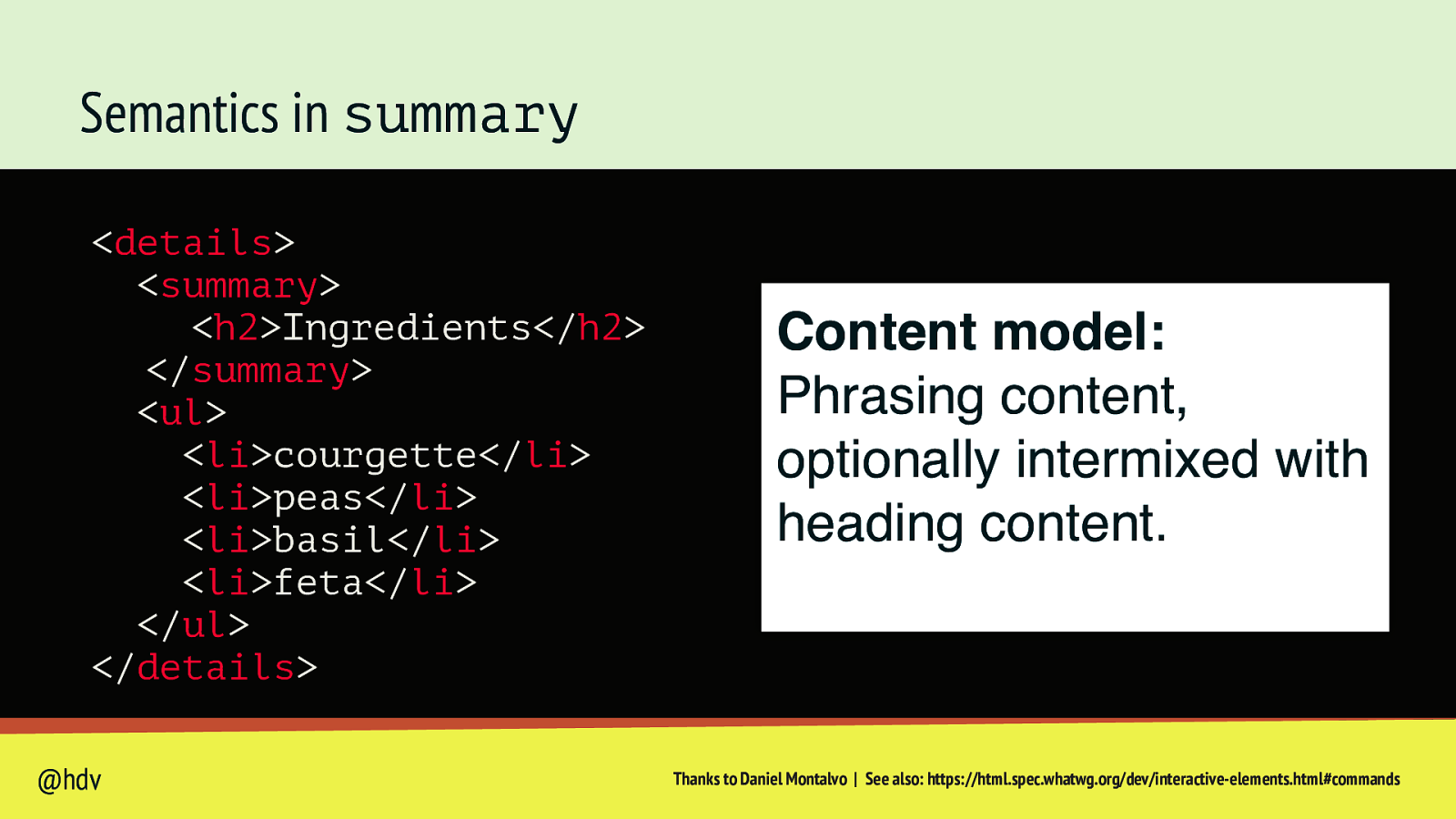
Semantics in summary <details> <summary> <h2>Ingredients</h2> </summary> <ul> <li>courgette</li> <li>peas</li> <li>basil</li> <li>feta</li> </ul> </details> @hdv Content model: Phrasing content, optionally intermixed with heading content. Thanks to Daniel Montalvo | See also: https://html.spec.whatwg.org/dev/interactive-elements.html#commands
Slide 77

