g n i t a r e l e Acc y t i l i b i s s e acc c o m p o n e n t in a based world Hidde de Vries ・ @hdv ・ Git Commit Show ・ 27 November 2021, online
Slide 1

Slide 2

Hi, I’m Hidde. Freelance accessibility and front-end consultant for organisations like the Dutch Government, Mozilla & W3C. I write at hidde.blog. @hdv LIKE AND SUBSCRIBE!
Slide 3

What is accessibility? @hdv
Slide 4

Accessibility: to ensure people with disabilities can use your website. @hdv
Slide 5

Accessibility: to ensure people with disabilities can buy your products. @hdv
Slide 6

Accessibility: to ensure people with disabilities can complete all steps. @hdv
Slide 7

Accessibility: to ensure people with disabilities can use your service. @hdv
Slide 8

1 5 in people on the planet are disabled @hdv Data source: WHO World Report on Disability (2011), 44.
Slide 9

People with disabilities face barriers on the web. Even for simple tasks like transferring money and making a vaccin appointment. We’ve @hdv T to smash those barriers! O G
Slide 10

Accessibility standards + Best practices + (You’ll need all of the above) @hdv User testing
Slide 11

Let’s talk components @hdv
Slide 12
Once upon a time… @hdv
Slide 13

Components changed how we design, develop and create for the web. @hdv
Slide 14

Reusability is key. With components, we can make some accessibility reusable. @hdv
Slide 15
don’t repeat inaccessible patterns repeat accessible patterns @hdv
Slide 16

Pick any framework. It’s the markup that matters. @hdv
Slide 17
DOM tree htmlparser.info @hdv
Slide 18
Accessibility Tree @hdv
Slide 19
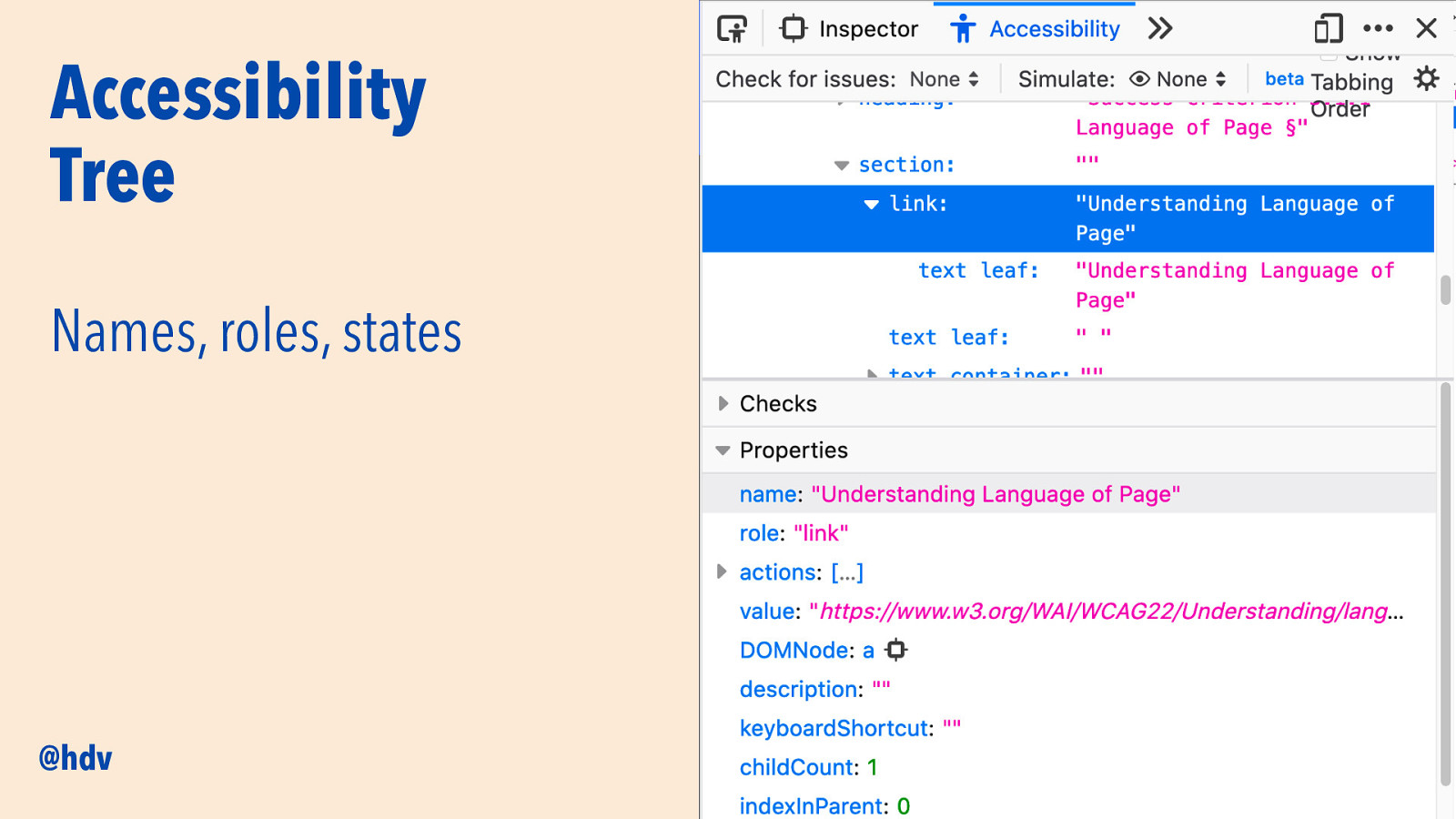
Accessibility Tree Names, roles, states @hdv
Slide 20
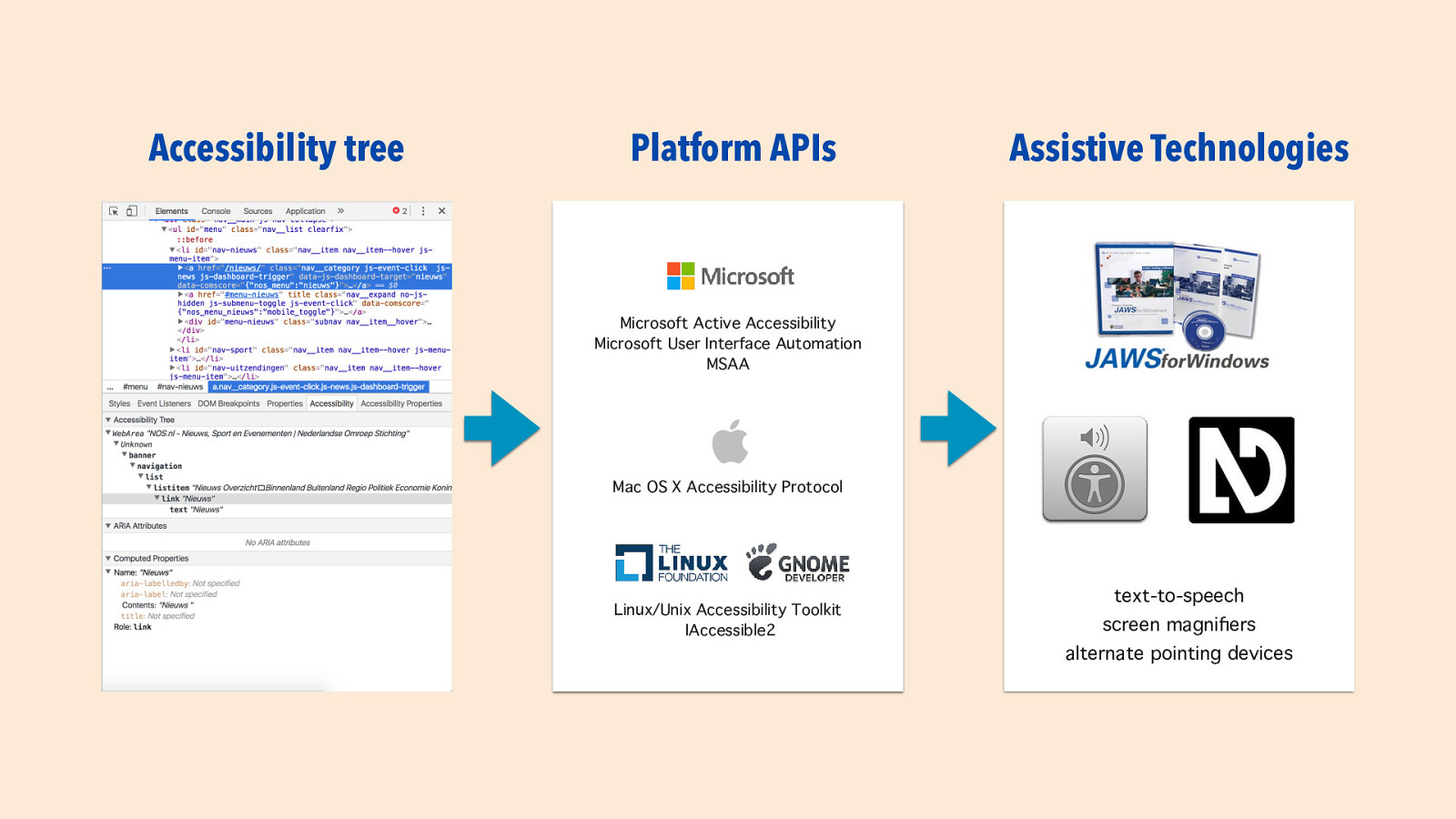
Accessibility tree Platform APIs Assistive Technologies Microsoft Active Accessibilit Microsoft User Interface Automatio MSAA Mac OS X Accessibility Protoco Linux/Unix Accessibility Toolki IAccessible2 text-to-speec screen magni er n l t y s h fi
alternate pointing devices
Slide 21
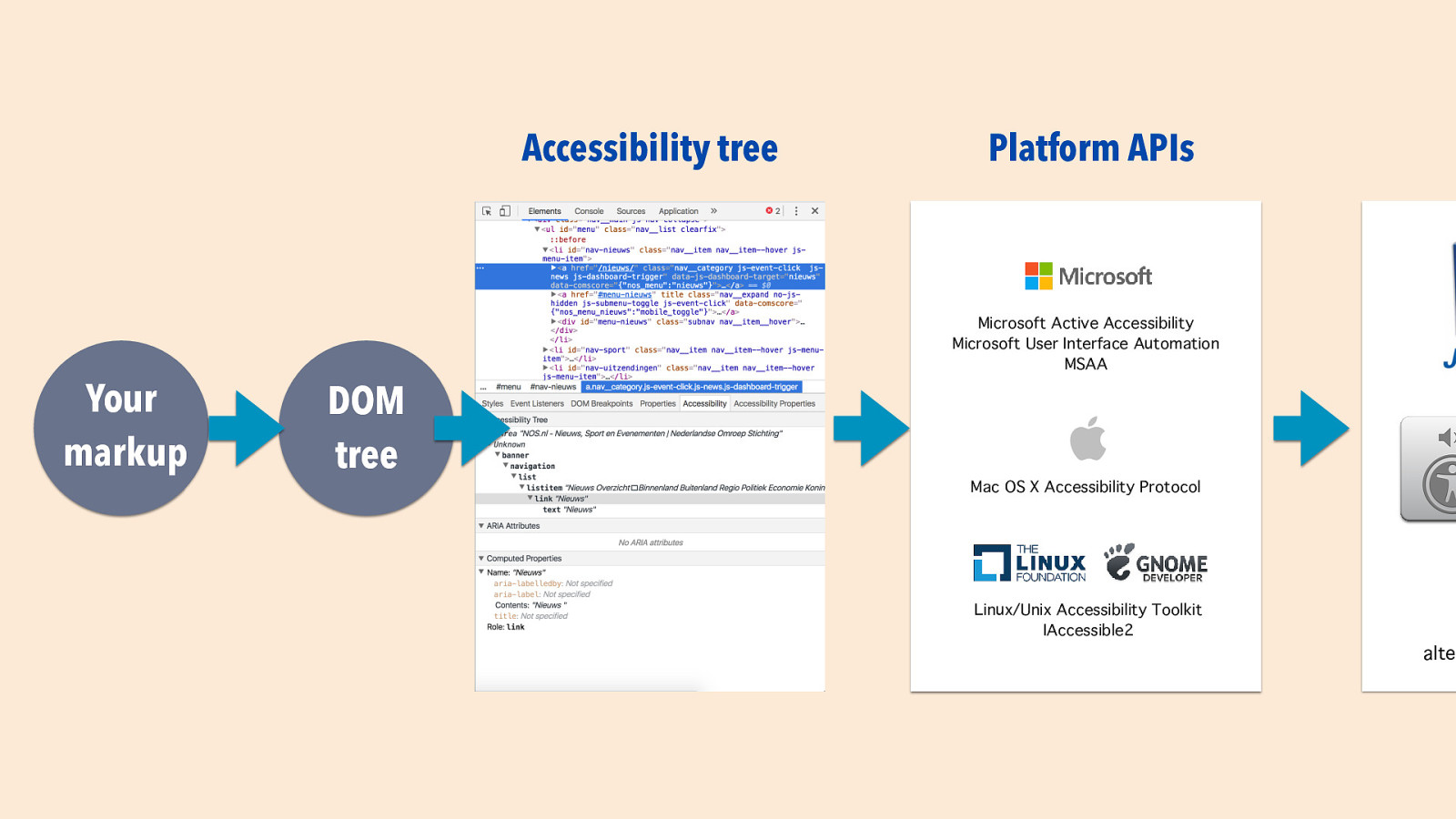
Accessibility tree Platform APIs Microsoft Active Accessibilit Microsoft User Interface Automatio MSAA Your markup DOM tree Mac OS X Accessibility Protoco Linux/Unix Accessibility Toolki IAccessible2 n t l y s h fi
alte
Slide 22