Heuristics in the platform and assistive technologies @hdv
Slide 78

When you set text-transform: uppercase, some assistive technologies will read it like an abbreviation @hdv “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/
Slide 79
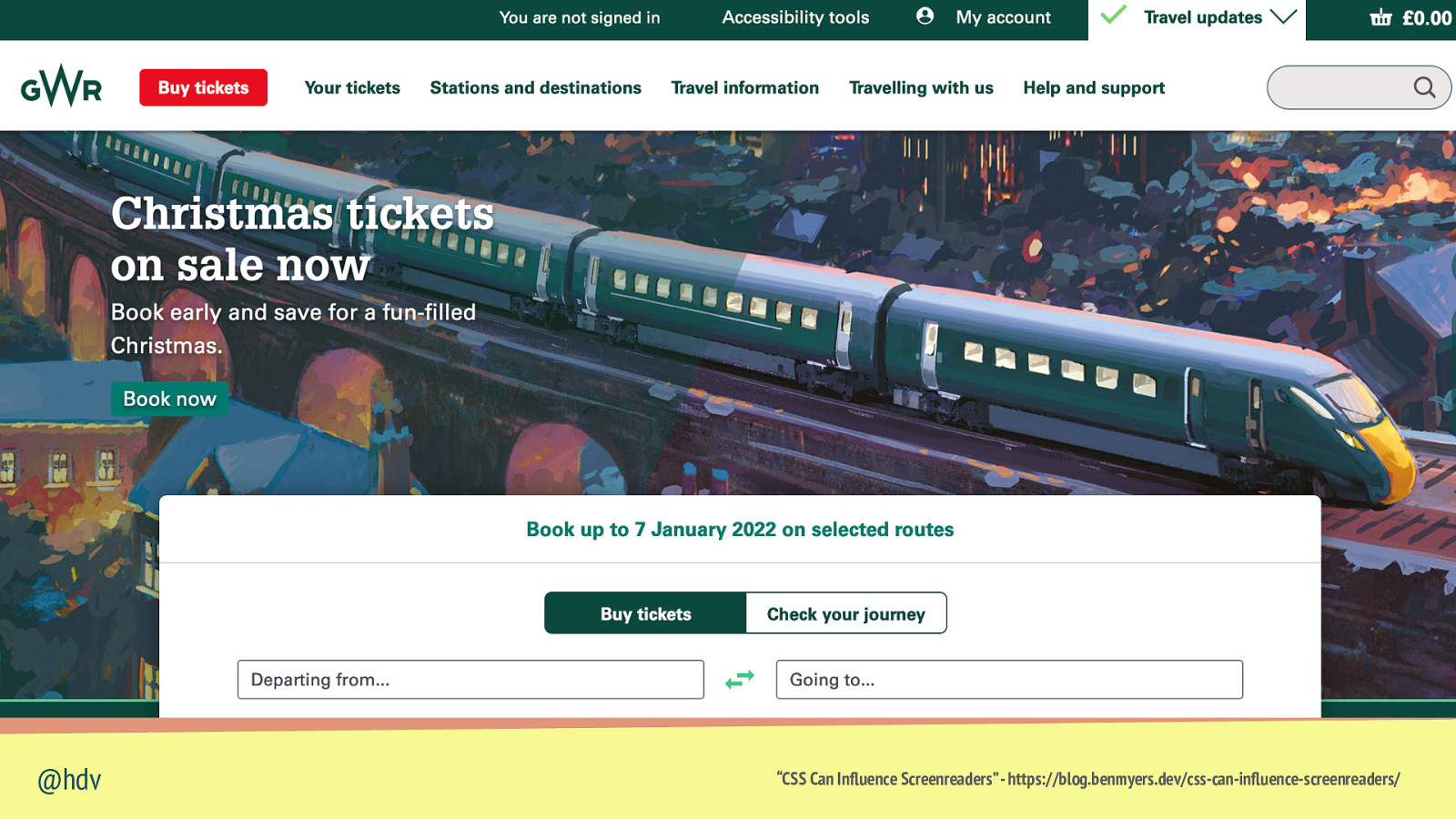
@hdv “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/
Slide 80

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation @hdv “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii
Slide 81

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation <button>Buy product</button> Buy product @hdv “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii
Slide 82