Some checks for each component @hdv
Slide 23

An accessible component… Works without mouse @hdv
Slide 24
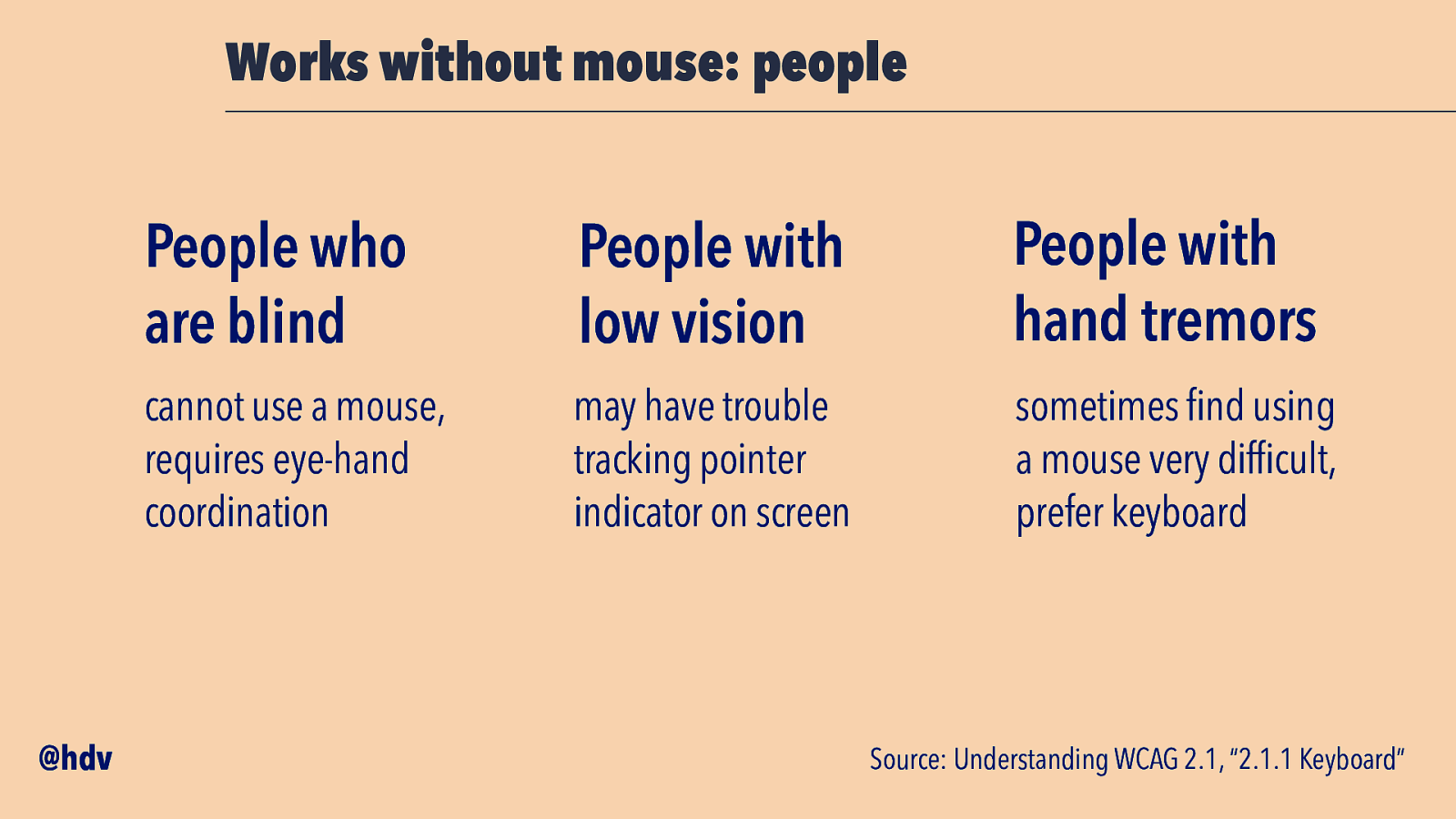
Works without mouse: people @hdv People who are blind People with low vision People with hand tremors cannot use a mouse, requires eye-hand coordination may have trouble tracking pointer indicator on screen sometimes find using a mouse very difficult, prefer keyboard Source: Understanding WCAG 2.1, “2.1.1 Keyboard”
Slide 25

Works without mouse: testing Is it clickable? It should also be TAB -able Links, buttons and other controls @hdv
Slide 26

Works without mouse: testing Is the active control highlighted? Override the browser default :focus and make it shine @hdv
Slide 27

Works without mouse: testing Does the order make sense? Ensure a “logical, usable source order” @hdv Source: Understanding WCAG 2.1, “2.4.3 Focus Order”
Slide 28

An accessible component… Has suf cient contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast contrast fi @hdv
Slide 29

Has suf cient contrast: people People with low vision or colour blindness often find it difficult to read text with low contrast @hdv fi Source: Understanding WCAG 2.1, “1.4.3 Contrast”
Slide 30

Has suf cient contrast: testing Use a(n automated) contrast checker fi Firefox, Accesssibility Tab element picker ↩ @hdv ↩ in Dev Tools, CI/CD Edge, accessibility info when inspecting element
Slide 31
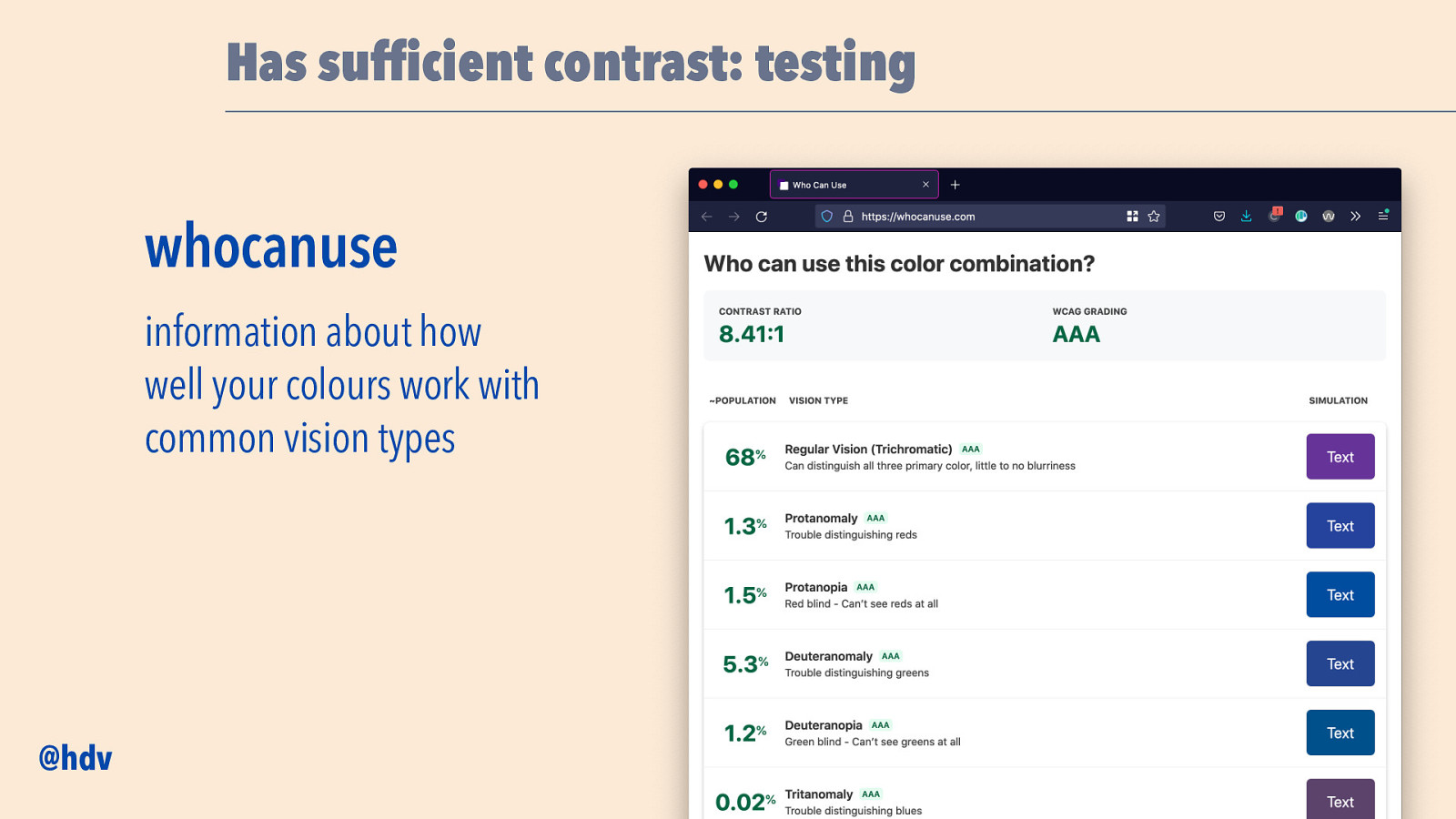
Has suf cient contrast: testing whocanuse information about how well your colours work with common vision types fi @hdv
Slide 32