::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation <button>Buy product</button> button::before { content: “💸”; } @hdv 💸 Buy product “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii
Slide 83
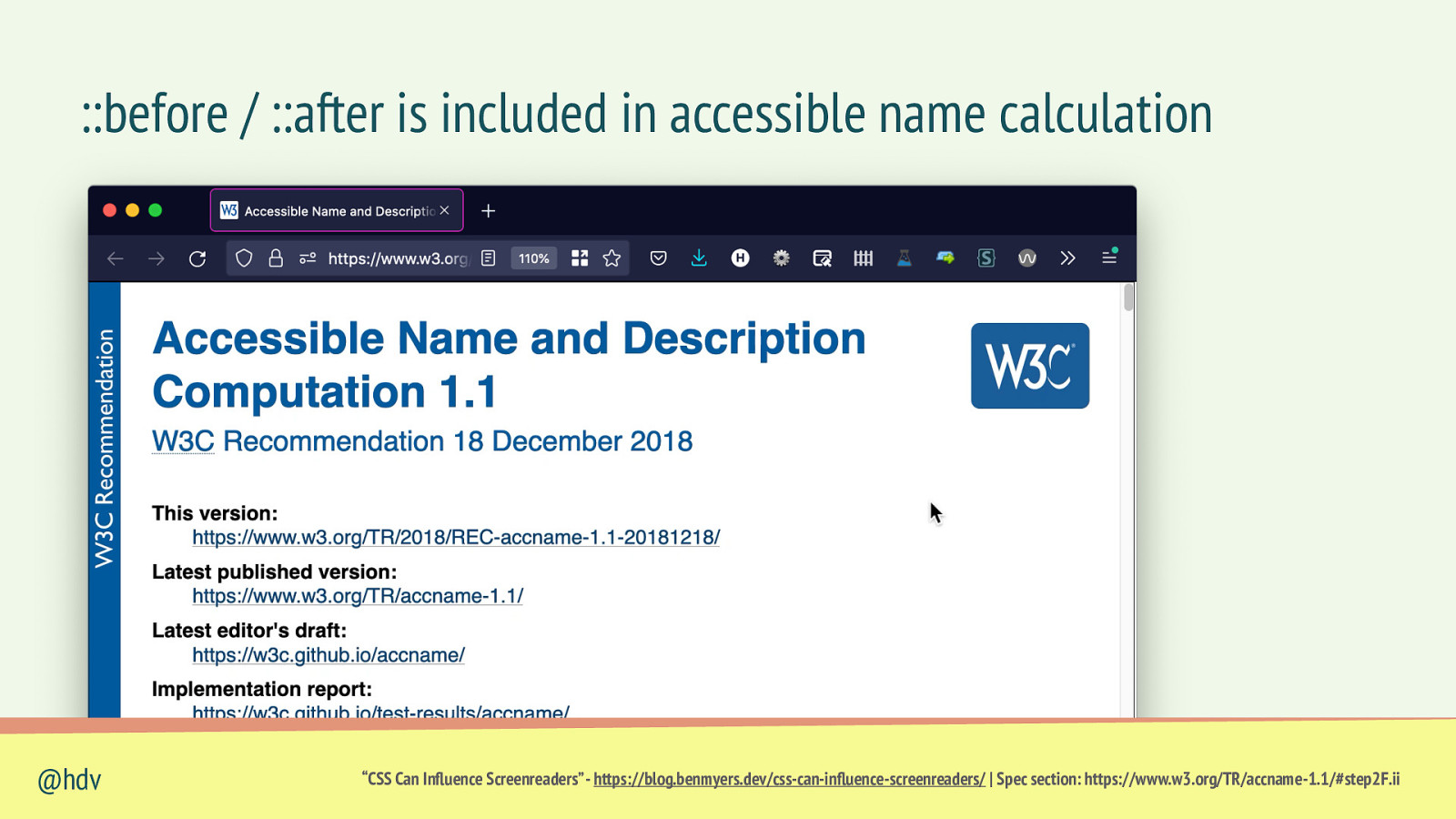
::before / ::after is included in accessible name calculation @hdv “CSS Can Influence Screenreaders” - https://blog.benmyers.dev/css-can-influence-screenreaders/ | Spec section: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/#step2F.ii
Slide 84

The future @hdv
Slide 85

Our design systems commonly contain things that are not built into HTML @hdv
Slide 86

Sometimes, our design systems contain things that do exist, but not with our desired level of style-ability @hdv
Slide 87

“ We hope to make it unnecessary to reinvent built-in UI controls @hdv Open UI Homepage, https://open-ui.org https://open-ui.org
Slide 88
Goals of OpenUI Document component names as they exist today @hdv A common language for describing UIs and design systems Browser standards for web app components Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 89
Goals of OpenUI Document component names as they exist today @hdv A common language for describing UIs and design systems Browser standards for web app components Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 90
Goals of OpenUI Document component names as they exist today @hdv A common language for describing UIs and design systems Browser standards for web app components Open UI Charter, https://open-ui.org/charter
Slide 91

Could AI guess semantics? @hdv
Slide 92

Conclusion @hdv
Slide 93
Semantics only works if shared (use the HTML standard) Semantic HTML has many benefits, some unexpected Beware of how CSS, ARIA and AT can impact semantics @hdv
Slide 94

Thanks for listening! hidde@hiddedevries.nl hidde.blog Links on talks.hiddedevries.nl @hdv