An accessible component… Names all controls @hdv
Slide 33
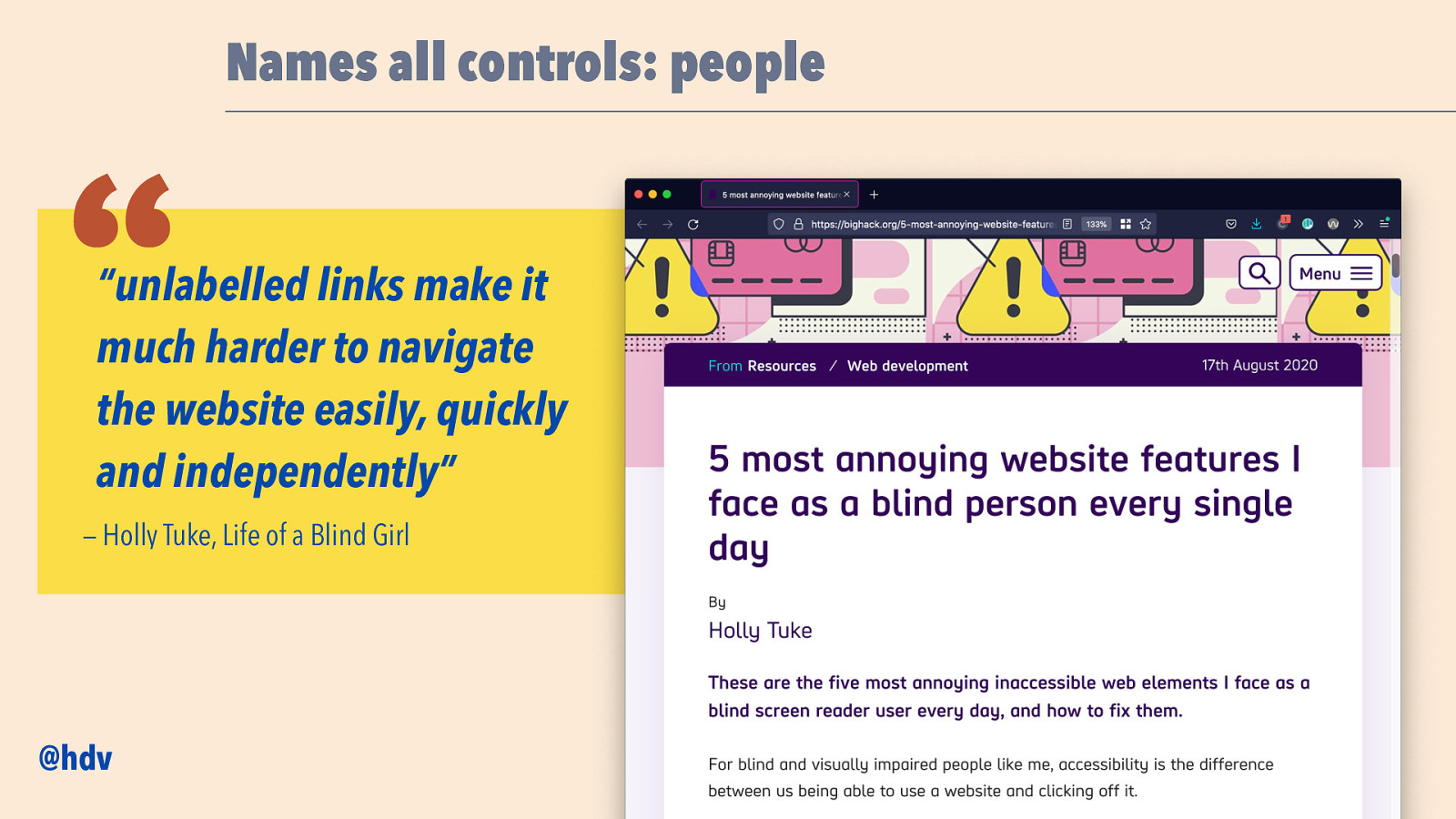
Names all controls: people “ “unlabelled links make it much harder to navigate the website easily, quickly and independently” — Holly Tuke, Life of a Blind Girl @hdv
Slide 34

Names all controls: people @hdv People with physical disabilities People who are blind may use voice recognition software to interact and use screenreaders
Slide 35

Names all controls: how to The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. 320 characters left fi @hdv
Slide 36
Names all controls: how to The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. 320 characters left fi @hdv
Slide 37
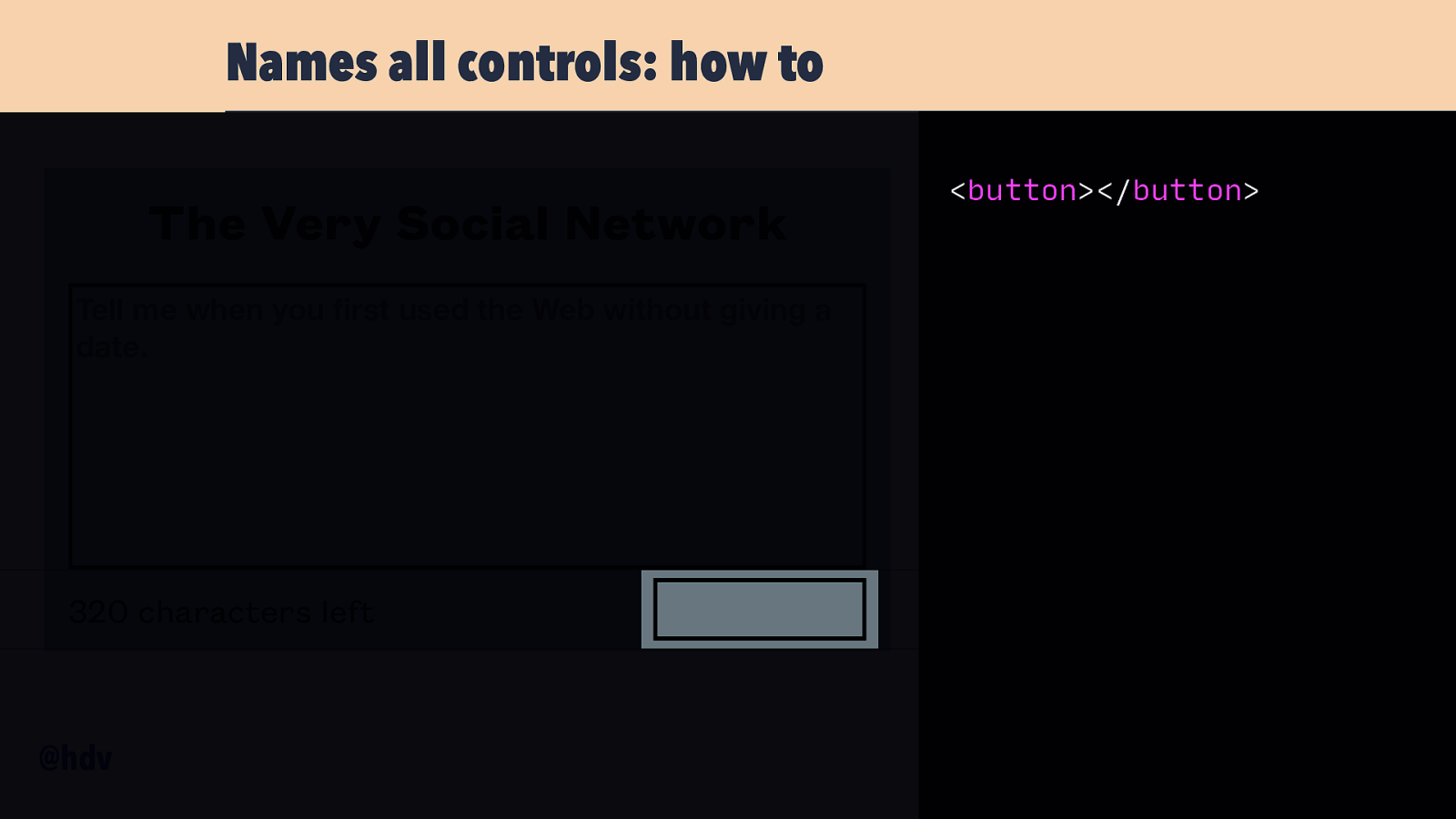
Names all controls: how to The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. 320 characters left fi @hdv <button></button>
Slide 38
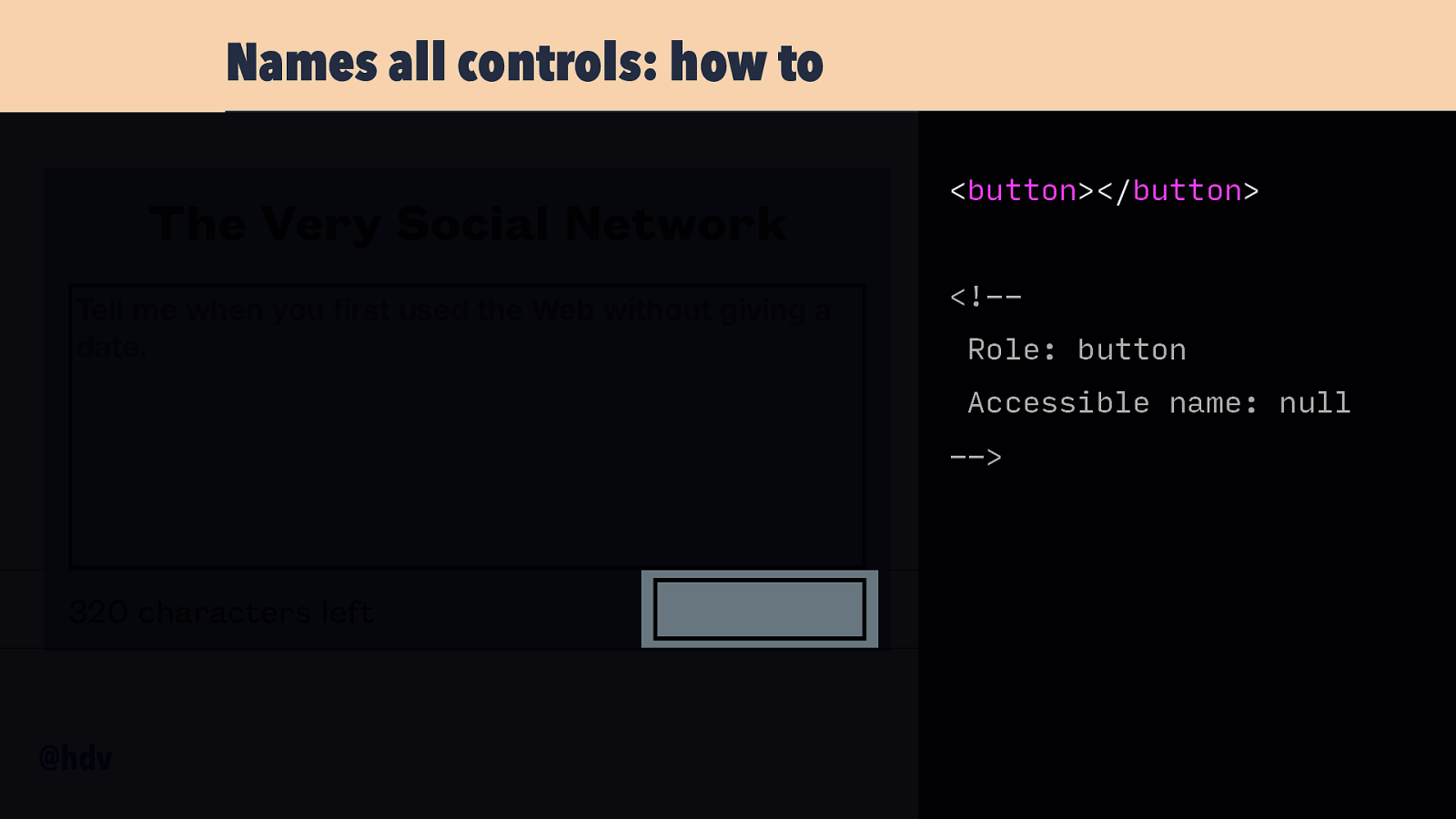
Names all controls: how to The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button></button> <!-Role: button Accessible name: null —> 320 characters left fi @hdv
Slide 39
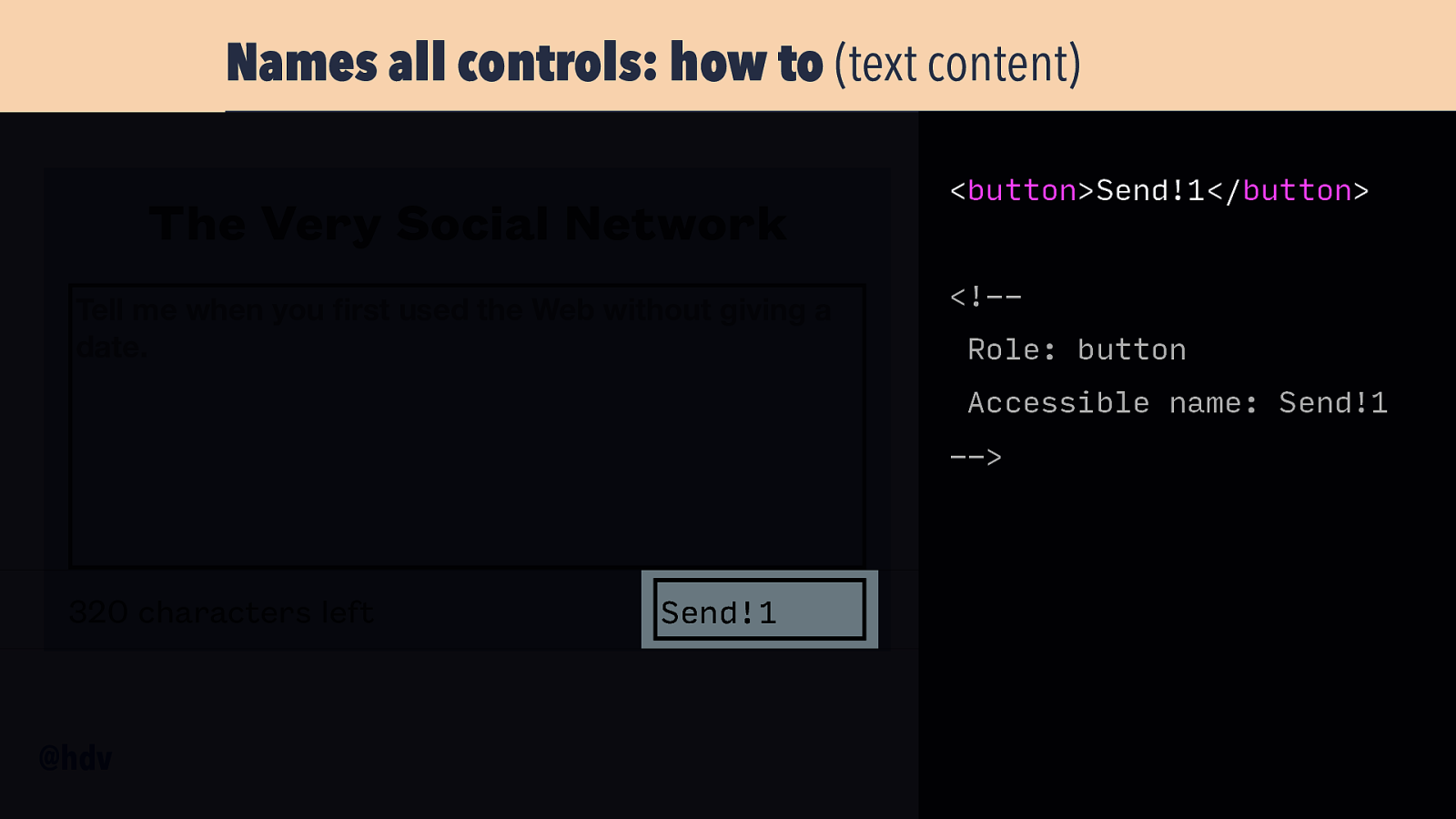
Names all controls: how to (text content) The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button>Send!1</button> <!-Role: button Accessible name: Send!1 —> 320 characters left fi @hdv Send!1
Slide 40

Names all controls: how to (text + image alt) The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button>Send!1 <img alt=”airplane” /> </button> <!-Role: button Accessible name: Send!1 airplane 320 characters left fi @hdv Send!1 —>
Slide 41
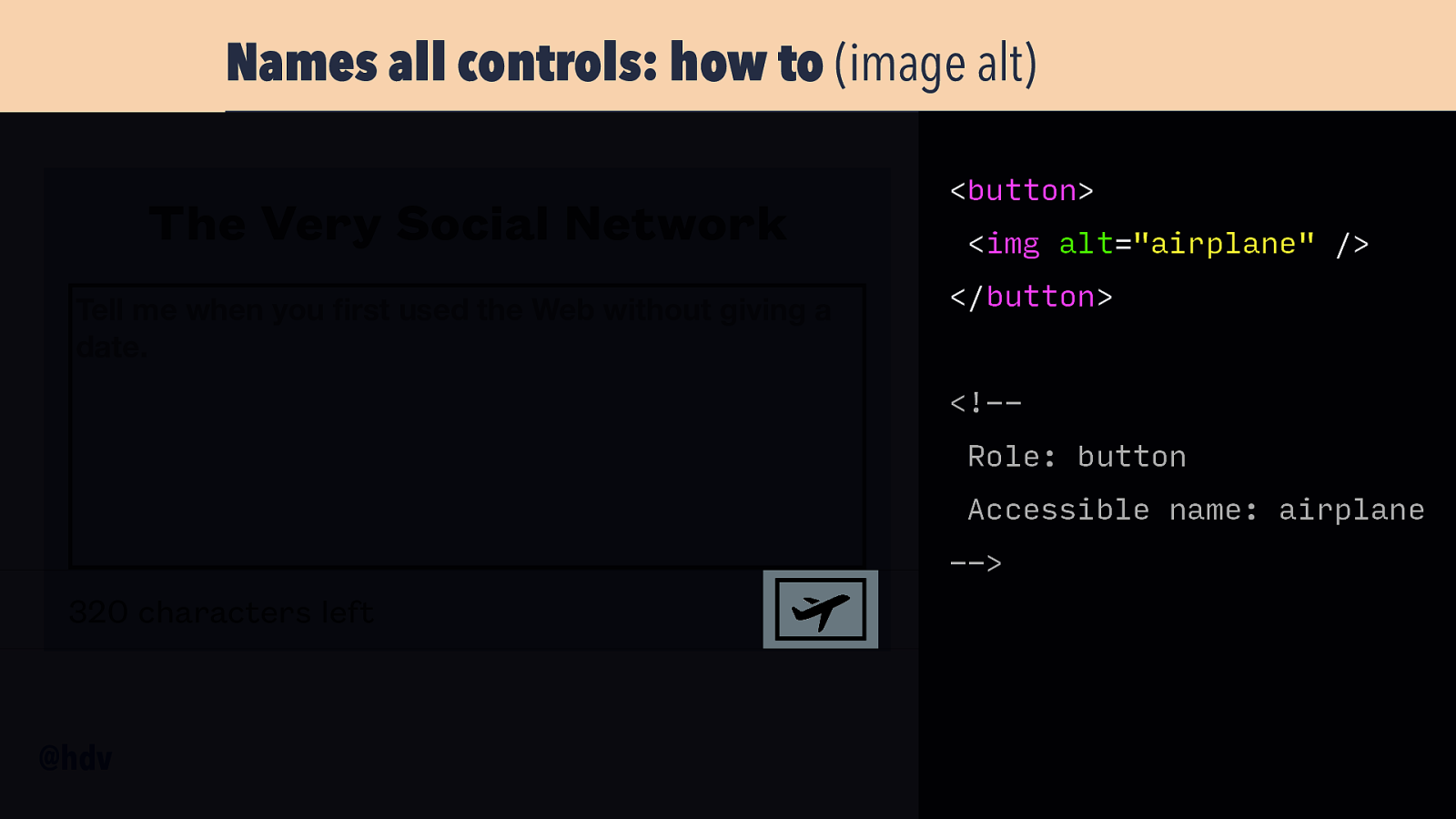
Names all controls: how to (image alt) The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button> <img alt=”airplane” /> </button> <!-Role: button Accessible name: airplane —> 320 characters left fi @hdv
Slide 42
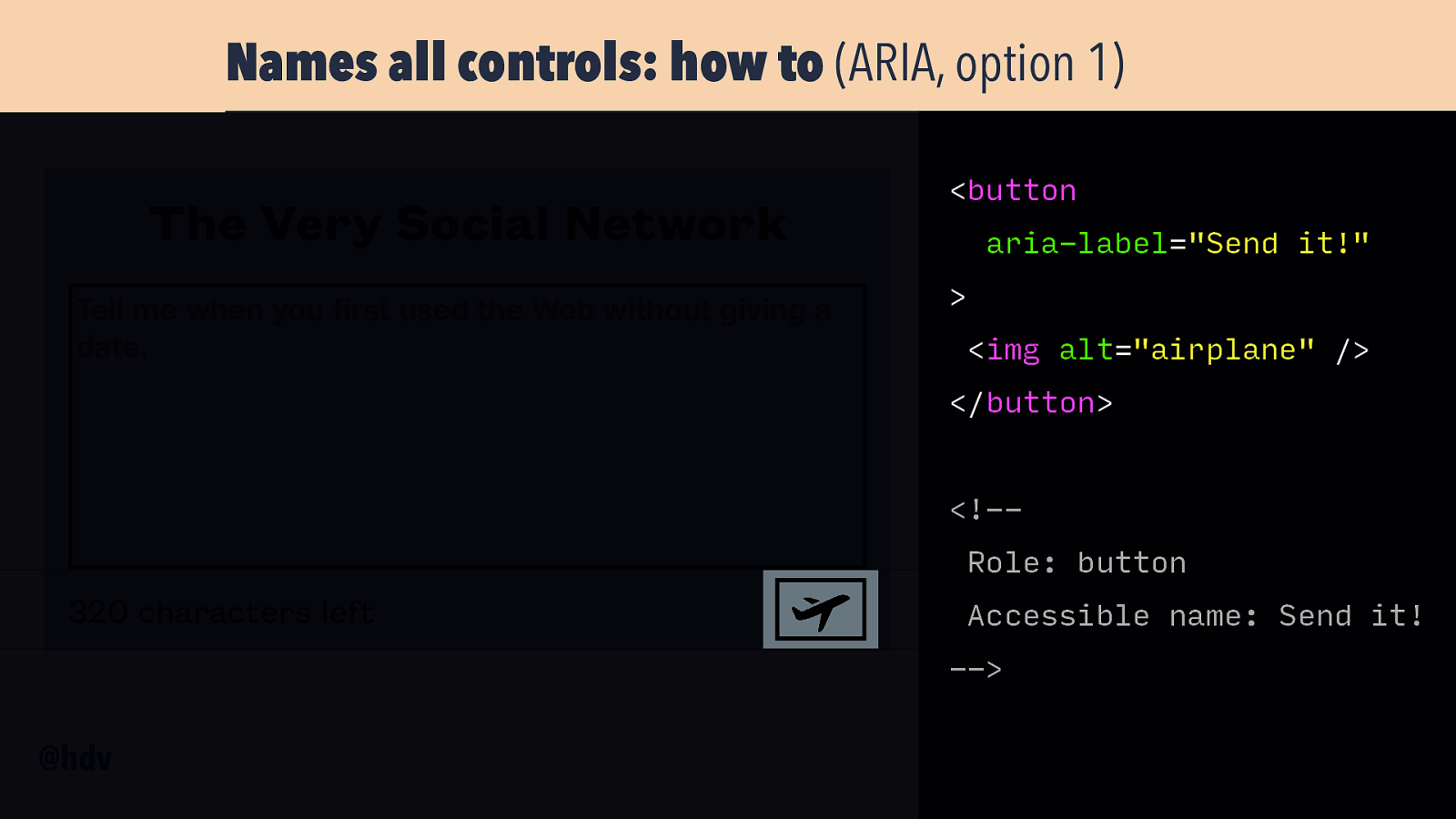
Names all controls: how to (ARIA, option 1) The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button aria-label=”Send it!” > <img alt=”airplane” /> </button> <!-Role: button 320 characters left Accessible name: Send it! —> fi @hdv
Slide 43
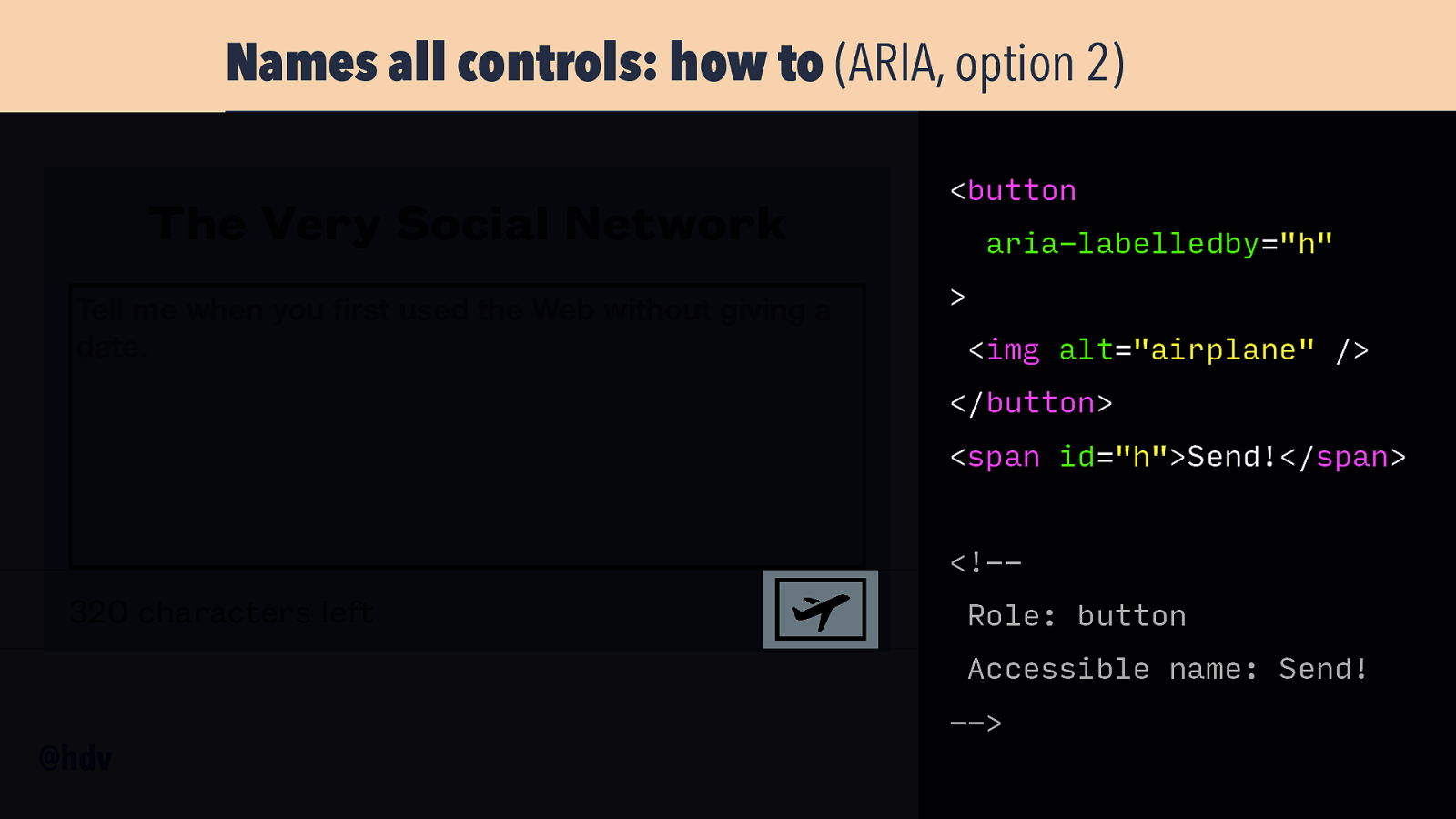
Names all controls: how to (ARIA, option 2) The Very Social Network Tell me when you rst used the Web without giving a date. <button aria-labelledby=”h” > <img alt=”airplane” /> </button> <span id=”h”>Send!</span> <!— 320 characters left Role: button Accessible name: Send! —> fi @hdv
Slide 44

Names all controls You’ll want to ensure your component has useful names for all buttons and links. For form fields, use <label>. @hdv
Slide 45

Names all controls: how it is picked
- Text content in control including ::before/::after and alt text
- aria-label 3. aria-labelledby See: https://www.w3.org/TR/accname-1.1/ @hdv
Slide 46
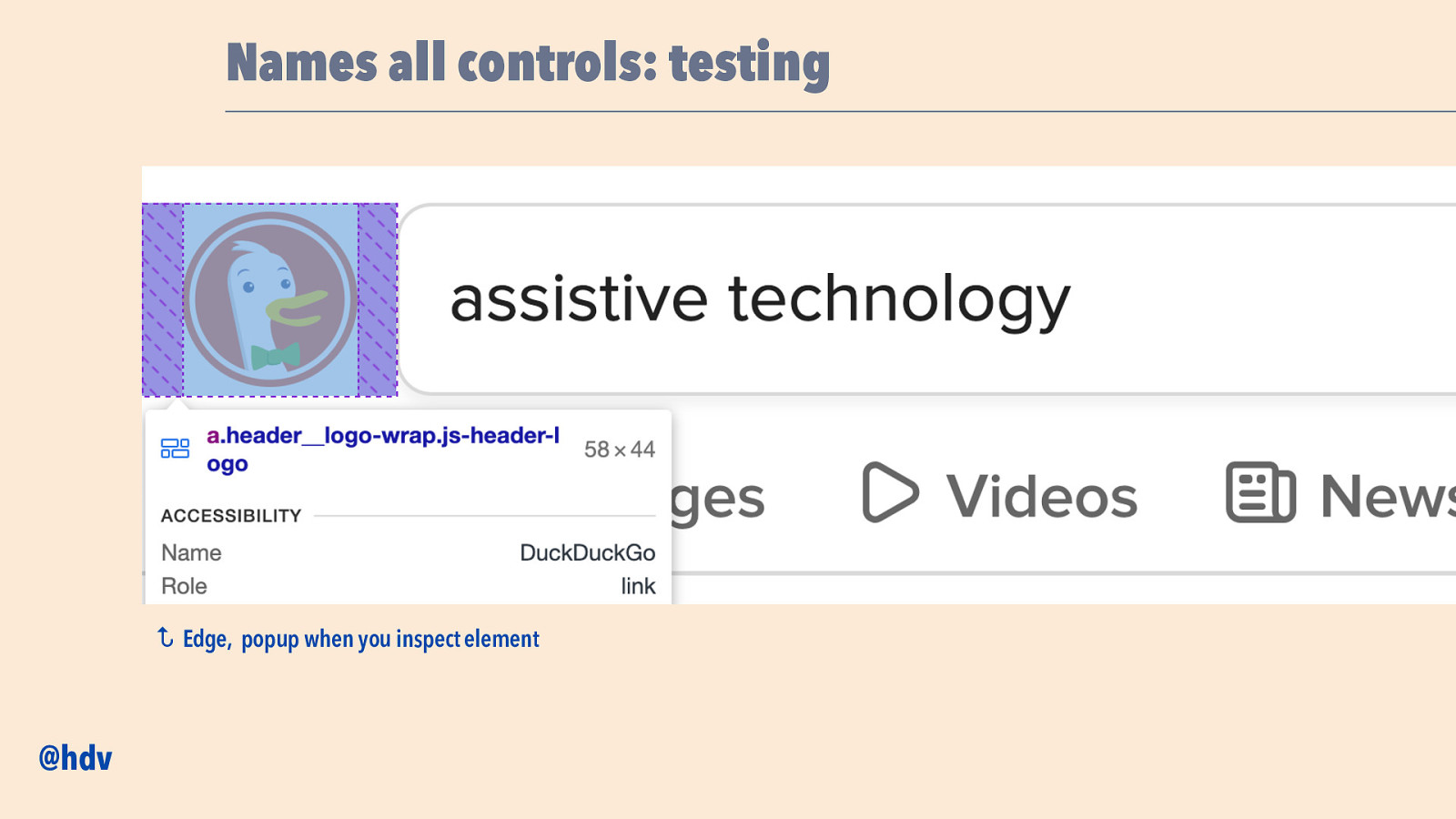
Names all controls: testing Is there a name and what is it? Is the name meaningful? Check the accessibility tree in the browser Function not form, concise, no roles ↩ @hdv Edge, popup when you inspect element
Slide 47

Names all controls: testing @hdv Is there a name and what is it? Is the name meaningful? Check the accessibility tree in the browser Function not form, concise, no roles
Slide 48

An accessible component… Allows for zoom @hdv
Slide 49

Allows for zoom: people People with low vision who use zoom so that they can read the content @hdv
Slide 50

Allows for zoom: testing Use browser zoom to 400% and verify nothing about your components breaks @hdv Previous image Next image
Slide 51

An accessible component… Conveys states to assistive tech @hdv
Slide 52

Conveys states to assistive tech: people People who use assistive technologies that are enabled by ARIA to provide a much better UI @hdv
Slide 53

Conveys states to assistive tech: how to <input type=checkbox /> Is it checked? Is it disabled? <input type=text disabled /> Is it expanded? <details><summary></details> <div hidden /> Is it hidden? <input type=email> Is it invalid? Is it pressed? <button> Is it selected? <select><option></select> @hdv
Slide 54

Conveys states to assistive tech: how to aria-checked Is it checked? Is it disabled? aria-disabled Is it expanded? aria-expanded aria-hidden Is it hidden? aria-invalid Is it invalid? Is it pressed? aria-pressed Is it selected? aria-selected @hdv Use HTM L if you ca n! Source: https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria
Slide 55
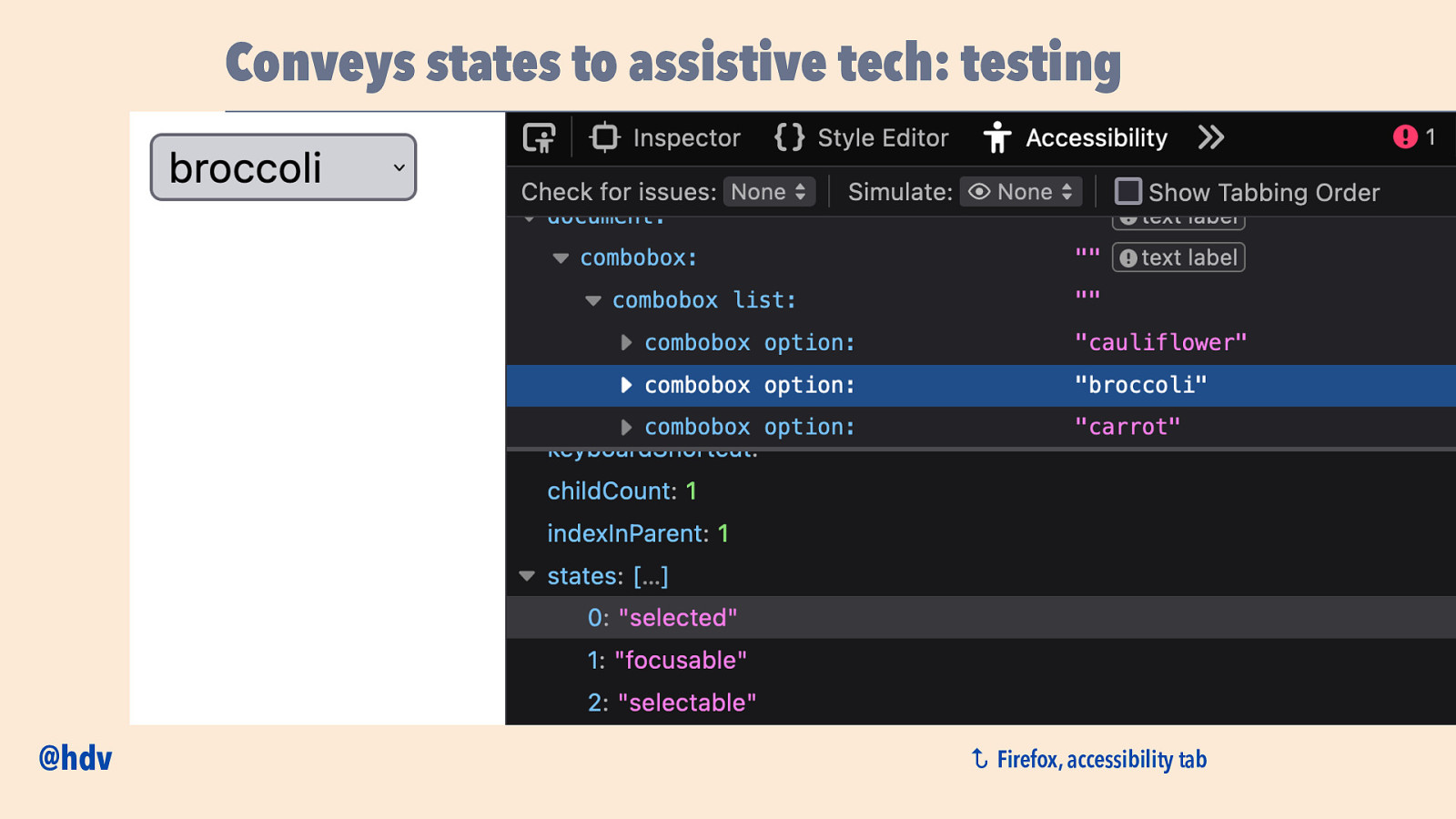
Conveys states to assistive tech: testing ↩ @hdv Firefox, accessibility tab
Slide 56

An accessible component… Honours user preferences @hdv
Slide 57
Honours user preferences: people People with low vision who use high contrast and/or forced color modes @hdv Source: Understanding WCAG 2.1, “2.1.1 Keyboard”
Slide 58
Honours user preferences: background Preferred color schemes Forced color palettes @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/css-color-adjust-1/
Slide 59

Honours user preferences: background color, fill, stroke, text-decoration-color, textemphasis-color, border-color, outline-color, column-rule-color, scrollbar-color, -webkit-tabhighlight-color, background-color, caret-color, flood-color, lighting-color, stop-color @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/css-color-adjust-1/
Slide 60

Honours user preferences: background box-shadow, text-shadow, background-image, color-scheme, scrollbar-color, accent-color @hdv https://www.w3.org/TR/css-color-adjust-1/
Slide 61

Honours user preferences: background box-shadow, text-shadow, background-image, color-scheme, scrollbar-color, accent-color if you use this for a focus outline and turn off outline, make sure outline is transparent not none @hdv https://twitter.com/alastc/status/1125681225828589569
Slide 62

Honours user preferences: how to In SVG, use currentColor for fills and strokes @hdv hidde.blog/2018-12-24-making-single-color-svg-icons-work-in-dark-mode
Slide 63

Honours user preferences: how to “web developers can now use new web standards to style their content for forced color modes like Windows high contrast” — Melanie Richards & Alison Maher @hdv https://blogs.windows.com/msedgedev/2020/09/17/styling-for-windows-high-contrast-with-new-standards-for-forced-colors/
Slide 64

Accessibility Object Model @hdv
Slide 65
“ “develop additions to the web platform to allow developers to provide information to assistive technology APIs, and to understand what information browsers provide to those APIs” — The AOM explainer document @hdv The Accessibility Object Model (AOM) ・ https://github.com/WICG/aom
Slide 66

“ “[AOM] lls the gaps in ARIA (…) is an API to provide your own accessibility (…) lets authors test them from JavaScript” — Domenic Mizzoni, Google @hdv fi What’s new in web accessibility (Google I/O ‘18) ・ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wkvslBGkhZY
Slide 67

const el = document.querySelector(“el”); el.role = “button”; el.ariaDisabled = false; Setting semantics without mark-up @hdv
Slide 68

<my-custom-element role=”button” aria-disabled=”false” … /> Avoids “sprouting” @hdv
Slide 69

Relationships without IDREFs @hdv
Slide 70

aria-activedescendant aria-colcount aria-colindex aria-colspan aria-controls aria-describedby aria-details aria-errormessage @hdv aria-flowto aria-labelledby aria-owns aria-posinset aria-rowcount aria-rowindex aria-rowspan aria-setsize
Slide 71

Events from Assistive Technologies Serious privacy concerns @hdv
Slide 72

// Implementing a canvas-based // spreadsheet’s semantics canvas.attachAccessibleRoot(); let table = canvas.accessibleRoot .appendChild(new AccessibleNode()); table.role = “table”; table.colCount = 10; table.rowcount = 100; Non-DOM nodes in the Accessibility Tree Will not happen, due to concerns including privacy, may be solved in ARIA let headerRow = table.appendChild( appendChild(new AccessibleNode()) ); @hdv Example from: AOM explainer ・ https://wicg.github.io/aom/ explainer.html#the-accessibility-object-model
Slide 73

Reading accessibility tree through JavaScript
Slide 74

Summary @hdv
Slide 75

Summary We’ve got to build accessible components It’s the markup that matters Use standards, best practices and user tests Consider keyboard, contrast, names, zoom, states and user preferences @hdv
Slide 76

THANKS!